Structure and Format of ASCED
This section contains the following subsection :
- Level of Education
- Field of Education
Level of Education
Classification structure
Broad levels
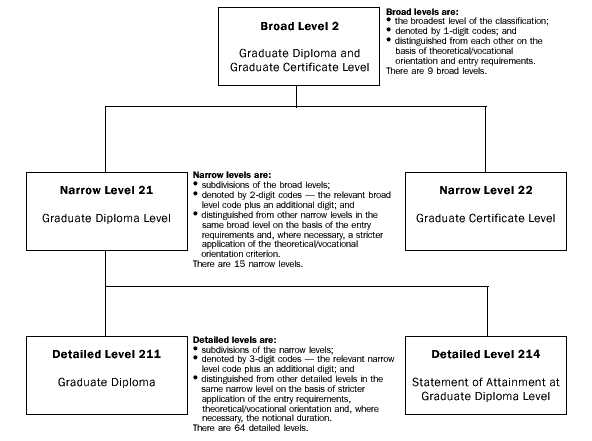
Broad levels are:
- the broadest categories of the classification;
- denoted by 1-digit codes; and
- distinguished from each other on the basis of theoretical/vocational orientation and entry requirements.
In general the relationship between the broad levels is ordinal, in the sense that educational activities in Broad Level 1 are higher than those in Broad Level 2 and so forth. This is not the case in all instances, however; in particular educational activities in Broad Level 5 Certificate Level may be of an equal, higher or lower level than those classified in Broad Level 6 Secondary Education.
There are 9 broad levels.
Narrow levels
Narrow levels are:
- subdivisions of the broad levels;
- denoted by 2-digit codes - the relevant broad level code plus an additional digit; and
- distinguished from other narrow levels in the same broad level on the basis of the entry requirements and, where necessary, a stricter application of the theoretical/vocational orientation criterion.
There are 15 narrow levels.
Detailed levels
Detailed levels are:
- subdivisions of the narrow levels;
- denoted by 3-digit codes - the relevant narrow level code plus an additional digit; and
- distinguished from other detailed levels in the same narrow level on the basis of stricter application of the entry requirements, theoretical/vocational orientation and, where necessary, the notional duration.
The detailed level also meets particular statistical needs by differentiating educational activity based on research rather than coursework, professional specialist qualifications, statements of attainment, and bridging and enabling courses.
There are 64 detailed levels.
Residual categories
The codes of “9”, “99” and “999” are residual codes for use for those educational activities which cannot be classified to a particular level of education.
Supplementary codes
Supplementary codes are used to process inadequately described responses in statistical collections. These codes are of two types:
- three digit codes ending in one or two zeros; and
- three digit codes commencing with one or two zeros, or codes with three zeros.
Codes ending in zero are described as “not further defined” (n.f.d.) and are used to code responses which cannot be coded to any detailed level in the classification but can be coded to a higher level of the classification structure.
For example, responses which cannot be identified as relating directly to a particular level category, but which are known to be within the range of levels within a particular broad level category are coded to that broad level. Such responses are allocated an “n.f.d.” code consisting of the one-digit code of the broad level followed by “00”. For instance, the response “Certificate” does not contain sufficient information to be coded directly to any particular detailed level category but can be coded to Broad Level 5 Certificate Level, which encompasses certificates. It is thus allocated the code 500 Certificate Level, n.f.d.
Codes commencing with zero are used to process responses which do not provide sufficient information to be coded to any level of the structure and when there is no level of education information given. Other codes commencing with zero may be defined by users to facilitate the processing and storage of data, when data sets coded to ASCED contain records for entities outside the scope of ASCED. For example, these codes might be used for educational activities that are excluded from ASCED (e.g. hobby/recreational programmes).
Format of the definitions
This publication contains definitions for the broad, narrow, and detailed levels. The format of the definitions may vary slightly between the hierarchical levels, but all contain similar elements.
The features of the broad, narrow and detailed level definitions for Level of Education are:
- a lead statement which defines the category and sets the boundaries of the category;
- information on the theoretical/vocational orientation;
- information on the minimum entry requirements;
- information on the notional duration;
- a list of lower level categories contained in the category (not applicable for detailed level); and. a list of inclusions or exclusions (as necessary).
