GLOSSARY
12/12 month rule
A method for measuring an overseas traveller's duration of stay or absence in which the 12 month usual residence criterion in population estimates is measured across a 12 month period. Under a 12/12 month rule, overseas travellers must be resident in Australia for a continuous 12 month period or more to be included in the estimated resident population. Similarly, Australian residents travelling overseas must be absent from Australia for a continuous 12 month period or more to be removed from the estimated resident population.
12/16 month rule
A method for measuring an overseas traveller's duration of stay or absence which takes an approach to measure usual residence that does not have to be continuous, as opposed to the continuous approach used under a 12/12 month rule. Under a 12/16 month rule, overseas travellers must have been resident in Australia for a total period of 12 months or more, during the 16 month follow-up period to be included in the estimated resident population.
The 12/16 month rule therefore takes account of those persons who may have left Australia briefly and returned, while still being resident for 12 months out of 16. Similarly, it takes account of Australians who live most of the time overseas but periodically return to Australia for short periods.
Age-specific death rates
Age-specific death rates are the number of deaths (occurred or registered) during the calendar year at a specified age per 1,000 of the estimated resident population of the same age at mid-point of the year (30 June). Pro rata adjustment is made in respect of deaths for which the age of the deceased is not given.
Age-specific fertility rates
Age-specific fertility rates are the number of live births (occurred or registered) during the calendar year, according to the age of the mother, per 1,000 of the female estimated resident population of the same age at 30 June. For calculating these rates, births to mothers under 15 years are included in the 15-19 years age group, and births to mothers aged 50 years and over are included in the 45-49 years age group.
Average annual growth rate
The average annual population growth rate, r, is calculated as a percentage using the formula:
r = 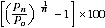
where P0 is the population at the start of the period, Pn is the population at the end of the period and n is the length of the period between Pn and P0 in years.
Balance of state/territory
The aggregation of all Statistical Divisions (SD) within a state or territory other than its Capital City SD. See Major Statistical Region in Australian Standard Geographical Classification (ASGC) (cat. no. 1216.0).
Baby boom
Baby boom refers to the generation born between the end of World War II and the mid-1960s. Baby boomers are usually taken to be those born in the years 1946 to 1965 inclusive.
Birth
The delivery of a child, irrespective of the duration of pregnancy, who, after being born, breathes or shows any evidence of life such as a heartbeat.
Capital city
Refers to the Capital City Statistical Divisions of states and territories as defined in Statistical Geography: Volume 1. Australian Standard Geographical Classification (ASGC) (cat. no. 1216.0).
Dependency ratio
The dependency ratio is a measure used to compare the size of the working age population to the size of the non-working age population, calculated as the sum of people aged 0-14 and 65 years and over (that is, 'dependents') divided by the number of people aged 15-64 years, multiplied by 100.
Estimated resident population
The official measure of the population of Australia is based on the concept of residence. It refers to all people, regardless of nationality or citizenship, who usually live in Australia, with the exception of foreign diplomatic personnel and their families. It includes usual residents who are overseas for less than 12 months. It excludes overseas visitors who are in Australia for less than 12 months.
Fertility schedule
A fertility schedule is a time series of age-specific fertility rates.
Infant mortality rate
The number of deaths of children under one year of age in a calendar year per 1,000 live births in the same calendar year.
Internal migration
The difference between the number of persons who have changed their place of usual residence by moving into a defined geographical area and the number who have changed their place of usual residence by moving out of that defined geographical area during a specified time period. This difference may be either positive or negative.
Life expectancy at birth
Life expectancy refers to the average number of additional years a person of a given age and sex might expect to live if the age-specific death rates of the given period continued throughout his or her lifetime.
Median value
For any distribution the median value (age, duration, interval) is that value which divides the relevant population into two equal parts, half falling below the value, and half exceeding it. Where the value for a particular record has not been stated, that record is excluded from the calculation.
Migration adjustment
The ABS applies a number of adjustments to overseas arrivals and departures (OAD) data in order to produce estimates of net overseas migration (NOM). These mainly comprise adjustments designed to reflect differences between stated travel intentions and actual travel behaviour, but also include adjustments to transform numbers of overseas movements into numbers of travellers. These adjustments are collectively referred to as 'migration adjustments', although they have been referred to in the past as 'category jumping' adjustments.
Natural increase
The excess of births over deaths.
