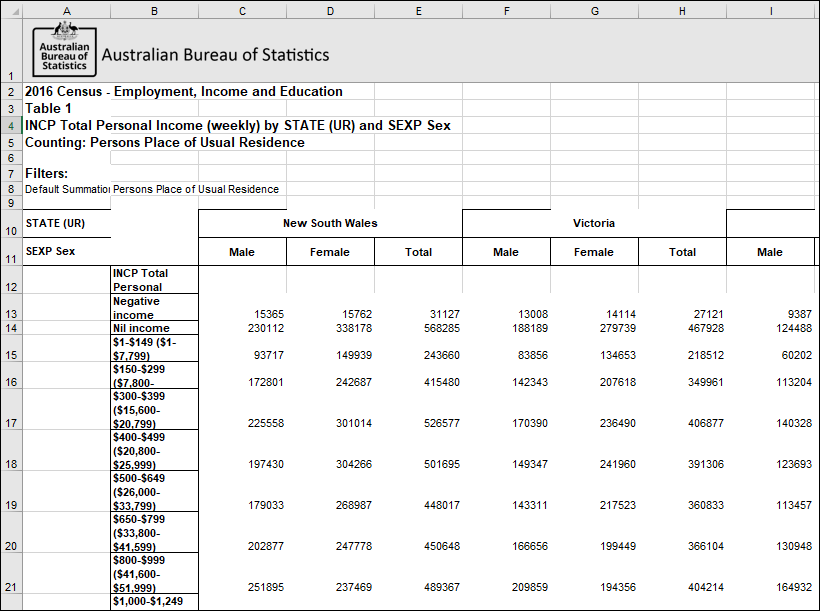
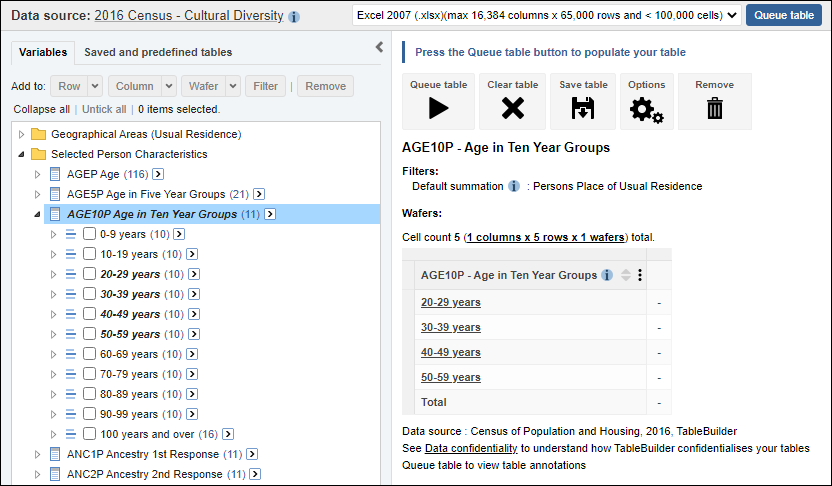
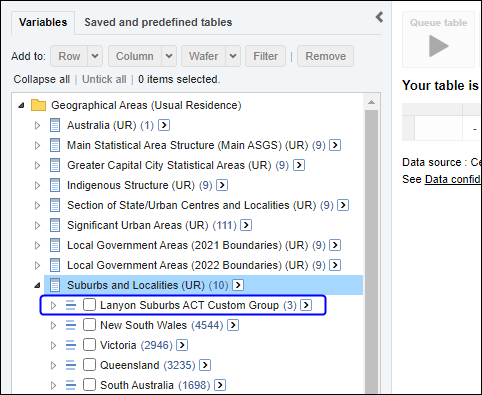
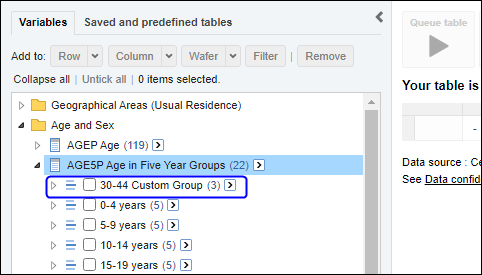
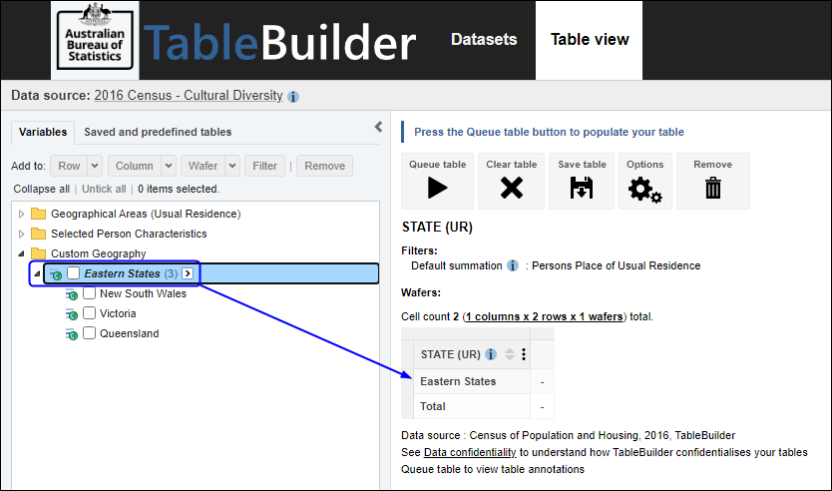
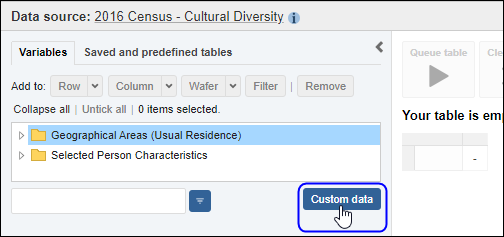
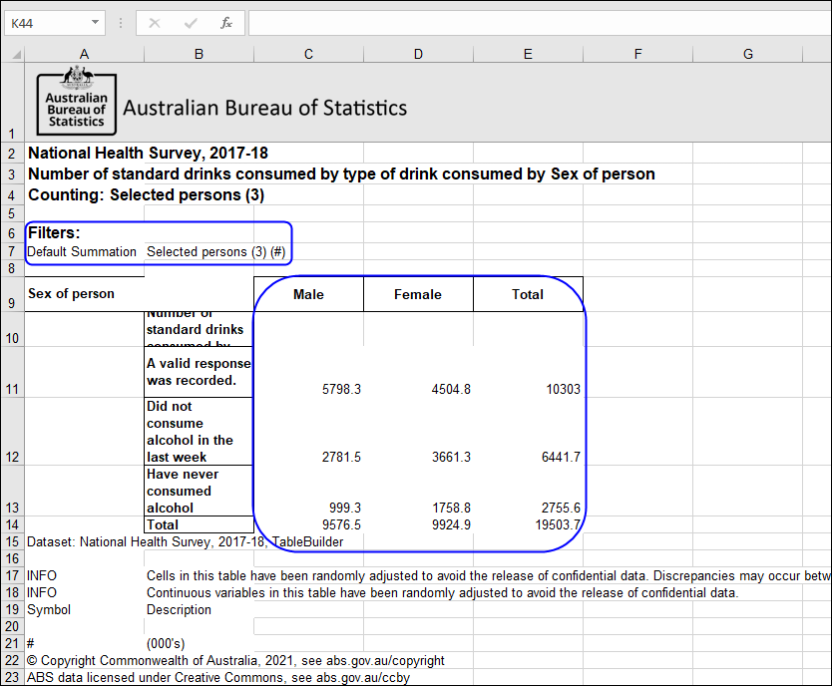
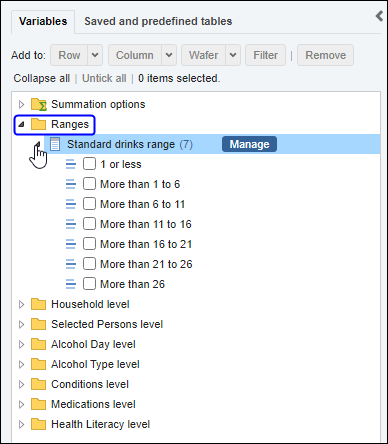
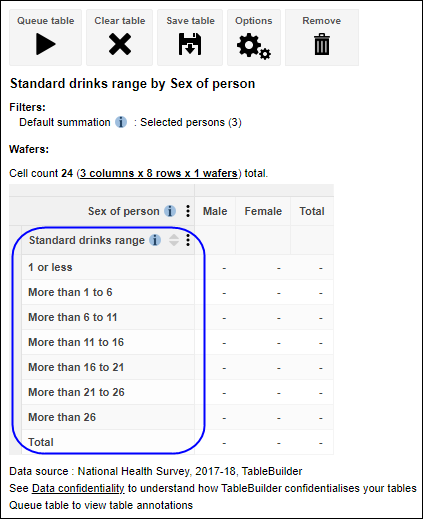
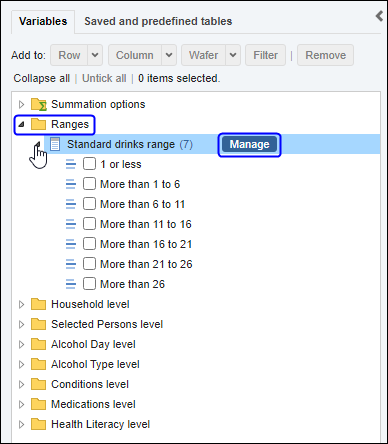
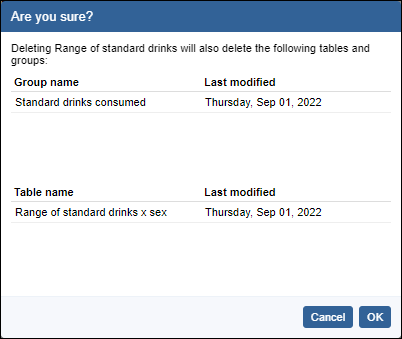
Proportions and percentages formed from the ratio of two estimates are also subject to sampling errors. The size of the error depends of the accuracy of both the numerator and denominator. For proportions where the denominator is an estimate of the number of persons in a group and the numerator is the number of persons in a sub-group of the denominator group, the formula to approximate the RSE is given below. The formula is only valid when x is a subset of y.
