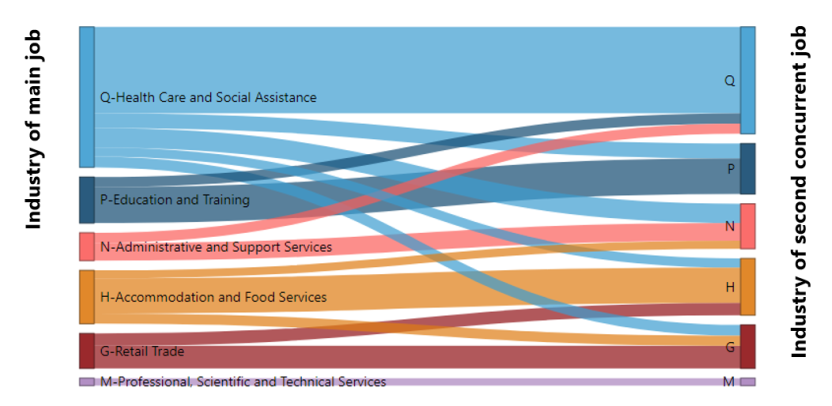
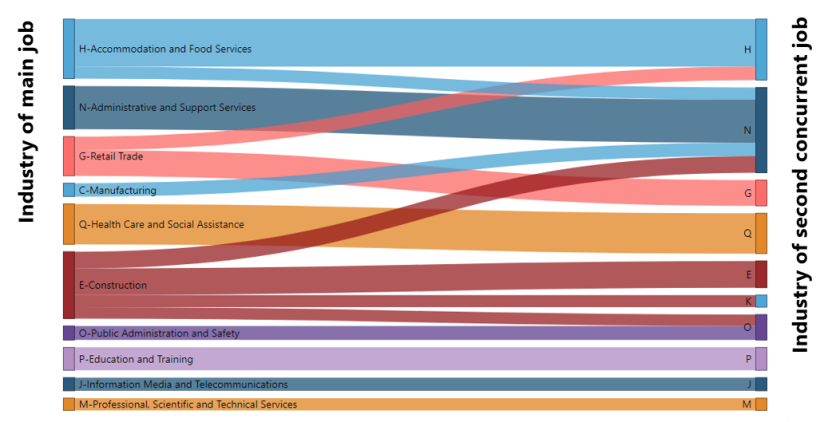
Multiple job-holders by sex, by actual full-time or part-time hours
[["Sep-03","Dec-03","Mar-04","Jun-04","Sep-04","Dec-04","Mar-05","Jun-05","Sep-05","Dec-05","Mar-06","Jun-06","Sep-06","Dec-06","Mar-07","Jun-07","Sep-07","Dec-07","Mar-08","Jun-08","Sep-08","Dec-08","Mar-09","Jun-09","Sep-09","Dec-09","Mar-10","Jun-10","Sep-10","Dec-10","Mar-11","Jun-11","Sep-11","Dec-11","Mar-12","Jun-12","Sep-12","Dec-12","Mar-13","Jun-13","Sep-13","Dec-13","Mar-14","Jun-14","Sep-14","Dec-14","Mar-15","Jun-15","Sep-15","Dec-15","Mar-16","Jun-16","Sep-16","Dec-16","Mar-17","Jun-17","Sep-17","Dec-17","Mar-18","Jun-18","Sep-18","Dec-18","Mar-19","Jun-19","Sep-19","Dec-19","Mar-20","Jun-20","Sep-20","Dec-20","Mar-21","Jun-21","Sep-21","Dec-21","Mar-22","Jun-22","Sep-22","Dec-22","Mar-23","Jun-23","Sep-23","Dec-23","Mar-24","Jun-24","Sep-24","Dec-24","Mar-25","Jun-25","Sep-25"],[[129100],[123700],[128100],[140200],[136200],[143700],[127500],[141500],[136700],[134900],[143100],[103800],[124700],[125300],[125400],[127000],[137300],[133400],[131700],[119000],[147100],[142600],[133900],[111900],[129000],[138200],[133200],[138500],[142200],[148100],[133700],[138900],[135600],[131800],[113200],[107600],[129500],[148100],[116600],[124600],[137900],[128600],[133200],[126300],[130300],[143100],[134400],[125000],[136100],[154100],[129800],[143500],[153800],[140800],[125900],[140100],[147000],[150200],[133600],[140000],[144200],[149100],[134800],[128800],[155600],[164200],[147600],[105300],[133700],[172800],[152500],[168200],[156900],[157400],[169100],[170400],[161900],[170300],[183000],[165100],[180800],[198300],[184700],[182900],[192000],[195500],[154700],[153800],[189600]],[[64400],[74900],[71900],[67100],[66500],[71000],[70400],[67700],[74400],[75400],[75900],[62900],[73800],[73900],[64800],[65900],[72100],[78300],[70900],[55700],[85200],[80400],[71400],[71700],[78700],[86300],[73400],[77800],[79700],[79600],[72800],[65000],[81800],[76100],[76300],[58100],[75200],[73100],[66700],[59100],[77400],[75900],[65000],[63900],[75900],[68600],[71800],[71900],[91000],[92700],[90600],[84500],[82200],[90600],[82400],[79400],[90300],[84300],[83700],[81200],[83100],[100700],[90400],[71200],[91300],[