Net interstate migration
The difference between the number of persons who have changed their place of usual residence by moving into a given state or territory and the number who have changed their place of usual residence by moving out of that state or territory during a specified time period. This difference can be either positive or negative.
Net overseas migration (NOM)
Net overseas migration is the net gain or loss of population through immigration to Australia or emigration from Australia. It is:
- based on an international travellers' duration of stay being in or out of Australia for 12 months or more;
- the difference between the number of incoming travellers who stay in Australia for 12 months or more and are added to the population (NOM arrivals) and the number of outgoing travellers who leave Australia for 12 months or more and are subtracted from the population (NOM departures).
When using the current method for estimating final net overseas migration this term is then based on a traveller's actual duration of stay or absence using the 12/16 month rule. Preliminary NOM estimates are modelled on patterns of traveller behaviours observed in final NOM estimates for the same period two years earlier.
NOM arrivals
NOM arrivals are all overseas arrivals that contribute to net overseas migration (NOM). It is the number of incoming international travellers who stay in Australia for 12 months or more and are added to the population.
When using the current method for estimating net overseas migration this term is then based on a traveller's actual duration of stay using the 12/16 month rule.
NOM departures
NOM departures are all overseas departures that contribute to net overseas migration (NOM). It is the number of outgoing international travellers (Australian residents and long-term visitors to Australia) who leave Australia for 12 months or more and are subtracted from the population.
When using the current method for estimating net overseas migration this term is then based on a traveller's actual duration of absence using the 12/16 month rule.
Other Territories
Other Territories comprises Christmas Island, Cocos (Keeling) Islands and Jervis Bay Territory.
Population growth
For Australia, population growth is the sum of natural increase and net overseas migration. For states and territories, population growth also includes net interstate migration. After the census, intercensal population growth also includes an allowance for intercensal discrepancy.
Rate of population growth
Population change over a period as a proportion (percentage) of the population at the beginning of the period.
Replacement fertility
Replacement level fertility is the number of babies a female would need to have over her reproductive life span to replace herself and her partner. Given the current mortality of females up to age 49 years, replacement fertility is estimated at 2.1 babies per female.
Sex ratio
The sex ratio relates to the number of males per 100 females. The sex ratio is defined for total population, at birth, at death and among age groups by appropriately selecting the numerator and denominator of the ratio.
Standardised death rate
Standardised death rates enable the comparison of death rates between populations with different age structures by relating them to a standard population. The ABS standard populations relate to the years ending in 1 (e.g. 1991). The current standard population is all persons in the 2001 Australian population. They are expressed per 1,000 or 100,000 persons. There are two methods of calculating standardised death rates:
- The direct method - -this is used when the populations under study are large and the age-specific death rates are reliable. It is the overall death rate that would have prevailed in the standard population if it had experienced at each age the death rates of the population under study. This is the method used in this publication.
- The indirect method - this is used when the populations under study are small and the age-specific death rates are unreliable or not known. It is an adjustment to the crude death rate of the standard population to account for the variation between the actual number of deaths in the population under study and the number of deaths which would have occurred if the population under study had experienced the age-specific death rates of the standard population.
Statistical Division
Statistical Divisions (SD) consist of one or more Statistical Subdivisions (SSD). The divisions are designed to be relatively homogenous regions characterised by identifiable social and economic units within the region, under the unifying influence of one or more major towns or cities. Further information concerning SDs is contained in
Australian Standard Geographical Classification (ASGC) (cat. no. 1216.0).
State or territory and Statistical Local Area of usual residence
State or territory and Statistical Local Area of usual residence refers to the state or territory and SLA of usual residence of:
- the population (estimated resident population)
- the mother (birth collection)
- the deceased (death collection).
In the case of overseas movements, state or territory of usual residence refers to the state or territory regarded by the traveller as the one in which he/she lives or has lived. State or territory of intended residence is derived from the intended address given by settlers, and by the Australian residents returning after a journey abroad. Particularly in the case of the former, this information does not necessarily relate to the state or territory in which the traveller will eventually establish a permanent residence.
Total fertility rate
The sum of age-specific fertility rates. It represents the number of children a female would bear during her lifetime if she experienced current age-specific fertility rates at each age of her reproductive life.
Usual residence
Usual residence within Australia refers to that address at which the person has lived or intends to live for a total of six months or more in a given reference year.
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All
 Quality Declaration
Quality Declaration