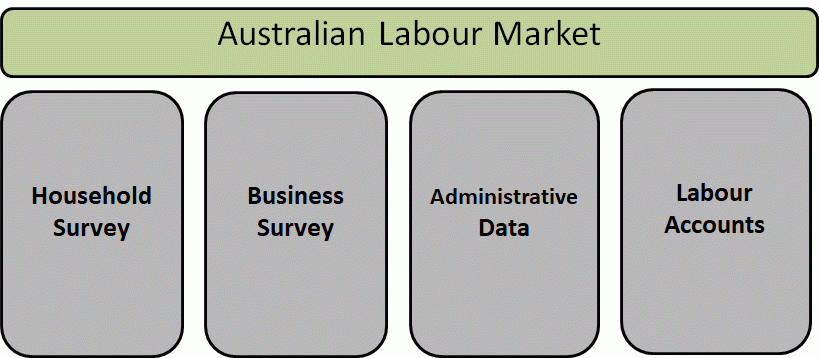
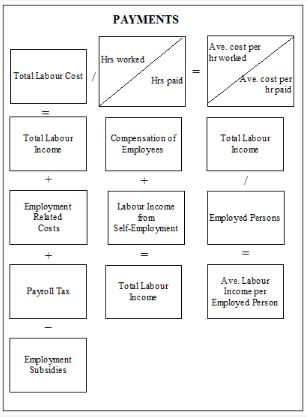
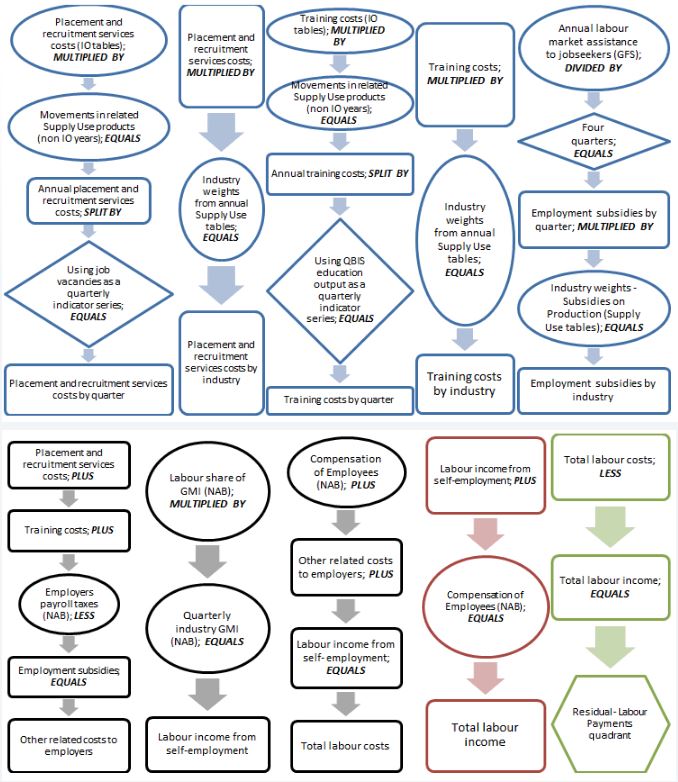
ABS labour-related household and business sample surveys use probability sampling techniques, drawing their samples from a population frame. This section briefly defines and explains key concepts and terms related to survey design. See the household and business surveys sections for more detail on aspects of survey design that are particular to these types of surveys.
Population
A survey is concerned with two types of population: the target population, and the survey population. The target population is the group of units about which information is sought, and is also known as the scope of the survey. It is the population at which the survey is aimed. The scope should state clearly the units from which data are required and the extent and time covered, e.g. households (units) in Australia (extent) in August 2020 (time).
However, the target population is a theoretical population, as there are usually a number of units in the target population which cannot be surveyed. These include units which are difficult to contact and units which are missing from the frame. The survey population is that part of the population that is able to be surveyed, and is also called the coverage population.
