GLOSSARY
Age-specific death rate
The number of deaths (occurred or registered) during the calendar year at a specified age per 1,000 of the estimated resident population of the same age at 30 June. Pro rata adjustment is made in respect of deaths for which the age of the deceased is not given. Reference: Deaths, Australia (ABS cat. no. 3302.0).
Apprentices and trainees
Persons undertaking new apprenticeships and traineeships are covered by formal agreements known as either Training Agreements or Contracts of Training. Under these agreements, the employer is obligated to provide training, help and supervision; and the trainee or apprentice is obligated to work as well as undertake the training. Reference: Australian Vocational Education and Training Management Information Statistical Standard – Standard for new apprenticeships 2005.
Assault
An incident, other than a robbery, where the respondent was physically attacked or threatened with force or violence. Reference: Crime and Safety, Australia (ABS cat. no. 4509.0).
Australian Standard Classification of Occupations (ASCO)
The Australian Standard Classification of Occupations (ASCO), Second Edition is the product of a review program undertaken jointly by a project team from the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) and the Department of Employment, Education, Training and Youth Affairs (DEETYA) for use in the collection, publication and analysis of occupation statistics. Reference: Australian Standard Classification of Occupations (ASCO), 1997 (ABS cat. no. 1220.0).
Average annual growth rate
The average annual growth rate, r, is calculated as a percentage using the formula:
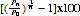
where P0 is the start of the period, Pn is the end of the period and n is the length of the period between Pn and P0 in years. Reference: Australian Demographic Statistics (ABS cat. no. 3101.0).
Biogas
Predominantly methane based gas derived from landfill and sewerage systems. Reference: Detailed Energy Statistics, Australia (ABS cat. no. 4648.0.55.001).
Biomass
The quantity of living plant and animal material or total mass (usually measured as dry weight) of all the living organisms in a given area, population, habitat or trophic level. It represents the amount of organic material accumulated. Reference: ABS Environmental Statistics Glossary.
Birth
The delivery of a child, irrespective of the duration of the pregnancy, who, after being born, breathes or shows any other evidence of life such as heartbeat. Reference: Births, Australia (ABS cat. no. 3301.0).
Black coal
Sometimes called bituminous coal or anthracite, black coal has low levels of impurities. It can be either coking coal (high purity coal used to produce coke), or steaming coal (used to produce heat and electricity). Reference: Detailed Energy Statistics, Australia (ABS cat. no. 4648.0.55.001).
Break and enter/attempted break and enter
An incident where a person's home, garage or shed had been broken into, or where an attempt was made to break into a person's home, garage or shed. Break and enter offences relating to a car or garden are excluded. Reference: Crime and Safety, Australia (ABS cat. no. 4509.0).
Casualty
Any person killed or injured as a result of a crash. Reference: Roads and Traffic Authority of NSW, Road Traffic Crashes in NSW, 2005.
Causes of death
Underlying causes of death are classified to the International Classification of Diseases 10th Revision (ICD-10 for 1997 and onwards). Reference: Causes of Death, Australia (ABS cat. no. 3303.0).
Cerebrovascular disease
Includes deaths where cerebral aneurysm, haemorrhage, infarction, stroke, are identified as the underlying cause ( ICD-10 codes I60–I69). Reference: International Classification of Diseases Tenth Revision (ICD-10), World Health Organisation, Geneva.
Chain volume measures
Estimates that exclude the direct effects of changes in prices. Unlike current measure estimates, they take account of changes to price relativities that occur from one year to the next. Annually re-weighted chain volume indexes are referenced to the current price values in a chosen reference year. Reference: Australian National Accounts: State Accounts (ABS cat. no. 5220.0).
Crash
Any apparently unpremeditated event reported to the police and resulting in death, injury or property damage attributable to the movement of a road vehicle on a road. Reference: Roads and Traffic Authority of NSW, Road Traffic Crashes in NSW, 2005.
Death
For the purposes of the Vitals and Causes of Death collections of the ABS, a death refers to any death which occurs in, or enroute to Australia and is registered with a state or territory Registry of Births, Deaths and Marriages. Reference: Deaths, Australia (ABS cat. no. 3302.0).
Drug-induced deaths
Any death where the underlying cause of death was due to:
- an acute episode of poisoning or toxicity to drugs. Included are deaths from accidental overdoses due to misuse of drugs, intentional self-harm, assault and deaths undetermined as to intent; or
- an acute condition caused by drug use where the deceased person was identified as drug dependent.