\(RSE\left(\frac{x}{y}\right)\cong\sqrt{RSE(x)^2-RSE(y)^2}\)
For proportions where the denominator and numerator are independent estimates, for example a ratio of rates relating to two separate populations such as Indigenous and Non-Indigenous, the formula to approximate the RSE is given below. The formula is only valid when x and y are estimated from separate independent populations, and when the RSEs on x and y are small.
\(RSE\left(\frac{y}{x}\right)\cong\sqrt{RSE(y)^2-RSE(x)^2}\)
Standard errors may also be used to calculate standard errors for the difference between two survey estimates (numbers or percentages). The sampling error of the difference between the two estimates depends on their individual standard errors and the relationship (correlation) between them. An approximate standard error of the difference between two estimates (x-y) may be calculated by the following formula:
\(SE(x-y)\cong\sqrt{SE(x)^2+SE(y)^2}\)
While this formula is only exact for differences between separate and uncorrelated characteristics of subpopulations, it is expected to provide a reasonable approximation for most differences likely to be of interest in relation to this survey.
In TableBuilder, it is the RSE of a percentage that is displayed, from which the standard error may be calculated. For example, if the estimated proportion is 30% with an RSE of 20%, then the standard error for the proportion is 6%.
In some cases, the formula for the approximation of the RSE of a proportion may be unsuitable to use because the RSE of the numerator is very close to, or below, the RSE of the denominator. In this case the RSE is suppressed. It is recommended to use the alternative formula below to calculate the RSE of the proportion if this occurs.
\(RSE\left(\frac{x}{y}\right)\cong\sqrt{RSE(x)^2+\left(1-\frac{2x}{y}\right)*RSE(y)^2}\)