PRINCIPAL OFFENCE
The following information only relates to defendants who were adjudicated, i.e. finalised via a plea of guilty or a decision by the Children's Court as to their guilt or innocence of the final charges laid. The offence categories referred to relate to the principal offence i.e. the most serious offence type with which the defendant was charged. For more information about principal offence see paragraphs 38 to 41 of the Explanatory Notes.
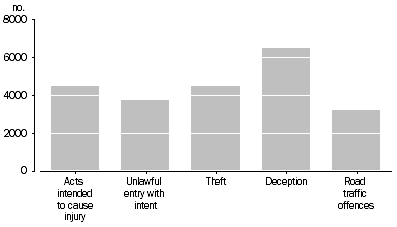
In 2006-07, those charged with a principal offence of deception formed the largest proportion of defendants (19%) in the Children's Courts. This was followed by: acts intended to cause injury and theft (both 13%), unlawful entry with intent (11%), and road traffic offences (9%). Combined, these principal offences accounted for two-thirds (66%) of defendants before the courts.
DEFENDANTS ADJUDICATED, Selected principal offence
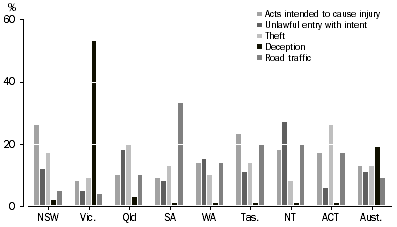
There was variation across states and territories in the types of principal offence that defendants were charged with in the Children's Courts. While acts intended to cause injury accounted for the highest proportion of final charges for defendants in New South Wales (26%) and Tasmania (23%), the most prevalent offence for defendants in the Northern Territory was unlawful entry with intent (27%). In South Australia, road traffic offences were most common (33%), while deception accounted for over half (53%) of all defendants adjudicated in Victoria. A major contributor to deception offences in Victoria were the large number of defendants adjudicated for fare evasion during 2006-07. Victorian defendants charged with fare evasion accounted for 97% (5,949) of defendants charged with deception in that state, and 92% of defendants charged with deception Australia-wide. See
Explanatory Notes paragraph 57 for further information.
DEFENDANTS ADJUDICATED, Selected principal offence by states and territories
Sex
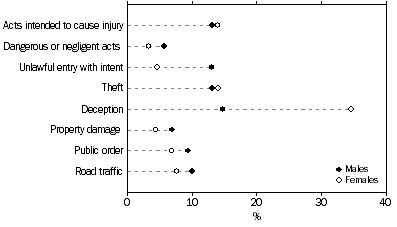
In 2006-07, over three quarters (77% or 25,993) of defendants heard in the Children's Courts were male, while females accounted for 23% (7,741).
The most prevalent principal offence for male defendants was deception (15%), followed by acts intended to cause injury, theft, and unlawful entry with intent (all 13%).
Deception was far more common for females than males with over a third (35%) of female defendants being charged with this offence. This was followed by theft, and acts intended to cause injury (both 14%). Unlawful entry with intent accounted for a lower proportion of female defendants (5%) than males (13%).
DEFENDANTS ADJUDICATED, Selected principal offence by sex
Age
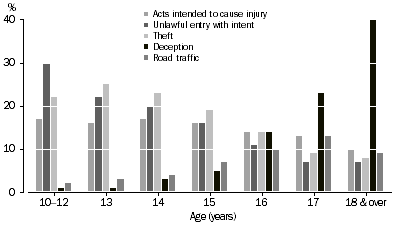
The largest proportion of defendants heard in the Children's Courts were aged 17 years at the time of finalisation (29% or 9,960), followed by those aged 16 years (22% or 7,522). Defendants aged 13 to 15 years accounted for 25% (8,516) and those aged 10 to 12 years comprised 2% (686).
The type of offence defendants were charged with in the Children's Courts varied by age:
- The largest proportion (29%) of the youngest defendants (those aged 10 to 12 years) had a principal offence of unlawful entry with intent;
- Defendants aged 13 to 15 years most commonly had a principal offence of theft (21%);
- Theft, deception, and acts intended to cause injury comprised the highest proportion of offences for 16 year olds (all 14%);
- The largest proportion of defendants aged 17 years had a principal offence of deception (23%), followed by acts intended to cause injury and road traffic offences (both 13%).
DEFENDANTS ADJUDICATED, Selected principal offence by age
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All