GLOSSARY
Age-sex pyramid
An age-sex pyramid is a bar chart graphically representing the age structure of the population, usually in five-year age groups, for males and females separately. The age structure of the population usually approximates the shape of a pyramid because mortality progressively reduces the number in each birth cohort as it ages. The age pyramid is useful to show the existence of unusually large or small cohorts, and in this way, not only conveys information about a country's past demographic history, but also a great deal about its demographic future.
Age-specific death rates
Age-specific death rates (ASDRs) are the number of deaths (occurred or registered) during the calendar year at a specified age per 1,000 of the estimated resident population of the same age at the mid-point of the year (30 June). Pro rata adjustment is made in respect of deaths for which the age of the deceased is not given.
Age-specific fertility rates
Age-specific fertility rates (ASFR) are the number of live births (occurred or registered) during the calendar year, according to the age of the mother, per 1,000 of the female estimated resident population of the same age at 30 June. In the calculation of these rates, births to mothers under 15 years are included in the 15-19 years age group, and births to mothers aged 50 years and over are included in the 45-49 years age group. Pro rata adjustment is made for births for which the age of the mother is not given.
Age-specific paternity rates
Age-specific paternity rates (ASPR) are the number of live births (occurred or registered) during the calendar year, according to the age of the father, per 1,000 of the male estimated resident population of the same age at 30 June. In the calculation of these rates, births to fathers under 15 years are included in the 15-19 years age group, and births to fathers aged 50 years and over are included in the 45-49 years age group. Pro rata adjustment is made for births for which the age of the father is not given.
Average annual growth rate
The average annual growth rate, r, is calculated as a percentage using the formula:
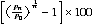
where P0 is the population at the start of the period, Pn is the population at the end of the period and n is the length of the period between P0 and Pn in years.
Birth
The delivery of a child, irrespective of the duration of pregnancy, who, after being born, breathes or shows any evidence of life such as heartbeat.
Completed fertility
Completed fertility represents the average number of births a cohort of females have borne over their reproductive lifetimes.
Death
Death is the permanent disappearance of all evidence of life after birth has taken place. The definition excludes all deaths prior to live birth. For the purposes of the Death Registrations collection, a death refers to any death which occurs in, or en route to Australia and is registered with a state or territory Registry of Births, Deaths and Marriages.
Estimated resident population (ERP)
The official measure of the population of Australia is based on the concept of usual residence. It refers to all people, regardless of nationality or citizenship, who usually live in Australia, with the exception of foreign diplomatic personnel and their families. It includes usual residents who are overseas for less than 12 months. It excludes overseas visitors who are in Australia for less than 12 months.
Indigenous
Persons who identify themselves as being of Aboriginal and/or Torres Strait Islander origin.
Indigenous birth
The birth of a live-born child where either the mother or the father was identified as being of Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander origin on the birth registration form.
Indigenous death
The death of a person who is identified as being of Aboriginal and/or Torres Strait Islander (Indigenous) origin on the Death Registration Form. From 2007, Indigenous origin for deaths registered in South Australia, Western Australia, Tasmania, the Northern Territory and the Australian Capital Territory is also derived from the Medical Certificate of Cause of Death.
Indigenous Region (IREG)
In 2006, the highest level of the Australian Indigenous Geographical Classification (AIGC) is made up of Indigenous Regions (IREGs). IREGs are based on the earlier Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Commission (ATSIC) Regions but reflect recent changes in local government areas. Changes in government administrative arrangements were also taken into account in defining the IREGs. Where possible and appropriate, the 2001 boundaries were maintained to allow the characteristics of Indigenous people within a Region to be compared across Censuses.
IREGs cover in aggregate, the whole of Australia without gaps or overlaps.
Intercensal period
The time period between 30 June in the previous census year and 30 June of the latest census year.
Life expectancy
Life expectancy refers to the average number of additional years a person of a given age and sex might expect to live if the age-specific death rates of the given period continued throughout his/her lifetime.
