JUNE QUARTER KEY FIGURES
 |  | Mar Qtr 2005 | Jun Qtr 2005 | Mar Qtr 2005 to Jun Qtr 2005 |  |
 |  | $m | $m | % change |  |
TREND ESTIMATES |  |
|  |
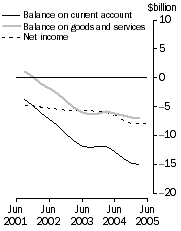
| Balance on current account | -15 097 | (a)-12 943 | . . |  |
| Balance on goods and services | -6 992 | (a)-4 996 | . . |  |
| Net income | -7 996 | -7 851 | 2 |  |
SEASONALLY ADJUSTED |  |
|  |
| Balance on current account | -15 006 | -12 640 | 16 |  |
| Balance on goods and services | -6 917 | -4 945 | 29 |  |
| Net income | -7 949 | -7 625 | 4 |  |
ORIGINAL |  |
|  |
| Balance on current account | -13 148 | -12 506 | 5 |  |
| Balance on capital and financial account | 13 647 | 11 797 | -14 |  |
Levels at end of period |  |
|  |
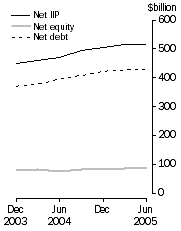
| Net international investment position (IIP) | 514 804 | 516 827 | - |  |
 | Net equity | 88 062 | 86 863 | -1 |  |
 | Net debt | 426 742 | 429 964 | 1 |  |
|  |
| . . not applicable |
| - nil or rounded to zero (including null cells) |
| (a) A trend break of $1.8b has been applied - see Changes in this issue for details. |
Current Account, Main aggregates - Trend estimates at current prices
| International Investment, Levels at end of period
|
JUNE KEY POINTS
BALANCE OF PAYMENTS
- The current account deficit, seasonally adjusted, fell $2,366m (16%) to $12,640m. The deficit on the balance of goods and services fell $1,972m (29%) to $4,945m. The income deficit fell $324m (4%) to $7,625m.
- In seasonally adjusted chain volume terms there was an increase of $357m (3%) in the deficit on goods and services. This could be expected to contribute -0.2 percentage points to growth in the June quarter 2005 volume measures of GDP.
- In original terms, the balance on current account for 2004-05 was a deficit of $57.2b, up $9.4b from the deficit of $47.8 in 2003-04.
INTERNATIONAL INVESTMENT POSITION
- Australia's net IIP rose by $2b to a net liability position of $517b at 30 June 2005. Transactions of $12b contributed to this increase. Partially offsetting the increase were price changes of -$8b. Net debt liabilities rose by $3b to $430b, while net equity liabilities fell by $1b to $87b. It should be noted that the net equity liabilities series has been significantly revised - see page 2 for details.
NOTES
REVISIONS
Table 35 summarises revisions, in original current price terms, since the last issue of this publication, for the last three years and six quarters.
Incorporation of the latest survey and administrative data has resulted in revisions to the current account back to June quarter 2001, increasing the 2003-04 current account deficit by $35m.
There have been revisions to the international investment position (IIP) data. This issue incorporates revisions to data from June quarter 2001. The revisions are the result of improved reporting, the identification and correction of errors and adjustments to approximate market valuation. These revisions have decreased Australia's net IIP liability as at 31 March 2005 by $39.9b. Net equity has been revised down by $42.0b and net debt has been revised up by $2.1b.
As identified in the International Monetary Fund's Balance of Payments Manual (BPM5, 1993), market valuation is the principle used for valuation of equity. Providers in the Survey of International Investment, the main source of information IIP data, are asked to value equity liabilities and equity assets on this basis. Some providers are unable to provide a market value and report net asset value. Where this creates a significant distortion, the ABS makes adjustments to approximate market valuation, a process that started in September quarter 2000. The adjustment process has been extended to more providers in this issue. These adjustments have been applied across the full time series presented in this issue and do not affect transactions recorded in the balance of payments.
