| RAP | Relative of average prices. Refer to Chapter 3 of Australian Consumer Price Index: Concepts, Sources and Methods, 2005. (cat. no. 6461.0) for more details.
Reference: Australian Consumer Price Index: Concepts, Sources and Methods. cat. no. 6461.0.
|
| Rate of population growth | Population change over a period as a proportion (percentage) of the population at the beginning of the period.
Reference: Demographic Estimates and Projections: Concepts, Sources and Methods. cat. no. 3228.0.
|
| Re-exports | Re-exports are defined as goods, materials or articles originally imported into Australia which are exported in either the same condition in which they were imported, or after undergoing some minor operations (e.g. blending, packaging, bottling, cleaning and sorting) which leave them essentially unchanged. Included in international merchandise export statistics.
Reference: International Merchandise Trade, Australia, Concepts, Sources and Methods. cat. no. 5489.0.
|
| Re-imports | Re-imports are goods, materials or articles originally exported which are imported in either the same condition in which they were exported or after undergoing repair or minor alterations (e.g. blending, packaging, bottling, cleaning and sorting) which leave them essentially unchanged. Included in international merchandise import statistics.
Reference: International Merchandise Trade, Australia, Concepts, Sources and Methods. cat. no. 5489.0.
|
| Real gross domestic income | Real gross domestic income is calculated by: taking the volume measure of gross national expenditure (GNE); adding exports of goods and services at current prices deflated by the implicit price deflator for imports of goods and services; deducting the volume measure of imports of goods and services; adding the current price statistical discrepancy for GDP(E) deflated by the implicit price deflator for GDP. In the derivation of the aggregate all of the adjustments are made using the chain volume aggregation method used to derive all of the ABS chain volume estimates.
Reference: Australian National Accounts: National Income, Expenditure and Product. cat. no. 5206.0.
|
| Real gross national income | Calculated by adjusting real gross domestic income for the real impact of primary income flows (property income and labour income) to and from overseas.
Reference: Australian National Accounts: National Income, Expenditure and Product. cat. no. 5206.0.
|
| Real net disposable income | The amount that Australians can consume in aggregate, without reducing real national wealth.
Reference: Australian National Accounts: National Income, Expenditure and Product. cat. no. 5206.0.
|
| Real net national disposable income | Real net national disposable income is calculated by: taking real gross domestic income; deducting real incomes payable to the rest of the world; adding real incomes receivable from the rest of the world; deducting the volume measure of consumption of fixed capital. Real incomes payable and receivable are calculated by dividing the nominal income flows by the implicit price deflator for gross national expenditure. In the derivation of the aggregate all of the adjustments are made using the chain volume aggregation method used to derive all of the ABS chain volume estimates.
Reference: Australian National Accounts: National Income, Expenditure and Product. cat. no. 5206.0.
|
| Reason for leaving last job | Unemployed persons who had worked for two weeks or more in the past two years classified by whether they left that job voluntarily, that is, job leavers; or left that job involuntarily, that is, job losers.
Reference: Australian Labour Market Statistics. cat. no. 6105.0.
|
| Reference base period | The period for which an index is given a value of 100.0. The reference base should not be confused with the weighting period - see Weighting base period below.
Reference: Labour Price Index: Concepts, Sources and Methods. cat. no. 6351.0.55.001.
|
| Reference period | In connection with price or volume indices, the reference period means the period to which the indices relate. It is typically set equal to 100 for price indexes and to the corresponding current price values of the reference year for volume indexes and it does not necessarily coincide with the base period. See also Base period. For a survey it refers to the period when the survey was undertaken.
Reference: Average Weekly Earnings, Australia. cat. no. 6302.0.
|
| Refinancing | For investment housing finance, it represents a commitment to refinance an existing loan. For secured housing finance for owner occupation, only those loans where the refinancing lender is not the original lender and the security is unchanged are included. The refinancing of a loan to fund a change of residence is treated as a new lending commitment.
Reference: Housing Finance, Australia. cat. no. 5609.0.
|
| Regimen | The selected goods and services priced for the purpose of compiling a price index.
Reference: Australian Consumer Price Index: Concepts, Sources and Methods. cat. no. 6461.0.
|
| Reinvested earnings | Reinvested earnings represent the undistributed income of resident direct investment enterprises attributable to their direct investment in another economy. Reinvested earnings are imputed transactions with offsetting entries in investment income and the financial account. They are separately categorised in the balance of payments but not in the international investment position, where they are included in equity capital.