Life table
A life table is a tabular, numerical representation of mortality and survivorship of a cohort of births at each age of life. The conventional life table is based on the assumption that as the cohort passes through life it experiences mortality at each age in accordance with a predetermined pattern of mortality rates which do not change from year to year. The life table thus constitutes a hypothetical model of mortality, and even though it is usually based upon death rates from a real population during a particular period of time, it does not describe the real mortality which characterises a cohort as it ages.
Due to differences in mortality patterns between males and females at different ages, life tables are generally constructed separately for each sex.
Median age
For any distribution the median value is that which divides the relevant population into two equal parts, half falling below the value, and half exceeding it. Thus, the median age is the age at which half the population is older and half is younger.
Migration
The movement of people across a specified boundary for the purpose of establishing a new or semi-permanent residence. Migration can be international (migration between countries) and internal (migration within a country).
Mortality
Death.
Natural increase
Excess of births over deaths.
Net interstate migration
Net interstate migration is the net gain or loss of population though interstate migration being the change of a person's place of usual residence from one state or territory to another state or territory.
Net overseas migration
Net overseas migration is the net gain or loss of population through immigration to Australia and emigration from Australia.
Net population growth
For Australia, net population growth is the sum of natural increase and net overseas migration. For the states and territories, net population growth also includes net interstate migration.
Net undercount
The difference between the actual census count (including imputations) and an estimate of the number of people who should have been counted in the census. This estimate is based on the Post Enumeration Survey conducted after each census. For a category of person (e.g. based on age, sex and state of usual residence), net undercount is the resultant of census undercount, over count, misclassification and imputation error.
Other Territories
Following the 1992 amendments to the Acts Interpretation Act to include the Indian Ocean Territories of Christmas Island and the Cocos (Keeling) Islands as part of geographic Australia, another category at the state and territory level has been created, known as Other Territories. Other Territories include Jervis Bay Territory, previously included with the Australian Capital Territory, as well as Christmas Island and the Cocos (Keeling) Islands.
Post Enumeration Survey (PES)
The Post Enumeration Survey (PES) is a household survey conducted three to four weeks after the census. The PES allows the ABS to estimate the number of people missed in the census and the number counted more than once. Usually more people are missed than counted more than once in Australia, leading to a net undercount. Results from the PES contribute to a more accurate calculation of the estimated resident population (ERP) for Australia and the states and territories which is then backdated to 30 June of the census year.
Rate of population growth
Population change over a period as a proportion (percentage) of the population at the beginning of the period.
Remoteness Area
Within the Australian Standard Geographical Classification (ASGC), the Remoteness classification comprises five categories, each of which identifies a (non-contiguous) region in Australia being a grouping of Collection Districts (CDs) sharing a particular degree of remoteness. The degrees of remoteness range from 'highly accessible' (i.e. major cities) to 'very remote'.
The degree of remoteness of each CD was determined using the Accessibility/Remoteness Index of Australia (ARIA. CDs have then been group into the appropriate category of Remotness to form non-contiguous areas within each state.
For more information, refer to Statistical Geography Volume 1: Australian Standard Geographical Classification (ASGC) 2006 (cat. no. 1216.0) and ABS Views on Remotness (cat. no. 1244.0).
Sex ratio
The sex ratio relates to the number of males per 100 females. The sex ratio is defined for total population, at birth, at death and among age groups by appropriately selecting the numerator and denominator of the ratio.
State/territory of usual residence
State or territory of usual residence refers to the state or territory of usual residence of:
- the population;
- the mother (Birth Registrations collection); and
- the deceased (Death Registrations collection).
Total fertility rate (TFR)
The sum of age-specific fertility rates (live births at each age of mother per female population of that age). It represents the number of children a female would bear during her lifetime if she experienced current age-specific fertility rates at each age of her reproductive life.
Total paternity rate (TPR)
The sum of age-specific paternity rates (live births at each age of father per male population of that age). It represents the number of children a male would bear during his lifetime if he experienced current age-specific paternity rates at each age of his reproductive life.
Unexplained growth
The intercensal growth in the Indigenous population counts that cannot be fully explained by births, deaths and migration.
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All
 Quality Declaration
Quality Declaration