CHANGES IN THIS ISSUE
SEASONALLY ADJUSTED AND TREND ESTIMATES
Investment Income
In past publications, seasonal adjustment has been made directly to the total investment income credits and total investment income debits series, taking no account for potential differing seasonal characteristics of more detailed series. From this issue, income on direct investment equity, direct investment debt, portfolio investment equity, portfolio investment debt and other investment are analysed separately for both credits and debits. This has resulted in revisions to the seasonally adjusted and trend income. In addition to other revisions, the seasonally adjusted net income deficit for March quarter 2005 has increased by $0.5b due to the change in methodology.
As a result of these changes to investment income credits and debits, AusStats Table 95 which presents the quarterly current price seasonal adjustment factors, has been expanded to include these new seasonal factors.
Non-rural Exports
The prices of coal and iron ore export commodities significantly increased in June quarter 2005 although the volumes of exports of these commodities remained relatively unchanged. This is apparent in the large value observed in the original estimates of goods credits for June quarter 2005. It is expected that the increased prices will continue to apply and will result in a shift in level of the current price measures of coal and iron ore. The seasonally adjusted estimates also reflect the level shift resulting from the increased prices, but the impact of this increased has been taken into account in determining the concurrent seasonal factors.
Since the price increase impact is likely to result in a permanent change in the level of the series (at least for the duration of the current contracts), an estimated trend break correction of $1b has been applied to coal and $800m to iron ore in June quarter 2005. As a minimum of three quarters is required for a trend break correction to be accurately estimated using time series techniques, the size of the trend break may be revised. Therefore, users should interpret the trend estimates for recent quarters with some caution. The June quarter 2005 trend observation is not visible in the charts in this issue affected by the trend break.
Chain Volume Estimates
A new base year, 2003-04, has been introduced into the chain volume estimates which has resulted in revisions to growth rates in subsequent quarters. In addition, the chain volume estimates have been re-referenced to 2003-04, thereby preserving additivity in the quarters after the reference year. Re-referencing affects levels of, but not the movements in, chain volume estimates.
CHANGES IN FORTHCOMING ISSUES
A new table will be introduced to the September quarter 2005 publication showing seasonally adjusted and trend income series at a finer level.
INQUIRIES
For further information contact Tom Jebbink on Canberra (02) 6252 5540 for balance of payments estimates, and Paul Mahoney on Canberra (02) 6252 5541 for international investment estimates.
TABLES ON AUSSTATS
TABLES AVAILABLE ON AUSSTATS
Data available on this web site include:
- longer time series of all tables contained in this publication
- additional tables as listed below:
51 Balance of payments: summary, original - Financial year
52 International investment position by net foreign equity and net foreign debt - Financial year
53 International investment position by foreign assets by equity and debt - Financial year
54 International investment position by foreign liabilities by equity and debt - Financial year
56 Goods and services: terms of trade, original - Financial year
57 Goods credits: original - Financial year
58 Goods debits: original - Financial year
63 Goods credits: implicit price deflators (Index numbers) - Financial year
64 Goods debits: implicit price deflators (Index numbers) - Financial year
65 Services credits: original - Financial year
66 Services debits: original - Financial year
68 Services credits: implicit price deflators (Index numbers) - Financial year
69 Services debits: implicit price deflators (Index numbers) - Financial year
70 Income credits: original - Financial year
71 Income debits: original - Financial year
72 Current transfers: original - Financial year
73 Capital account - Financial year
74 Financial Account - Financial year
75 International investment: Australian investment abroad - Financial year
76 International investment: foreign investment in Australia - Financial year
77 International investment: levels of Australian investment abroad - Financial year
78 International investment: levels of foreign investment in Australia - Financial year
79 International investment: foreign debt levels at the end of period - Financial year
80 International investment: gross external debt liabilities - Financial year
82 Balance of payments: exchange rates - Financial year
83 International investment: foreign assets and liabilities - Financial year
84 Balance of payments: ratios of current account measures to GDP - Financial year
88 International investment position: historical summary - Financial year
95 Quarterly combined current price seasonal adjustment factors, September 1959 to June 2006