The term 'drug' refers to substances classified as drugs, medicaments or biological substances under ICD-10 guidelines. These drugs may by used for medicinal or therapeutic purposes, or to produce a psychoactive effect. The term excludes alcohol, tobacco and volatile solvents (e.g. petrol).
Reference: Information paper: Drug-Induced Deaths – A Guide to ABS Causes of Death Data (ABS cat. no. 4809.055.001).
Employed
All persons aged 15 years and over who, during the reference week:
- worked for one hour or more for pay, profit, commission or payment in kind, in a job or business, or on a farm (comprising employees, employers and own account workers); or
- worked for one hour or more without pay in a family business or on a farm (i.e. contributing family workers); or
- were employees who had a job but were not at work; or
- were employers or own account workers, who had a job, business or farm but were not at work.
Reference: Australian Labour Market Statistics (ABS cat. no. 6105.0).
Fatality
A person who dies within 30 days of a crash as a result of injuries received in that crash. Reference: Roads and Traffic Authority of NSW, Road Traffic Crashes in NSW, 2005.
Fatigue
The identification of fatigue as a contributing factor in road crashes cannot always be determined directly from police reports. Fatigue is considered to have been involved as a contributing factor to a road crash if that crash involved at least one fatigued motor vehicle controller. A motor vehicle controller is assessed as having been fatigued if the following conditions are satisfied together or separately:
- the vehicle’s controller was described by police as being asleep, drowsy or fatigued;
- the vehicle performed a manoeuvre which suggested loss of concentration of the controller due to fatigue.
Reference: Roads and Traffic Authority of NSW,
Road Traffic Crashes in NSW, 2005.
Greenhouse gas
Gases that contribute to global warming, including carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), and sulphur hexafluoride (SF6). In addition, the photochemically important gases – NMVOCs, oxides of nitrogen (NOx) and carbon monoxide (CO)– are also considered. NMVOC, NOx and CO are not direct greenhouse gases. However, they contribute indirectly to the greenhouse effect by influencing the rate at which ozone and other greenhouse gases are produced and destroyed in the atmosphere. Reference: NSW Department of Environment and Heritage, Nationals Greenhouse Gas Inventory, 2002.
Gross domestic product (GDP)
The total market value of goods and services produced in Australia within a given period after deducting the cost of goods and services used up in the process of production but before deducting allowances for the consumption of fixed capital. Thus GDP, as here defined, is 'at market prices'. It is equivalent to gross national expenditure plus exports of goods and services less imports of goods and services. Reference: Australian National Accounts, State Accounts (ABS cat. no. 5220.0).
Gross State Product (GSP)
GSP is defined equivalently to gross domestic product (GDP) but refers to production within a state or territory rather than to the nation as a whole. Reference: Australian National Accounts: State Accounts (ABS cat. no. 5220.0).
Higher education student
A person who has been admitted to a higher education institution and who is enrolled (either full-time, part-time or externally) in a higher education award course, an enabling course or a non-award course to be undertaken in the semester used as the reference period. Reference: Department of Education Science and Training, Students 2003: Selected Higher Education Statistics.
Household
A group of two or more related or unrelated people who usually reside in the same dwelling, who regard themselves as a household, and who make common provision for food or other essentials for living; or a person living in a dwelling who makes provision for his/her own food and other essentials for living, without combining with any other person. Reference: Family Characteristics, Australia (ABS cat. no. 4442.0).
Hydro-electricity
Electric power generated using the fall of water. Reference: Detailed Energy Statistics, Australia (ABS cat. no. 4648.0.55.001).
Indigenous
A person is defined to be of Indigenous origin if he or she identifies themselves as of Aboriginal and/or Torres Strait Islander origin. Reference: 2001 Census Dictionary (ABS cat. no. 2901.0).
Industry value added (IVA)
Represents the value added by an industry to the intermediate inputs used by the industry. IVA is the measure of the contribution by businesses, in the selected industry, to gross domestic product. Reference: Australian Industry (ABS cat. no. 8155.0).
Injured
A person who is injured as a result of a crash, and who does not die as a result of those injuries within 30 days of the crash. Reference: Roads and Traffic Authority of NSW, Road Traffic Crashes in NSW, 2005.