Statistical units
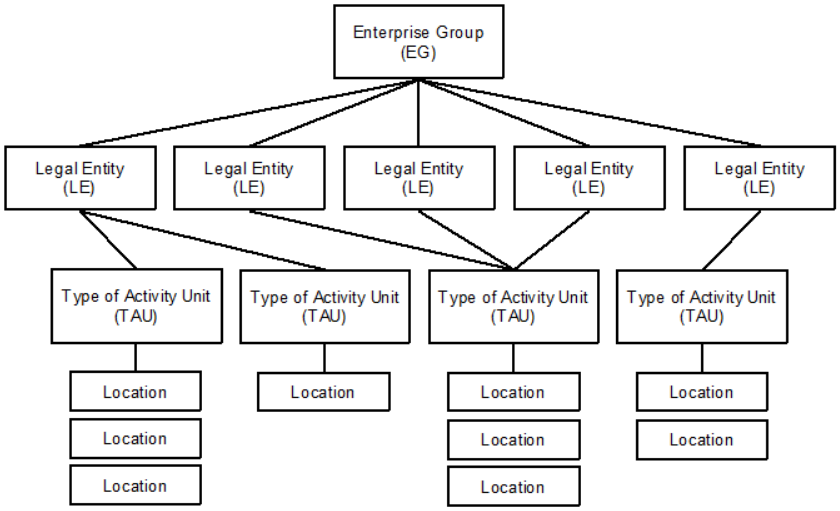
Statistical units are used in the design, collection, analysis and dissemination of statistical data. There are several types of units, including: sampling units (the units selected in the sample survey), collection units (the units from which data are collected), reporting units (the units about which data are collected), and analysis units (the units used for analysis of the data). The units used in a survey may change at various stages in the survey cycle. For example, the Labour Force Survey uses a sample of households (sampling unit) from which information is collected from any responsible adult (collection unit) about each person in the household in scope of the survey (reporting units). The results of the survey may then be analysed for families (analysis unit).
Frames
The frame comprises a list of statistical units (e.g. persons, households or businesses) in the population, together with auxiliary information about each unit. It serves as a basis for selecting the sample. Two types of frames are used in ABS labour-related surveys:
- List based frames - List based frames comprise a list of all sampling units in the survey population. List based frames are commonly used in surveys of businesses. ABS business surveys currently draw their list frames from the ABS Business Register.
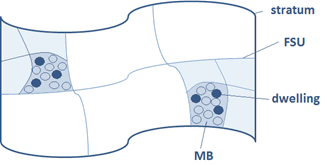
- Area based frames - Area based frames comprise a list of non-overlapping geographic areas. These areas may be defined by geographical features such as rivers and streets. They are usually used in household surveys. Once an area is selected, a list is made of the households in the area, and a sample of households selected from the list. Examples of geographic areas that may be used to create area frames include: local government areas; census collection districts; and postcodes.
Auxiliary variables are characteristics of each unit for which information is known on the frame prior to the survey. Auxiliary variables can be used in the sample design to better target the population of interest, if the information on the frame is of sufficiently high quality and is correlated with the variables of interest in the survey. They can also be used in the estimation process in conjunction with the survey data: for example, industry of businesses.
For most sampling methodologies, it is desirable to have a complete list from which to select a sample. However, in practice it can be difficult to compile such a complete list and therefore frame bias may be introduced. Frame bias occurs when an inappropriate frame is used or there are problems with the composition of the frame, with the result that the frame is not representative of the target population. Frames become inaccurate for many reasons. One of the most common problems is that populations change continuously, causing frames to become out of date. Frames may also be inaccurate if they are compiled from inaccurate sources. The following are some of the problems that can occur in the composition of frames.
Under coverage occurs when some units in the target population that should appear on the frame do not. These units may have different characteristics from those units which appear on the frame, and therefore results from the survey will not be representative of the target population.