101 Merchandise exports by SITC division on a Balance of payments basis, chain volume measures
102 Merchandise exports by SITC division on a Balance of payments basis, implicit price deflators
103 Merchandise exports by SITC division and section on a Recorded trade basis, chain volume measures
104 Merchandise exports by SITC division and section on a Recorded trade basis, implicit price deflators
105 Merchandise imports by End-Use categories on a Balance of payments basis, chain volume measures
106 Merchandise imports by End-Use categories on a Balance of payments basis, implicit price deflators
107 Merchandise imports by SITC division and section on a Recorded trade basis, chain volume measures
108 Merchandise imports by SITC division and section on a Recorded trade basis, implicit price deflators
109 Services credits and debits, confidentialised version, chain volume measures
110 Services credits and debits, confidentialised version, implicit price deflators
111 Balance of payments: current account transactions, seasonally adjusted and trend estimates (percentage change) - Quarter
112 Balance of payments: goods and services, implicit price deflators, original (index) - Quarter
113 Balance of payments: original and seasonally adjusted chain volume measures and indexes (percentage change) - Quarter
114 Balance of payments: goods credits, chain volume measures, original - Quarter
115 Balance of payments: goods debits, chain volume measures, original - Quarter
116 Balance of payments: services credits and debits, current prices, original and seasonally adjusted - Quarter
117 International investment: foreign assets, by direction and type of investment - Quarter
118 International investment: foreign liabilities, by direction and type of investment - Quarter
119 International investment: foreign debt transactions - Quarter
120 International investment: interest income on foreign debt - Quarter
214 Balance of payments: goods credits, chain volume measures, original - Financial year
215 Balance of payments: goods debits, chain volume measures, original -Financial year
216 Balance of payments: services credits and debits, current prices, original and seasonally adjusted - Financial year
217 International investment: foreign assets, by direction and type of investment - Financial year
218 International investment: foreign liabilities, by direction and type of investment - Financial year
219 International investment: foreign debt transactions - Financial year
220 International investment: interest income on foreign debt - Financial year
ANALYSIS AND COMMENTS
BALANCE OF PAYMENTS
CURRENT ACCOUNT
The trend estimate of the balance on current account for the June quarter 2005 was a deficit of $12,943m, a decrease of $2,154m (14%) on the revised deficit recorded for the March quarter 2005. The main contributor to the decrease in the deficit was goods credits which rose $2,844m (9%) partly offset by goods debits which rose $745m (2%). See Changes in this issue for a description of treatment of the move to significantly higher contract prices for selected commodities. These higher price levels are a major contributor to the increase in goods credits.
In seasonally adjusted terms, the current account deficit fell $2,366m (16%) to $12,640m between the March and June quarters 2005 where:
- the net goods deficit fell $2,102m (33%) to $4,296m
- the net income deficit fell $324m (4%) to $7,625m
- the net services deficit rose $130m (25%) to $649m.
Goods and Services
The trend estimate of the balance on goods and services at current prices was a deficit of $4,996m, a decrease of $1,996m on the March quarter 2005 deficit after the trend break correction of $1,800m - see Changes in this issue for more details.
In seasonally adjusted current price terms, the balance on goods and services was a deficit of $4,945m, a decrease of $1,972m on the March quarter 2005 deficit. The deficit on goods was $4,296m, a decrease of $2,102m (33%) on the deficit of $6,398m in the March quarter 2005. The deficit on services was $649m, an increase of $130m (25%) on the deficit of $519m in the March quarter 2005.
The decrease in the goods deficit resulted from higher goods exports, up $4,148m (13%), partly offset by higher goods imports, up $2,046m (5%).
The increase in goods credits was driven by:
- non-rural goods, up $3,728m (16%)
- other goods, up $244m (13%)
- rural goods, up $176m (3%).
The increase in goods debits was driven by:
- intermediate and other merchandise goods, up $1,607m (10%)
- capital goods, up $306m (3%)
- other goods, up $131m (11%)
- consumption goods, up $2m.
In seasonally adjusted volume terms, the deficit on goods and services was $10,944m, an increase of $357m (3%) on the $10,587m deficit recorded in the March quarter 2005. The net deficit on goods rose $189m (2%) to $9,965m. Goods credits rose $908m (3%) while goods debits rose $1,097m (3%). The net services balance was a deficit of $979m, an increase of $168m (21%) on the March quarter 2005 deficit of $811m.
The increase of $357m in the deficit on goods and services in volume terms could be expected to make a contribution to growth of -0.2 percentage points in the June quarter 2005 volume measure of GDP, assuming no significant revision to the GDP chain volume estimate for the March quarter 2005.
