HOSPITALS
There were 612 private hospitals operating in Australia in 2013-14, a net increase of 11 from 2012-13. There were four additional Acute and psychiatric hospitals and seven additional Free-standing day hospitals in 2013-14.
TABLE 1.1: PRIVATE HOSPITALS, Australia—2013-14
|
 | Acute and psychiatric hospitals | Free-standing day hospital facilities | All private hospitals |
 |
| New South Wales | 91 | 102 | 193 |
| Victoria | 79 | 86 | 165 |
| Queensland | 56 | 52 | 108 |
| South Australia | 28 | 27 | 55 |
| Western Australia | 22 | 40 | 62 |
| Tasmania, Northern Territory and Australian Capital Territory (a) | 10 | 19 | 29 |
| Australia | 286 | 326 | 612 |
|
| (a) Tasmania, Northern Territory and Australian Capital Territory have been aggregated to protect the confidentiality of the small number of hospitals in these states/territories. |
There were 30,920 beds and chairs available in private hospitals in 2013-14. Acute and psychiatric hospitals accounted for 27,943 or 90.4% of all beds and chairs, with the remaining 2,977 located in Free-standing day hospital facilities.
There were over 4.3 million patient separations in 2013-14, with 74.1% of those separations reported by acute and psychiatric hospitals. Total patient separations have increased by 4.0% from 2012-13 to 2013-14.
Private hospitals provided close to 10 million patients days of care in 2013-14. Acute and psychiatric hospitals provided 8.8 million, or 88.7% of all patient days. Within acute and psychiatric hospitals, overnight-stay patients accounted for 6.9 million patient days and same day patients accounted for a further 1.9 million. Free-standing day hospitals only deal with same-day patients, accounting for 1.1 million patient days overall.
Private hospitals reported a total of 1,448 operating theatres in 2013-14 with 1,097 (75.8%) located in Acute and psychiatric hospitals.
There were 62,413 full-time equivalent staff working in private hospitals in 2013-14 with 58,170 (93.2%) working in Acute and psychiatric hospitals and 6.8% working in Free-standing day hospitals.
Total private hospital income was $12.7 billion in 2013-14, with 95.6% of that income attributed to patients. Total income from private Acute and psychiatric hospitals was $11.7 billion, which accounted for 92.2% of all private hospital income.
Total private hospital expenditure was $11.4 billion in 2013-14. For Acute and psychiatric hospitals, wages and salaries accounted for 49.2% of total expenditure, while for Free-standing day hospitals wages and salaries accounted for 41.9% of total expenditure.
Gross capital expenditure for all private hospitals was $765.3 million, with $718.3 or 93.9% attributed to Acute and psychiatric hospitals.
TABLE 1.2: PRIVATE HOSPITALS, Summary—2013-14
|
 | Acute and psychiatric hospitals | Free-standing day hospital facilities | All private hospitals |
|
| Hospitals (no.) | 286 | 326 | 612 |
| Beds/Chairs (no.) (a) | 27,943 | 2,977 | 30,920 |
| Separations ('000) | 3,220 | 1,124 | 4,344 |
| Sex ('000) (b) |
 | Males | 1,449 | 495 | 1,944 |
 | Females | 1,771 | 605 | 2,376 |
| Aged 65 and over (%) | 41.2 | 44.5 | 42.1 |
| Patient days ('000) |
 | Same-day patient (c) | 1,939 | 1,124 | 3,063 |
 | Overnight-stay patient | 6,894 | - | 6,894 |
 | Total | 8,833 | 1,124 | 9,957 |
| Operating theatres | 1,097 | 351 | 1,448 |
| Co-located with a public hospital (no.) | 47 | 10 | 57 |
| Full-time equivalent staff (no.) (d) | 58,170 | 4,243 | 62,413 |
| Income (e) |
 | Total ($'000) | 11,740,226 | 990,904 | 12,731,130 |
 | Patient income (%) (f) | 95.6 | 95.7 | 95.6 |
| Expenditure (g) |
 | Total ($'000) | 10,535,797 | 815,164 | 11,350,961 |
 | Wages and salaries, including on-costs, as a proportion of total expenditure (%) | 49.2 | 41.9 | 48.7 |
| Gross Capital expenditure ($'000) (h) | 718,316 | 47,020 | 765,336 |
| Net Capital Expenditure ($'000) (h) | 700,424 | 46,445 | 746,869 |
|
— nil or rounded to zero (including null cells)
(a) Available beds/chairs (average for the year).
(b) Excludes patients with sex not stated, therefore sum may not add to total separations.
(c) Same-day patients are counted as having a stay of one day.
(d) Staff represented are typical full-time equivalent numbers for the year. Full-time equivalent represents the sum of full-time staff and full-time equivalent of part-time staff. See Glossary for further information.
(e) Income includes income from patients, recoveries and other income such as investment income and income from charities, bequests, meals and accommodation but excludes income payments from state and territory governments. See Glossary for further information.
(f) Includes income received by, and due to, the hospital in respect of patient liability for accommodation and other fees. See Glossary for further information.
(g) Expenditure refers to expenditure on goods and services, which does not result in the creation or acquisition of fixed assets (new or second-hand). See Glossary for further information.
(h) Capital expenditure refers to expenditure in a period on the acquisition or enhancement of an asset (excluding financial assets). See Glossary for further information. |
Net operating margin
Net operating margin is derived by subtracting recurrent expenditure from income and expressing the result as a proportion of income. The net operating margin for Acute and psychiatric hospitals during 2013-14 was 10.3%, up from 9.2% in 2012-13. The net operating margin for Free-standing day hospital facilities decreased from 18.7% in 2012-13 to 17.8% in 2013-14.
Private Hospitals, Net operating margin
: 2009-10 to 2013-14
.
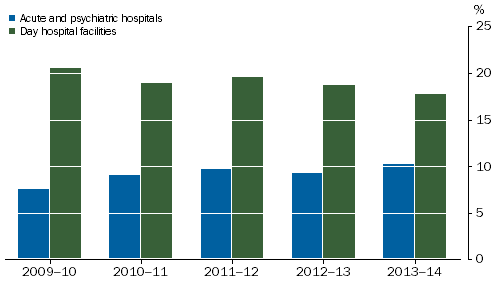
 Quality Declaration
Quality Declaration  Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All