Profile of the Level of Education structure
The structure of ASCED Level of Education has three levels:
- broad level;
- narrow level; and
- detailed level.
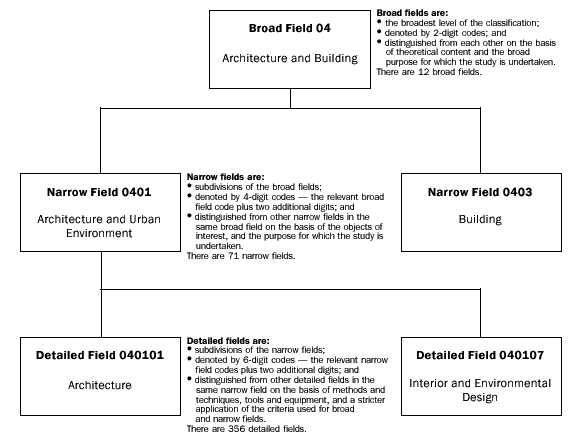
The following is an illustration of a representative part of the Level of Education structure:
Illustration of a representative part of the Level of Education structure.
Field of Education
Classification Structure
Broad fields
Broad fields are:
- the broadest categories of the classification;
- denoted by 2-digit codes; and
- distinguished from each other on the basis of theoretical content and the broad purpose for which the study is undertaken.
There are 12 broad fields.
Narrow fields
Narrow fields are:
- subdivisions of the broad fields;
- denoted by 4-digit codes - the relevant broad field code plus two additional digits; and
- distinguished from other narrow fields in the same broad field on the basis of the objects of interest, and the purpose for which the study is undertaken.
There are 71 narrow fields.
Detailed fields
Detailed fields are:
- subdivisions of the narrow fields;
- denoted by 6-digit codes - the relevant narrow field code plus two additional digits; and
- distinguished from other detailed fields in the same narrow field on the basis of methods and techniques, tools and equipment, and a stricter application of the criteria used for broad and narrow fields.
There are 356 detailed fields.
Residual categories
Codes ending in “99” are allocated to fields of education which may belong to a particular broad or narrow field of education but which do not represent sufficient observations to be a distinct detailed field of education in their own right. These are the “other” or “not elsewhere classified” (n.e.c.) categories. These categories should not be used to code responses which are inadequately described or ambiguous.
Supplementary codes
Supplementary codes for field of education are:
- 6-digit codes ending in two or four zeros; and
- codes commencing with two or more zeros.
Codes ending in two or four zeros are described as “not further defined” (n.f.d.) codes and are used to assign Field of Education codes to responses to questions in statistical or administrative data collections which cannot be coded to any specific detailed field in the classification but can be coded to a higher level of the classification structure.
For example if the Field of Education is given as “law” it is not possible to identify which of the seven detailed categories of Law it should be coded to, but it can be coded to Narrow Field 0909 Law and would therefore be assigned the 6-digit code of 090900 Law, n.f.d. Similarly, responses which do not contain sufficient information to be related directly to a particular narrow field category but which are known to be within the range of a particular broad field are coded to that broad field. For example, if the Field of Education is given as “health” it can be coded to Broad Field 06 Health and allocated the code 060000 Health, n.f.d.
Codes commencing with two or more zeros are used to process responses which do not provide sufficient information to be coded to any field of the structure and when there is no field of education given. Other codes commencing with zero may be defined by users to facilitate the processing and storage of data, when data sets coded to ASCED contain records for entities outside the scope of ASCED. For example, these codes might be used for educational activities that are excluded from ASCED (e.g. hobby/recreational programmes).
Format of the definitions
This publication contains definitions for the broad, narrow, and detailed fields. The format of the definitions may vary between the hierarchical levels, but all contain similar elements.
The features of the broad, narrow and detailed field definitions are:
- a lead statement which describes the theoretical orientation of the programme;
- main purpose (not applicable for detailed field);
- skills learnt/theoretical content/subjects undertaken;
- a list of lower level fields contained in the field (not applicable for detailed field); and
- a list of inclusions or exclusions (as necessary).
Profile of the Field of Education structure
The structure of ASCED Field of Education has three levels:
- broad field;
- narrow field; and
- detailed field.
The following is an illustration of a representative part of the Field of Education structure:
Illustration of a representative part of the Field of Education structure.