94000],[82900],[67900],[82200],[112400],[95000],[83800],[90100],[121500],[102000],[107000],[108400],[126200],[129800],[116700],[117900],[122100],[108400],[108900],[116200],[136500],[127600],[105900],[138800]],[[86100],[87600],[92700],[99000],[91100],[79500],[92600],[94400],[88400],[86200],[86400],[103900],[92500],[84800],[88200],[101600],[102700],[93300],[95500],[102100],[83200],[85000],[94800],[106700],[100100],[105400],[97400],[92000],[85100],[98800],[96100],[101200],[90300],[84700],[101400],[112100],[95200],[86900],[101300],[101700],[111800],[95200],[104000],[97000],[96200],[94400],[116900],[121000],[114600],[107900],[122800],[120400],[112500],[112200],[111400],[117600],[112800],[111700],[127900],[125100],[121300],[127100],[146000],[138400],[124500],[118200],[146900],[123900],[127600],[117000],[138700],[128200],[107500],[144400],[134000],[143800],[162500],[158000],[156900],[166400],[140700],[153400],[161300],[154700],[157400],[170800],[164000],[153400],[149900]],[[184900],[178900],[189800],[194800],[185200],[191900],[201700],[195500],[190000],[207300],[181500],[190600],[194500],[193100],[195400],[196200],[200300],[192000],[197700],[209900],[208500],[205300],[218600],[206700],[203800],[206100],[215100],[211500],[220700],[214800],[202500],[215800],[224100],[207900],[204600],[204800],[204100],[195000],[220300],[226700],[216600],[198300],[205000],[192600],[230000],[232800],[235200],[253700],[243000],[242700],[234700],[229600],[243300],[234600],[235300],[243100],[246200],[245600],[257500],[240200],[276200],[285100],[272900],[275000],[276300],[270200],[276400],[202600],[245900],[252400],[273000],[262800],[252700],[295000],[274100],[283600],[283400],[285000],[294900],[295400],[323200],[299200],[301400],[287600],[323700],[312300],[325200],[328800],[301000]]]
[]
[{"value":"0","axis_id":"0","axis_title":" ","axis_units":"","tooltip_units":"","table_units":"","axis_min":null,"axis_max":null,"tick_interval":"4","precision":"-1","data_unit_prefix":"","data_unit_suffix":"","reverse_axis":false}][{"value":"0","axis_id":"0","axis_title":"Multiple job-holders","axis_units":"","tooltip_units":"","table_units":"","axis_min":null,"axis_max":"900000","tick_interval":"100000","precision":"-1","data_unit_prefix":"","data_unit_suffix":"","reverse_axis":false}]