Reference: Australian System of Government Finance Statistics: Concepts, Sources and Methods. cat. no. 5514.0.55.001.
|
| Relative standard error (RSE) | The standard error expressed as a percentage of the estimate for which it was calculated. It is a measure which is independent of both the size of the sample, and the unit of measurement and as a result, can be used to compare the reliability of different estimates. The smaller an estimate's RSE, the more likely it is that the estimate is a good proxy for that which would have been obtained if the whole population had been surveyed.
|
| Remarriage rates | Remarriage rates are the number of remarrying males or females per 1,000 population of widowed and divorced males or females of the same age at 30 June. The rates are separately calculated for widowed or divorced males or females by appropriately adjusting the numerator and denominator of the rates.
Calculation of this rate requires a disaggregation of the population by marital status. Estimates of the population by marital status were last calculated as at 30 June 2001.
Reference: Marriages, Australia. cat. no. 3306.0.55.001) |
 |  |
 |  |
| Rent | A form of property income and expense that refers to rent for the use of land and other non-produced assets.
Reference: Australian System of Government Finance Statistics: Concepts, Sources and Methods. cat. no. 5514.0.55.001.
|
| Replacement fertility | Replacement fertility is the number of babies a female would need to have over her reproductive life span to replace herself and her partner. Given the current mortality of females up to age 49 years, replacement fertility is estimated at 2.1 babies per female.
Reference: Births, Australia. cat. no. 3301.0.
|
| Requited transactions | Transactions in which each transactor receives something of economic value.
Reference: Australian System of Government Finance Statistics: Concepts, Sources and Methods. cat. no. 5514.0.55.001.
|
| Reserve Assets | From the gold standard era, when attention was focused on monetary gold, to the present day, when the focus has shifted to a range of reserve assets, it has been regarded as desirable that balance of payments statements should identify the components comprising transactions in reserve assets. The concept of reserve assets relates to those foreign financial assets that are effectively controlled by the monetary authorities and are available for use in meeting balance of payments needs. In Australia’s case, reserve assets include monetary gold, Special Drawing Rights, reserve position in the IMF, and foreign exchange (currency, deposits and debt securities) held by the Reserve Bank as part of Australia’s official reserve assets.
Reference: Australian System of Government Finance Statistics: Concepts, Sources and Methods. cat. no. 5514.0.55.001.
|
| Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) | See Central bank.
|
Reserve position |
Reserve position in the IMF consists of two elements: foreign currency amount that a country may draw from the IMF at short notice and without conditions, and indebtedness of the IMF under a loan agreement.
Reference: Australian System of Government Finance Statistics: Concepts, Sources and Methods. cat. no. 5514.0.55.001.
|
| Reserves against outstanding claims | Reserves against outstanding claims are reserves that insurance enterprises hold in order to cover the amounts they expect to pay out in respect of claims that are not yet settled or claims that may be disputed. Reserves against outstanding claims are considered to be assets of the beneficiaries. See also Financial assets.
Reference: Australian National Accounts: Financial Accounts. cat. no. 5232.0.
|
| Resident | Residents are those entities that have a closer association with the territory of Australia than with any other territory. Examples are: general government bodies; financial and trading enterprises and non-profit bodies producing goods or services or both within the territory of Australia; and persons whose centre of interest is considered to lie in Australia. (For a precise definition see Balance of Payments and International Investment Position, Australia: Concepts, Sources and Methods. cat. no. 5331.0) paragraphs 2.10 to 2.11.) Any entity which is not determined to be a resident of Australia is classified as a resident of the rest of the world.
Reference: Australian National Accounts: Financial Accounts. cat. no. 5232.0.
|
| Resident unit | A unit with a centre of economic interest in the economic territory of the country.
Reference: Australian System of Government Finance Statistics: Concepts, Sources and Methods. cat. no. 5514.0.55.001.
|
| Residential building | A residential building is a building consisting of one or more dwelling units. Residential buildings can be either houses or other residential buildings.
Reference: Building Approvals, Australia. cat. no. 8731.0.
|
| Residents temporarily overseas | Residents temporarily overseas are Australian residents who are overseas for a period less than 12 months.
Reference: Demographic Estimates and Projections: Concepts, Sources and Methods. cat. no. 3228.0.
|
| Rest of the world (ROW) | The rest of the world consists of all non-resident institutional units that enter into transactions with resident units, or have other economic links with resident units.