Out of scope units are units that appear on the frame but are not elements of the target population. Selection of a number of out of scope units in the sample reduces the effective sample size, and increases sampling error. Furthermore, out of scope units appearing on the frame may be incorrectly accounted for in the estimation process, which may lead to bias in survey estimates.
Duplicates are units that appear more than once on the frame. The occurrence of duplicates means that the probability of selection of the units on the frame is not as it should be for the respective sample design. In particular, the duplicate units will have more than the correct chance of selection, introducing bias towards the characteristics of these units. Duplicates also increase sampling error.
Deaths are units that no longer exist in the population but are still on the frame. Deaths have the same impact on survey results as out of scope units.
The quality of auxiliary variables can affect the survey estimates of the variables of interest, through both the survey design and the estimation process.
The ABS attempts to minimise frame problems and uses standardised sample and frame maintenance procedures across collections. Some of the approaches taken are to adjust estimates using new business provisions, and to standardise across surveys the systems for handling estimation, imputation and outliers.
Probability samples
Probability samples are samples drawn from populations such that every unit in the population has a known, or calculable, non-zero probability of selection which can be obtained prior to selection. In order to calculate the probability of selection, a population frame must be available. The sample is then drawn from this frame. Alternatives to probability samples are samples formed without a frame, such as phone-in polls.
Probability sampling is the preferred ABS method of conducting major surveys, especially when a population frame is available. Probability samples allow estimates of the accuracy of the survey estimates to be calculated. They are also used in ABS surveys as a means of avoiding bias in survey results. Bias is avoided when either the probability of selection is equal for all units in the target population or, where this is not the case, the effect of non-equal probabilities is allowed for in estimation.
Stratified sampling
Stratified sampling is a technique which uses auxiliary information available for every unit on the frame to increase the efficiency of a sample design. Stratified sampling involves the division (stratification) of the population frame into non-overlapping, homogeneous (similar) groups called strata, which can be treated as totally separate populations. A sample is then selected independently from each of these groups, and can therefore be selected in different ways for different strata, e.g. some strata may be sampled using 'simple random sampling' while others may be 'completely enumerated'. These terms are explained below. Stratification variables may be geographical (e.g. State, capital city/balance of State) or non-geographical (e.g. number of employees, industry, turnover).
All surveys conducted by the ABS use stratification. Household surveys use mainly geographic strata. Business surveys typically use strata which are related to the economic activity undertaken by the business, for example industry and size of the business (the latter based on employment size).
Completely enumerated strata
Completely enumerated strata are strata in which information is obtained from all units. Strata that are completely enumerated tend to be those where: each population unit within the stratum is likely to contribute significantly to the estimate being produced (such as strata containing large employers where the estimate being produced is employment); or there is significant variability across the population units within the stratum.
Simple random sampling
Simple random sampling is a probability sampling scheme in which each possible sample of the required size has the same chance of selection. It follows that each unit of the population has an equal chance of selection.
Simple random sampling can involve units being selected either with or without replacement. Replacement sampling allows the units to be selected multiple times, whereas without replacement sampling allows a unit to be selected only once. In general, simple random sampling without replacement produces more accurate results as it does not allow sample to be 'wasted' on duplicate selections. All ABS surveys that use simple random sampling use the 'without replacement' variant. Simple random sampling without replacement is used in most ABS business surveys.
