Financing resources and investment table
Financial market summary table
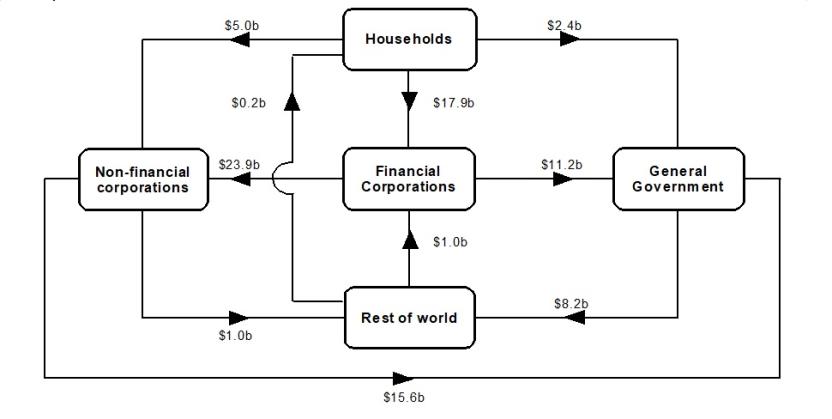
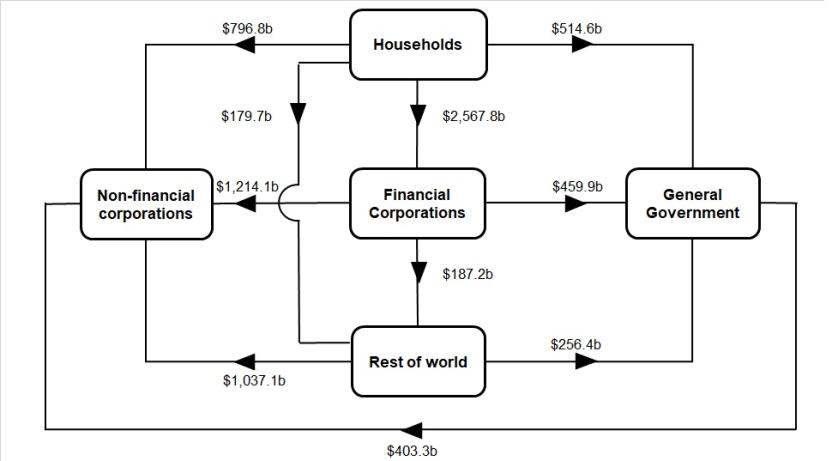
Flow of funds diagrams
National investment
National investment rose $19.2b to $139.4b in the December quarter.
- General government investment increased $2.6b to $22.5b, driven by state and local general government gross fixed capital formation.
- Non-financial corporations' investment increased $10.0b to $62.9b, driven by gross fixed capital formation and build up of inventories by private non-financial corporations.
- Household investment increased by $6.4b to $50.9b, driven by gross fixed capital formation and build up of inventories.
Financial investment
Australia was a net lender of $6.3b to rest of world (ROW). The main contributors were a:
- $59.9b acquisition in ROW equity assets, driven by pension funds, other private non-financial corporations (OPNFC) and non-money market funds.
- offset by $46.0b purchase of Australian debt securities by ROW, driven mainly by one name paper issued by authorised deposit taking institutions (ADI).
Pension funds, OPNFC and non-money market funds continued to invest in overseas equity markets. ADIs sourced funding from offshore debt markets through issuance of short-term debt securities.
Households
Households' $26.6b net lending position was due to a $84.3b acquisition of financial assets, partly offset by a $57.7b incurrence of liabilities.
The acquisition of assets was driven by:
- $45.7b in deposits
- $28.1b in net equity in pension funds
While liabilities were driven by:
- $54.6b in loan borrowings
Deposits assets continued to grow, though at a reduced pace as spending increased following the easing of COVID-19 related restrictions and seasonal holiday spending. Acquisition of net equity in pension funds reflected continued growth in employment. Increased activity in the property market saw continued strength in demand for housing loans by owner-occupiers and investors.
Non-financial corporations
Non-financial corporations' $17.3b net borrowing position was due to a $28.1b acquisition of financial assets, offset by $45.4b incurrence of liabilities. Liabilities were driven by:
- $41.8b in equity raising
- $1.2b in loan borrowing
Businesses sought to raise funds through equities markets with continued investor demand from ROW. Loans from ADIs continued to strengthen as private businesses borrowed to fund operations as economic activity increased resulting from eased restrictions and resumption of interstate travel.
General government
General government's $22.8b net borrowing position was due to a $0.2b disposal of assets and a $22.6b incurrence of liabilities.
Assets were driven by:
- $11.8b sale of equity holdings
While liabilities were driven by:
- $10.4b net issuance of bonds
- $6.5b net issuance of short term debt securities
Sale of equity assets were driven by privatisation activity during the quarter. Bonds issued by the Commonwealth government were modest reflecting decreased social assistance benefits paid to residents associated with the decline in COVID-19 outbreaks and reopening of state borders.