Reference: Australian System of Government Finance Statistics: Concepts, Sources and Methods. cat. no. 5514.0.55.001.
|
| Retail turnover | Retail turnover includes retail sales; wholesale sales; takings from repairs, meals and hiring of goods (except for rent, leasing and hiring of land and buildings); commissions from agency activity (e.g. commissions received from collecting dry cleaning, selling lottery tickets, etc.); and net takings from gaming machines etc. From July 2000, turnover includes the goods and services tax.
Reference: Retail Trade, Australia. cat. no. 8501.0
|
| Return migration | Return migration is the emigration of former settlers to their country of birth.
Reference: Demographic Estimates and Projections: Concepts, Sources and Methods. cat. no. 3228.0.
|
| Revaluations | Changes to the value of assets, liabilities and equity arising from price changes, including exchange rate movements.
Reference: Australian System of Government Finance Statistics: Concepts, Sources and Methods. cat. no. 5514.0.55.001.
|
| Revenue(s) | Transactions that increase net worth.
Reference: Australian System of Government Finance Statistics: Concepts, Sources and Methods. cat. no. 5514.0.55.001.
|
| Reverse investment | Reverse investment refers to the acquisition by a direct investment enterprise of a financial claim on its direct investor. Because direct investment is recorded on a directional basis, capital invested by the direct investment enterprise in its direct investor (reverse investment) is regarded as an offset to capital invested in the direct investment enterprise by a direct investor and its related enterprises, except in instances when the equity participation are at least 10 percent in both directions.
Reference: Australian System of Government Finance Statistics: Concepts, Sources and Methods. cat. no. 5514.0.55.001.
|
| Revolving credit | Generally has the following characteristics:
- a commitment for a credit or borrowing limit is given for a specific period after which the commitment is reviewed
- the extent of the borrowing used at any time during the period may be for any amount up to the authorised limit; and
- repayments (other than of charges and interest) made during the period reduce the extent of the borrowing used and thereby increase the amount of unused credit available up to the authorised limit. Examples include credit cards, lines of credit and approved overdrafts.
Reference: Housing Finance, Australia. cat. no. 5609.0.
|
| Retail turnover | Retail turnover includes retail sales; wholesale sales; takings from repairs, meals and hiring of goods (except for rent, leasing and hiring of land and buildings); commissions from agency activity (e.g. commissions received from collecting dry cleaning, selling lottery tickets, etc.); and net takings from gaming machines etc. From July 2000, turnover includes the goods and services tax.
Reference: Australian National Accounts: Concepts, Sources and Methods. cat. no. 5216.0.
|
| Rooms | The maximum number of rooms available for accommodating short-term paying guests at each licensed hotel and resort, motel and guest house and serviced apartment during the survey period. Units, apartments and suites are treated as rooms for these types of establishments in these survey results.
Reference: Tourist Accommodation, Australia. cat. no. 8635.0.
|
| Room occupancy rate | The room occupancy rate represents room occupancy expressed as a percentage of total capacity available during the survey period,
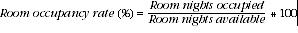
providing that, for establishments closing (other than for seasonal reasons) or opening during the survey period, the denominator of the above expression includes only operating periods.
Reference: Tourist Accommodation, Australia. cat. no. 8635.0.
|
| Rotating panel methodology | The sample selection methodology used to refresh the sample of businesses in the LPI survey.
Reference: Labour Price Index: Concepts, Sources and Methods. cat. no. 6351.0.55.001.
|
| Rotation group | The sample of households for the monthly Labour Force Survey is divided into eight groups of approximate equal size, called rotation groups. They are called rotation groups because each group stays in the sample for eight consecutive months and is then rotated out of the sample and is replaced by another group that is rotated into the sample for another period of eight months.
Reference: Demographic Estimates and Projections: Concepts, Sources and Methods. cat. no. 3228.0.
|
| Rural Goods | The category 'rural goods' is broad, and attempts to provide an indication of those exports most closely associated with the agriculture, forestry and fishing industries. For example, while meat and meat preparations, cereal preparations, canned fruit salad and timber boards are all classified as 'rural goods', beverages (including wine) are excluded. Non-rural exports, therefore, can include agricultural production embedded in other products. Because of this, and because of different valuation bases, BOP and production data cannot be directly compared. For more details see the Feature Article on Understanding Agricultural Exports Data, Year Book Australia, 2002 cat. no. 1301.0. |
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All