Goods and Services(a)
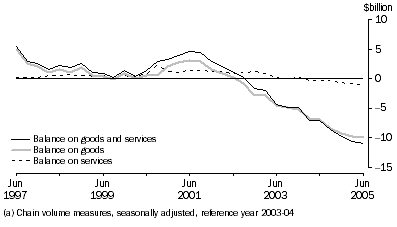
Goods Credits
The trend estimate of goods credits rose $2,844m to $34,452m in the June quarter 2005 after the trend break correction of $1,800m - see Changes in this issue for more details. Seasonally adjusted, goods credits were $35,150m, up $4,148m (13%) on the March quarter 2005, driven by increases in exports of non-rural goods.
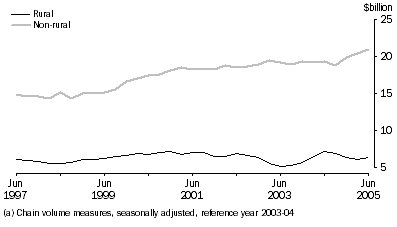
Rural goods (seasonally adjusted, current prices) rose $176m (3%) to $6,224m, mainly due to increased volumes. The largest increases were in:
- other rural, up $235m (10%), with volumes up 11% and prices down 1%
- wool and sheepskins, up $113m (17%), with volumes up 23% and prices down 5%
- meat and meat preparations, up $89m (5%), with volumes and prices both up 3%.
These increases were partly offset by a fall in cereal grains and cereal preparations, down $261m (22%), with volumes down 23% and prices up 2%.
Non-rural goods (seasonally adjusted, current prices) rose $3,728m (16%) to $26,821m, volumes up 3% and prices up 13%. The largest increases were in:
- coal, coke and briquettes, up $1,424m (35%), on increased prices
- metal ores and minerals, up $1,117m (23%), with volumes down 3% and prices up 27%
- transport equipment, up $386m (35%), with volumes up 33% and prices up 2%
- other mineral fuels, up $360m (13%), with volumes up 2% and prices up 11%.
These increases were partly offset by a fall in machinery, down $80m (4%), on decreased volumes.
Other goods (seasonally adjusted, current prices) rose $244m (13%) to $2,105m, driven by rises in goods procured in ports and goods for processing.
General Merchandise Credits(a)
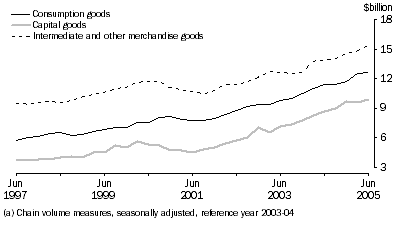
Goods Debits
The trend estimate of goods debits rose $745m (2%) to $38,808m in the June quarter 2005. In seasonally adjusted current price terms, goods debits rose $2,046m (5%) to $39,446m.
Consumption goods imports (seasonally adjusted, current prices) rose $2m to $12,091m, with a rise in volumes of 1%. The largest increases were in:
- food and beverages, mainly for consumption, up $53m (4%), with volumes down 1% and prices up 5%
- toys, books and leisure goods, up $43m (5%), with volumes up 5% and prices down 1%
- consumption goods n.e.s., up $33m (1%), with volumes up 2% and prices down 1%.
These increases were offset by falls in:
- non-industrial transport equipment, down $112m (3%), with volumes down 2% and prices down 1%
- household electrical items, down $26m (3%), with volumes up 1% and prices down 4%.
Capital goods imports (seasonally adjusted, current prices) rose $306m (3%) to $9,081m, largely due to increased volumes. The largest increases were in:
- civil aircraft, up $469m, largely on increased volumes
- machinery and industrial equipment, up $95m (3%), with volumes up 1% and prices up 2%
- ADP equipment, up $73m (5%), with volumes up 9% and prices down 4%.
Partly offsetting these increases was a fall in telecommunications equipment, down $328m (25%), with volumes down 23% and prices down 2%.
Intermediate and other merchandise goods (seasonally adjusted, current prices) rose $1,607m (10%) to $16,958m, with volumes up 4% and prices up 6%. The largest increases were in:
- fuels and lubricants, up $1,383m (43%), with volumes up 18% and prices up 21%
- other merchandise goods, up $116m (57%), on increased volumes
- processed industrial supplies, up $82m (2%), on increased prices.
