PRINCIPAL OFFENCE
The following information only relates to defendants who were adjudicated, i.e. finalised via a plea of guilty or a decision by the Magistrate as to their guilt or innocence of the final charges laid. The offence categories referred to relate to the principal offence i.e. the most serious offence type with which the defendant was charged. For more information about principal offence see Explanatory Notes paragraphs 38-41.
Road traffic offences accounted for the highest proportion (43%) of defendants heard in the Magistrates' Courts in 2006-07. This was similar to the proportion of defendants with this offence in the previous year. See the section in this chapter titled 'Road traffic and motor vehicle regulatory offences' for more detail on defendants charged with this offence.
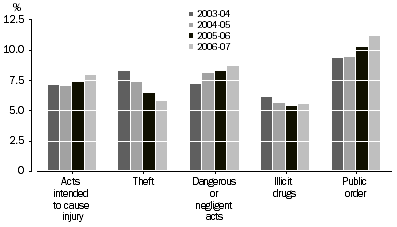
Following road traffic offences, the largest proportion of defendants were charged with: public order offences (11%); dangerous or negligent acts endangering persons (9%); acts intended to cause injury (8%); offences against justice procedures (6%); and theft (6%).
The proportion of defendants charged with public order offences increased from 9% (43,322) in 2003-04 to 11% (58,498) in 2006-07. Over the same period, the proportion of defendants charged with theft decreased from 8% (38,366) to 6% (30,260).
DEFENDANTS ADJUDICATED, Selected principal offence, 2003-04 to 2006-07
Sex
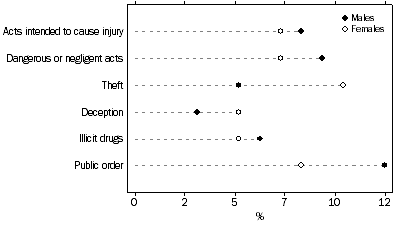
In 2006-07, defendants were over three times more likely to be male (77%) than female (21%).
The three offences for which males were most commonly charged, apart from road traffic offences, were: public order offences (12%); dangerous or negligent acts endangering persons (9%); and acts intended to cause injury (8%).
The three offences for which females were most commonly charged, apart from road traffic offences, were: theft (10%); public order offences (8%); and dangerous or negligent acts endangering persons (7%). This was a similar pattern of offences to 2005-06.
DEFENDANTS ADJUDICATED, Selected principal offence by sex
Age
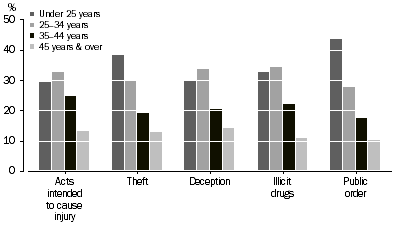
A third (33%) of defendants heard in the Magistrates' Courts were aged under 25 years, followed by those aged 25 to 34 years (29%), 35 to 44 years (19%), and 45 years and over (14%).
Defendants aged under 25 years accounted for the highest proportion charged with unlawful entry with intent (47%), property damage (46%), public order offences (43%), dangerous or negligent acts (41%), and theft (38%). The highest proportion of defendants charged with deception (34%), illicit drug offences (34%), and acts intended to cause injury (33%) were those aged 25 to 34 years.
DEFENDANTS ADJUDICATED, Selected principal offence by age groups
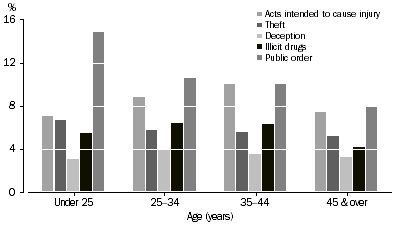
While the largest proportion of defendants in all age groups were charged with road traffic offences, there were differences in the remaining offences by age. The second most common charge for defendants aged under 25 years was public order offences (15%), whereas defendants aged 35 to 44 years were equally likely to be charged with acts intended to cause injury and public order offences (both 10%).
DEFENDANTS ADJUDICATED, Age groups by selected principal offence
Road traffic and motor vehicle regulatory offences
In 2006-07, 43% (227,238) of defendants adjudicated in the Magistrates' Courts were charged with road traffic offences as their principal offence. Nearly a third (29%) of these defendants were aged under 25 years. In total, 58% of defendants charged with road traffic offences were aged under 35 years.
Within the broad category of road traffic offences defendants were charged as follows:
- driving licence offences (31%);
- exceeding the prescribed content of alcohol limit (27%);
- exceeding the legal speed limit (12%);
- road vehicle registration and roadworthiness offences (9%); and
- parking offences (9%).
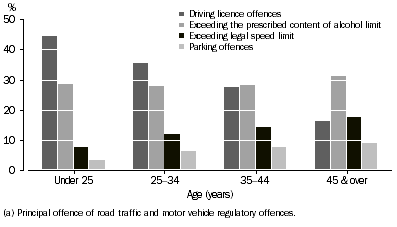
Younger defendants were more likely to be charged with driving licence offences than older defendants; 44% of defendants aged under 25 years compared with 16% of those aged 45 years and over. Driving licence offences include driving without a licence or driving while a licence is cancelled or suspended.
A greater proportion of defendants aged 45 years and over were charged with offences of exceeding the legal speed limit, as well as parking offences, compared with younger defendants. The proportion of defendants charged with exceeding the prescribed content of alcohol limit was similar across all age groups (around 30%).
DEFENDANTS ADJUDICATED FOR ROAD TRAFFIC OFFENCES(a), Selected offences by age group
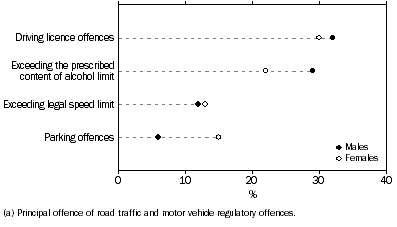
Of defendants charged with road traffic offences as their principal offence, 170,355 were males and 51,593 were females. The largest proportion of both males and females were in court for driving licence offences (32% and 30% respectively). However, males were more likely to have a principal offence of exceeding the alcohol limit (29%) than females (22%), while females were more than twice as likely to be charged with parking offences (15%) than males (6%).
DEFENDANTS ADJUDICATED FOR ROAD TRAFFIC OFFENCES(a), Selected offences by sex
Of defendants charged with road traffic offences, 96% (218,475) were proven guilty. The most common sentence for these defendants was a monetary order (84%), while 5% were issued with custodial sentences. Of all road traffic offences, driving licence offences had the highest proportion of defendants sentenced to custodial orders (10% or 6,639), followed by exceeding the alcohol limit (5% or 3,299).
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All