Asynchronous batch coding
Coding a large volume of data.
In addition to real-time coding of single records and small batches of data, the Coding Service has been designed to code large datasets through asynchronous batching (that is, returning data after a short period of time).
The asynchronous service can be used for as little as one record, up to millions of records.
Note: Asynchronous batch coding should be used if you need to code or recode a large volume of data. While it is the most efficient method of coding larger datasets, it is not real-time, and may be subject to queueing during high load periods.
Getting an upload URL for input data to a batch coding operation
This endpoint is used to create an asynchronous batch inference operation. The API will return a location where you can upload your input file and begin your batch inference operation.
Request syntax
Depending on whether you are specifying a model against which to code your records, your request will follow one of the following formats:
1. Coding records against the latest model
POST /v1/topics/{topic}/batch-code HTTP/1.1
Host: string
Content-type: application/json
Authorization: string2. Coding records against a specific model
POST /v1/topics/{topic}/models/{model}/batch-code HTTP/1.1
Host: string
Content-type: application/json
Authorization: string| topic | The uriName of the topic against which the record is coded. This can be acquired by listing the available topics. Required: Yes |
|---|---|
| model | The model GUID for the model you would like to use to code records. This can be acquired by listing the available models for your topic. Required: No |
Request body
The request does not have a request body.
Response syntax
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-type: application/json
{
"requestUploadUrl": "string",
"operationId": "string",
"bucketKmsKeyArn": "string"
}If the action is successful, the service sends back an HTTP 200 response. The following data is returned in JSON format by the service:
| requestUploadUrl | A URL where the records file is to be uploaded. Type: String |
|---|---|
| operationId | The identifier of the operation, to be used to check the status of this job. This must be recorded at this point to maintain access to the operation. Type: String, in GUID format. |
| bucketKmsKeyArn | A parameter used by the ABS system to ensure the operation’s input data is from the same user who created the operation. This must be passed into the x-amz-server-side-encryption-aws-kms-key-id header when uploading your input file. Type: String |
Errors
For information about asynchronous coding errors, see Errors and suggested actions.
Examples
| Creating a new operation to code against the latest model: | |
|---|---|
| Sample request | |
| Sample response | |
| Creating a new operation to code against a specified model: | |
|---|---|
| Sample request | |
| Sample response | |
Uploading data for inference
Once you have created an inference operation, you will need to upload your data to the provided requestUploadUrl. This is a pre-signed HTTP request which is managed by the AWS S3 server, and the expected input is outlined below.
- Both occp_text and tasks_test fields are required (although one may be empty, indicated by “”).
Request Syntax
PUT requestUploadUrl HTTP/1.1
x-amz-server-side-encryption: aws:kms
x-amz-server-side-encryption-aws-kms-key-id: string
{ "recordId": "string", "occp_text": "string", "tasks_text": "string" }
...| requestUploadUrl | The location where the input file is being uploaded. This is provided when you first create the inference operation. Type: String |
|---|
Please note: the x-amz-server-side-encryption header is not variable and should always have the value aws:kms.
| x-amz-server-side-encryption-aws-kms-key-id | A parameter used by the ABS system to ensure the input data is from the same user who created the operation. This is provided in the bucketKmsKeyArn field when you first create your inference operation. Type: String |
|---|
The request accepts your input file in JSONL format. The maximum input file size is 5GB. All lines of input must contain the same fields, and these fields should satisfy the Record type for the relevant topic/model as specified when creating the upload URL. You may specify the additional field outlined below:
| recordId | An identifier for the record being coded. This need not be unique. Type: String Required: No |
|---|
Response Syntax
HTTP/1.1 200 OKErrors
For information about the errors that are common to all actions, see Errors and suggested actions.
Examples
| Specifying a record identifier: | |
|---|---|
| Sample request | |
| Sample response | |
| Specifying no record identifier: | |
|---|---|
| Sample request | |
| Sample response | |
Checking the status of a batch inference operation
This endpoint is used to check the status of your batch inference job. When the status of your job is complete, the service will return a URL to copy into your web browser to retrieve your coded data.
Request Syntax
Depending on whether you are specifying a model against which to code your records, your request will follow one of the following formats. The application backend handles these requests identically, so you don’t need to worry about recording the model which you used when you began the operation.