International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10)
The World Health Organization (WHO) International Classification of Diseases (ICD) is used to code illness and death to produce Australia's morbidity and mortality statistics. As a statistical classification, it is designed to encompass the entire range of morbid conditions within a manageable number of categories. Further details of the ICD-10 codes are available from the World Health Organization 1994, International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, Tenth Revision (ICD-10). Reference: Illicit Drug Use, Sources of Australian Data (ABS cat. no. 4808.0).
Ischaemic heart disease deaths
Deaths where coronary heart diseases, including heart attack (acute myocardial infarction, coronary occlusion) and angina (angina pectoris), are identified as the underlying cause (ICD-10 codes I20–I25 for 1997 onwards). Reference: Causes of Death, Australia (ABS cat. no. 3303.0).
Killed
A person who dies within 30 days of a crash as a result of injuries received in that crash. Reference: Roads and Traffic Authority of NSW, Road Traffic Crashes in NSW, 2005.
Life expectancy
Life expectancy refers to the average number of additional years a person of a given age and sex might expect to live if the age-specific death rates of the given period continued throughout his or her lifetime. Reference: Deaths, Australia (ABS cat. no. 3302.0).
Motor vehicle theft
An incident where a motor vehicle was stolen from any member of the household. It includes privately owned motor vehicles as well as business/company vehicles used exclusively by any members of the household. A motor vehicle includes cars, motorbikes and trucks; while caravans, trailers and floats were excluded. Reference: Crime and Safety, Australia (ABS cat. no. 4509.0).
Natural increase
Excess of births over deaths. Reference: Australian Demographic Statistics (ABS cat. no. 3101.0).
Net interstate migration
The difference between the number of persons who have changed their place of usual residence by moving into a given state or territory and the number who have changed their place of usual residence by moving out of that state or territory during a specified time period. This difference can be either positive or negative. Reference: Australian Demographic Statistics (ABS cat. no. 3101.0).
Net overseas migration
Net overseas migration is net permanent and long term overseas migration, adjusted for change in traveller duration, intention and multiple movement error. Reference: Australian Demographic Statistics (ABS cat. no. 3101.0).
Occupation
A collection of jobs which are sufficiently similar in their main tasks to be grouped together for the purposes of classification. The Australian Standard Classification of Occupations (ASCO) Second Edition, which is used for the classification of occupations, applies skill level and skill specialisation as major criteria. Reference: Australian Standard Classification of Occupations (ASCO), Second edition (ABS cat. no. 1220.0).
Population growth
For Australia, population growth is the sum of natural increase and net overseas migration. For states and territories, population growth also includes net interstate migration. After the Census, intercensal population growth also includes an allowance for intercensal discrepancy. Reference: Australian Demographic Statistics (ABS cat. no. 3101.0).
Qualification
Formal certification, issued by a relevant approved body, in recognition that a person has achieved learning outcomes or competencies relevant to identified individual, professional, industry or community needs. Statements of attainment awarded for partial completion of a course of study at a particular level are excluded. Reference: Education and Work, Australia (ABS cat. no. 6227.0).
Recorded criminal incidents
A criminal incident is defined as an activity detected by or reported to police which:
- involved the same offender(s);
- involved the same victim(s);
- occurred at the one location;
- occurred during one uninterrupted period of time;
- falls into one offence category;
- falls into one incident type (e.g. 'actual', attempted', 'conspiracy').
One incident may involve two offenders assaulting the same victim. This would be recorded as one assault incident. Alternatively, suppose a man reports to police that his neighbour demanded money from him, then assaulted him when he did not comply. For such an event, two criminal incidents are recorded because two distinct offence types are involved, even though the same parties were involved at the same time and in the same place.
Reference: Bureau of Crime Statistics and Research,
NSW Recorded Crime Statistics.
Recorded victims
For murder and manslaughter only, the counting units used are victims. Under the definition of a criminal incident one murder or manslaughter incident could involve two or more persons being killed. Because of the seriousness of these offences and their relatively small numbers, it was considered to be more appropriate to count the number of victims, rather than the number of criminal incidents. Hence, where one murder incident involves a person killing six people, six murder victims are counted. Reference: Bureau of Crime Statistics and Research, NSW Recorded Crime Statistics.