Systematic sampling
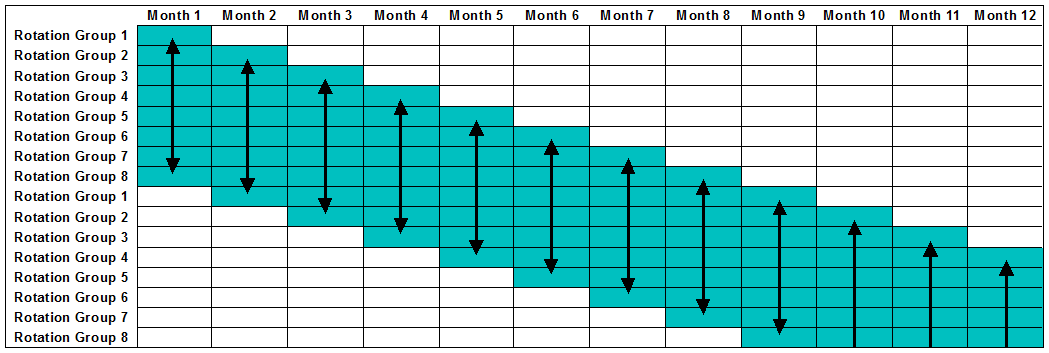
Systematic sampling is used in most ABS household surveys, and provides a simple method of selecting the sample. It involves choosing a random starting point within the frame and then applying a fixed interval (referred to as the 'skip') to select members from a frame.
Information on auxiliary variables can be used in systematic sampling to improve the efficiency of the sample. The units in the frame can be ordered with respect to auxiliary variables prior to calculating the skip interval and starting point. This approach ensures that the sample is spread throughout the range of units on the frame, ensuring a more representative sample with respect to the auxiliary variable.
Systematic sampling with ordering by auxiliary variables is only useful if the frame contains auxiliary variables about each of the units in the population, and if these variables are related to the variables of interest. The relationship between the variables of interest and the auxiliary variables is often not uniform across strata. Consequently, it is possible to design a sample survey with only some of the strata making use of auxiliary variables.
Probability proportional to size sampling
Probability proportional to size sampling is a selection scheme in which units in the population do not all have the same chance of selection. With this method, the larger the unit with respect to some measure of size, the greater the probability that unit will be selected in the sample. Probability proportional to size sampling will lead to unbiased estimates, provided the different probabilities of selection are accounted for in estimation.
Cluster sampling
Cluster sampling involves the units in the population being grouped into convenient clusters, usually occurring naturally. These clusters are non-overlapping, well-defined groups which usually represent geographical areas. The sample is selected by selecting a number of clusters, rather than directly selecting units. All units in a selected cluster are included in the sample.
Multi-stage sampling
Multi-stage sampling is an extension of cluster sampling. It involves selecting a sample of clusters (first-stage sample), and then selecting a sample of population units within each selected cluster (second-stage sample). The sampling unit changes at each stage of selection. Any number of stages can be employed. The sampling units for any given stage of selection each form clusters of the next-stage sampling units. Units selected in the final stage of sampling are called final-stage units (or ultimate sampling units). The Survey of Employee Earnings and Hours uses multi-stage sampling - businesses (the first-stage units) selected in the survey are asked to select a sample of 'employees' (the final-stage units) using employee payrolls. Household surveys also use multi-stage sampling.
Multi-phase sampling
Multi-phase sampling involves collecting basic information from a sample of population units, then taking a sub-sample of these units (the second-phase sample) to collect more detailed information. The second-phase sample is selected using the information collected in the first phase, and allows the second-phase sample to be targeted to the specific population of interest. Population totals for auxiliary variables, and values from the first-phase sample, are used to weight the second-phase sample for the estimation of population totals.
Multi-phase sampling aims to reduce sample size and the respondent burden and collection costs, while ensuring that a representative sample is still selected from the population of interest. It is often used when the population of interest is small and difficult to isolate in advance, or when detailed information is required. Multi-phase sampling is also useful when auxiliary information is not known for all of the frame units, as it enables the collection of data for auxiliary variables in the first-phase sample.
The first-phase sample is designed to be large to ensure sufficient coverage of the population of interest, but only basic information is collected. The basic information is then used to identify those first-phase sample units which are part of the population of interest. A sample of these units is then selected for the second-phase sample. Therefore, the sampling unit remains the same for each phase of selection. If multi-phase sampling was not used, detailed information would need to be collected from all first-phase sample units to ensure reasonable survey estimates. In this way, multi-phase sampling reduces the overall respondent burden.