1. Checking an operation by specifying the topic only
GET /v1/topics/{topic}/batch-code/operations/{operation_id} HTTP/1.1
Host: string
Content-type: application/json
Authorization: string
2. Checking an operation by specifying both the topic and model
GET /v1/topics/{topic}/models/{model}/batch-code/operations/{operation_id} HTTP/1.1
Host: string
Content-type: application/json
Authorization: string| topic | The uriName of the topic against which the record is coded. This can be acquired by listing the available topics. Required: Yes |
|---|---|
| model | The model GUID for the model you would like to use to code records. This can be acquired by listing the available models for your topic. Required: No |
| operation_id | The GUID of the operation to get the status of. This value is provided when you first create your inference operation. Required: Yes |
Request Body
The request does not have a request body.
Response Syntax
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-type: application/json
{
"operationStatus": "string",
"responseDownloadUrl": "string",
"error": "string"
}If the specified operation exists, the service sends back an HTTP 200 OK status code. The status of the operation will dictate the contents of the response. This data is returned in JSON format by the service:
| operationStatus | The status of the operation. Type: String Valid Values: awaiting_input | in_progress | complete | timed_out | failed |
|---|---|
| responseDownloadUrl | A URL where the output data file can be downloaded. This field is optional and is returned only if operationStatus is complete. Type: String |
| metadataDownloadUrl | A URL where the output metadata file can be downloaded. This file includes information about the model used to code your data.This field is optional and is returned only if operationStatus is complete. Type: String |
| error | Information on why the operation failed. This field is optional and is returned only if operationStatus is failed. |
A note about presigned URLs
The responseDownloadUrl and metadataDownloadUrl are presigned URLs. Anyone with this link will be able to download your output file, so it is your responsibility to keep the link secret.
The link will expire after one hour, after which you will have to get a new URL for your output file.
Your output files will be deleted from the system within 24 hours after your inference operation succeeds.
A state machine indicating the progression of operations is shown below:
Image
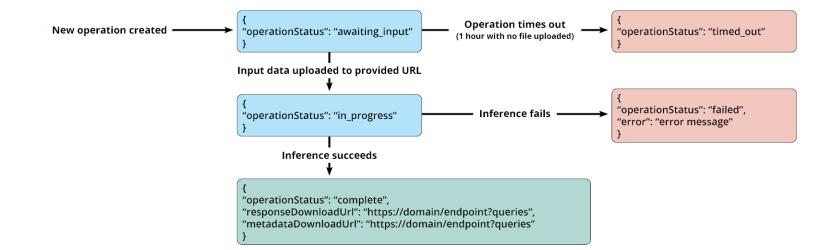
Description
Flow chart of operational steps showing output messages if operation times out, if inference fails and if inference is successful.
If operation times out, output returned is "operation status: timed out".
If inference fails, output returned is "operation status: failed" and a relevant error message is provided.
If inference is successful, output is "operation status: complete" and the relevant response URLs are provided.
Errors
For information about asynchronous coding errors, see Errors and suggested actions.
Examples
| Getting the status of an operation: | |
|---|---|
| Sample request | |
| Sample request specifying the model used | |
| Sample responses | and any of the following: |
| Request sample | Expected response body | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| New operation (data not yet uploaded) | |
|
Just uploaded
| |
|
Never uploaded
| |
|
| Operation complete | |
|
| Operation failed | |
|
Downloading processed data from a complete operation
Once your asynchronous inference operation is complete, you can download the output file by accessing (copying into a web browser) the responseDownloadUrl that is provided when you check the status of a complete operation. The same process may be used to view the operation metadata, available at the metadataDownloadUrl.
This is a generic HTTP GET request which is managed by the AWS S3 server, and the expected format is outlined below.
Response Elements
The asynchronous batch coding service outputs a jsonl file with each line corresponding to the record from the original input file. Each line is an AsynchronousCodeResponse object.
Examples
| In response to input which specifies a record identifier: | |
|---|---|
| Sample request | |
| Sample response | |
| In response to input which specifies no record identifier: | |
|---|---|
| Sample request | |
| Sample response | |