Partly offsetting these increases were falls in:
- organic and inorganic chemicals, down $50m (5%), with volumes down 8% and prices up 3%
- plastics, down $38m (6%), with volumes down 11% and prices up 6%.
Other goods (seasonally adjusted, current prices) rose $131m (11%) to $1,316m driven by a rise in goods for processing.
General Merchandise Debits(a)
Services
The trend estimate of net services was a deficit of $640m, a rise of $103m (19%) on the March quarter 2005 deficit of $537m. In seasonally adjusted current price terms, net services recorded a deficit of $649m, a rise of $130m on the March quarter 2005.
Services credits, in seasonally adjusted terms at current prices, fell $234m (3%) to $8,726m, with volumes down 4% and prices up 1%. The largest decreases in services credits were in:
- travel services, down $172m (4%), with volumes down 5% and prices up 1%
- passenger and other services, down $28m (2%), largely on reduced volumes.
Services debits, in seasonally adjusted terms at current prices, fell $104m (1%) to $9,375m, largely on decreased volumes. The largest decrease in services debits was in passenger and other transportation services, down $81m (6%) with both volumes and prices down 3%.
Seasonally adjusted, tourism related services credits fell $191m (3%) to $5,431m while tourism related services debits fell $7m to $4,785m.
Implicit Price Deflator
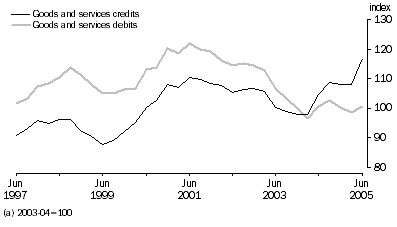
In seasonally adjusted terms, the implicit price deflator (IPD) for total goods and services credits rose 8.0%. In original terms, it rose by 10.4%. The chain Laspeyres price index for goods and services credits rose 7.7%, indicating that the compositional effects had an upward influence on the movement in the IPD. In seasonally adjusted terms, the IPD for goods credits rose 9.9% and the IPD for services credits rose 1.0%.
The total goods and services debits IPD rose 2.0% in seasonally adjusted terms. In original terms, it rose by 1.4%. The chain Laspeyres price index for debits rose 2.0%.
IMPLICIT PRICE DEFLATOR(a)
Relationship to IPI and EPI
In original terms, the implicit price deflator for total goods credits rose 9.3%. The chain Laspeyres price index for goods exports rose 9.7%. The export price index (EPI) rose 9.3% during the June quarter 2005.
During the June quarter 2005, the goods imports IPD (in original terms) rose 1.6% and the chain Laspeyres price index for goods imports rose 2.3%. The import price index (IPI) rose 1.7%.
Terms of trade
Australia's seasonally adjusted terms of trade rose 5.8%, with an increase of 8.0% in the IPD for goods and services credits and a 2.0% increase in the goods and services debits IPD. The trend estimate of the terms of trade increased 6.2%.
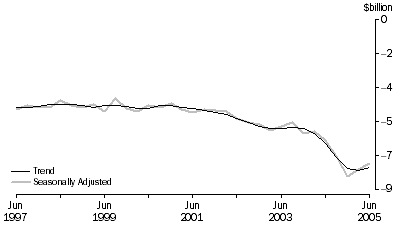
Income
The trend estimate of the net income deficit fell $145m (2%) to $7,851m. In seasonally adjusted terms, the net income deficit fell $324m (4%) to $7,625m.
Income credits, seasonally adjusted, rose $406m (8%) to $5,357m and income debits rose $82m (1%) to $12,982m.
In original terms, income credits rose $531m (11%) to $5,421m and income debits fell $235m (2%) to $12,906m.
Net Income
Current Transfers
In seasonally adjusted terms, the net current transfers deficit was $70m, a decrease of $70m on the $140m deficit recorded in the March quarter 2005. Current transfer credits fell $3m and current transfer debits fell $73m (6%).