Renewable energy
Energy resources that can be used indefinitely. Sources include hydro-electricity, solar, wind, geothermal, ocean or tidal, and biomass such as wood, bagasse, manure and crops (to produce fuel such as ethanol). Reference: ABS Environmental Statistics Glossary.
Reported rate
The total number of victims of an offence who reported the most recent incident to police, expressed as a percentage of the total victims of that offence. Reference: Crime and Safety, Australia (ABS cat. no. 4509.0).
Robbery
An incident where individual(s) stole something from a person by threatening or attacking them. It includes incidents of attempted robbery where individual(s) attempted to steal something from the person but nothing was actually stolen. Reference: Crime and Safety, Australia (ABS cat. no. 4509.0).
Secondary education
Secondary education typically commences after completion of primary education, at around age 12 years, and lasts for five or six years. Reference: Schools, Australia (ABS cat. no. 4221.0).
Service industries
The combination of the following divisions of the Australian and New Zealand Standard Industrial Classification (ANZSIC): Wholesale trade; Retail trade; Accommodation, cafes and restaurants; Transport and storage; Communication services; Finance and insurance; Property and business services; Government administration and defence; Education; Health and community services; Cultural and recreational services; and Personal and other services. Reference: Australian and New Zealand Standard Industrial Classification 1993 (ABS cat. no. 1292.0).
Sexual assault
An incident which was of a sexual nature involving physical contact: includes rape, attempted rape, indecent assault, and assault with intent to sexually assault. Sexual harassment (that did not lead to an assault) was excluded. Only females aged 18 years and over were asked sexual assault questions. Reference: Crime and Safety, Australia (ABS cat. no. 4509.0).
Skill level
Skill level is measured by: formal education and training, and previous experience usually required for entry into an occupation. ASCO Second Edition assigns each of the nine major groups in the classification to one of five ranked skill levels. Skill Level 1 – Managers and administrators and Professionals Skill Level 2 – Associate professionals Skill Level 3 – Tradespersons and related workers and Advanced clerical and service workers Skill Level 4 – Intermediate production and transport workers and Intermediate clerical, sales and service workers Skill Level 5 – Elementary clerical, sales and service workers and Labourers and related workers. Reference: Australian Standard Classification of Occupations (ASCO), Second edition (ABS cat. no. 1220.0).
Solar power
Energy derived from direct conversion of sunlight and heat. Reference: Detailed Energy Statistics, Australia (ABS cat. no. 4648.0.55.001)
Standardised death rate
Standardised death rates enable the comparison of death rates between populations with different age structures by relating them to a standard population. The current standard population is all persons in the 2001 Australian population. The indirect method of standardisation is used when the populations under study are small and the age-specific death rates are unreliable or not known. It is an adjustment to the crude death rate of the standard population to account for the variation between the actual number of deaths in the population under study and the number of deaths which would have occurred if the population under study had experienced the age-specific death rates of the standard population. Reference: Deaths, Australia (ABS cat. no. 3302.0).
Student
An individual who was enrolled in a subject or completed a qualification during the reporting period.
Reference: National Centre for Vocational Education Research, Australian vocational education and training statistics: Students and courses 2003.
Suicide
Suicide refers to the deliberate taking of one's life. To be classified as a suicide a death must be recognised as due to other than natural causes and established by a coronial inquiry that death results from a deliberate act of the deceased with the intention of taking his or her own life. Reference: Suicides Australia, 2005 (ABS cat. no. 3309.0).
Total factor income
That part of the cost of producing the gross domestic product which consists of gross payments to factors of production (labour and capital). It represents the value added by these factors in the process of production and is equivalent to gross domestic product less taxes plus subsidies on production and imports.
Reference: Australian National Accounts, State Accounts (ABS cat. no. 5220.0).
Underlying cause of death
The disease or injury which initiated the train of morbid events leading directly to death. Accidental and violent deaths are classified according to the external cause, that is, to the circumstances of the accident or violence which produced the fatal injury rather than to the nature of the injury. Reference: Causes of Death, Australia (ABS cat. no. 3303.0).
Victim (Estimated crime)
A household or person reporting at least one of the offences surveyed. Victims were counted once only for each type of offence, regardless of the number of incidents of that type. Reference: Crime and Safety, Australia (ABS cat. no. 4509.0).
Victimisation rate
The number of victims of an offence in a given population expressed as a percentage of that population. Reference: Crime and Safety, Australia (ABS cat. no. 4509.0).
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All