CAPITAL AND FINANCIAL ACCOUNT
Capital Account
In original terms, the capital account surplus was $238m, down $116m (33%) on the March quarter 2005 surplus. Capital transfer credits fell $60m (8%) to $648m, while capital transfer debits fell $19m (5%) to $388m.
Financial Account
In original terms, the balance on financial account recorded a net inflow of $11.6b, with a $1.0b inflow of debt and a $10.6b inflow of equity.
Direct investment in Australia recorded an outflow of $57.9b in the June quarter 2005, a $62.3b turnaround on the March quarter 2005 inflow of $4.5b. Australia's direct investment abroad recorded an inflow of $75.6b, which is $79.2b higher than the previous quarter's outflow of $3.6b. This is the first quarterly inflow since the March quarter 2001.
Portfolio investment recorded a net inflow of $11.8b, a $5.3b increase on the net inflow of $6.6b in the March quarter 2005.
Other investment recorded a net outflow of $9.8b, a turnaround of $15.2b on the net inflow of $5.4b last quarter.
Reserve assets recorded a net outflow of $9.1b, a turnaround of $9.9b on the inflow of $0.8b last quarter due to an increase in foreign exchange reserves.
INTERNATIONAL INVESTMENT POSITION
INTERNATIONAL INVESTMENT
Australia's net international investment position at 30 June 2005 was a net foreign liability of $516.8b, up $2.0b (0.4%) on 31 March 2005. The increase consisted of:
- net transactions of $11.6b
- price changes of -$8.4b
- exchange rate changes of -$1.2b.
During the June quarter 2005, the level of net debt liabilities rose $3.2b (0.8%) to $430.0b. Price changes of $3.1b, net debt raisings of $1.0b and other adjustments of $0.6b were offset by exchange rate changes of -$1.5b.
During the June quarter 2005, the level of net equity liabilities fell $1.2b (1.4%) to $86.9b, reflecting price changes of -$11.5b and other adjustments of -$0.6b. Partially offsetting the decrease was transactions of $10.6b.
FINANCIAL YEAR: 2004-05 SITUATION
BALANCE OF PAYMENTS
In original terms, the balance on current account for 2004-05 was a deficit of $57.2b, a 20% increase on the deficit of $47.8b recorded for 2003-04. The balance on goods and services deficit was $25.5b, an increase of $1.8b on the deficit of $23.8b recorded in 2003-04. Goods exports increased $17.8b or 16% (due largely to an increase in prices) and goods imports increased $17.9b or 13% (due largely to an increase in volumes).
The 2004-05 services deficit was $1.9b, an increase of $1.7b on the deficit of $0.3b in 2003-04.
The 2004-05 net income deficit rose $7.5b (32%), with an increase in income credits of $3.7b (22%) and an increase in income debits of $11.2b (28%).
The balance on financial account recorded a net inflow of $55.7b, with a net inflow on debt of $53.6b and a net inflow on equity of $2.0b. This result was up $9.7b on the net inflow recorded for the previous year as a result of:
- a decrease of $74.2b on the net inflow on portfolio investment
- a turnaround of $73.0b to a net inflow on direct investment
- a turnaround of $12.4b to a net inflow on other investment
- a decrease of $3.0b on the net outflow on reserve assets
- a turnaround of $1.6b to a net inflow on financial derivatives.
INTERNATIONAL INVESTMENT POSITION
Australia's net international investment position as at 30 June 2005 was a net foreign liability of $516.8b. This was up $46.3b (9.8%) on the position a year earlier as a result of:
- net transactions of $55.7b
- price changes of -$12.6b
- exchange rate changes of $4.0b
- other adjustments of -$0.6b.
During 2004-05, the level of net equity liabilities rose to $86.9b, up $11.1b (14.6%) on the previous year, with exchange rate changes of $22.3b and transactions of $2.0b partially offset by price changes of -$13.1b and other changes of -$0.2b.
Net foreign debt rose to $430.0b, up $35.3b (8.9%) on the previous year, with transactions of $53.6b and price changes of $0.4b, offset by exchange rate changes of -$18.3b and other adjustments of -$0.4b.
At 30 June 2005, the ratio of Australia's net international position to GDP using the latest available GDP figure (for the year ended 31 March 2005 using current prices) was 60.8%. This compares with 57.8% one year ago and 52.7% one decade ago.
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All