TECHNICAL NOTE DATA QUALITY
INTRODUCTION
1 Since the estimates in this publication are based on information obtained from occupants of a sample of dwellings, they are subject to sampling variability. That is, they may differ from those estimates that would have been produced if all dwellings had been included in the survey. One measure of the likely difference is given by the standard error (SE), which indicates the extent to which an estimate might have varied by chance because only a sample of dwellings was included. There are about two chances in three (67%) that a sample estimate will differ by less than one SE from the number that would have been obtained if all dwellings had been included, and about 19 chances in 20 (95%) that the difference will be less than two SEs. Another measure of the likely difference is the relative standard error (RSE), which is obtained by expressing the SE as a percentage of the estimate.
2 Due to space limitations, it is impractical to print the SE of each estimate in the publication. Instead, a table of SEs is provided to enable readers to determine the SE for an estimate from the size of that estimate (see table T1). The SE table is derived from a mathematical model, referred to as the 'SE model', which is created using data from a number of past Labour Force Surveys. It should be noted that the SE model only gives an approximate value for the SE for any particular estimate, since there is some minor variation between SEs for different estimates of the same size.
CALCULATION OF STANDARD ERROR
3 An example of the calculation and the use of SEs in relation to estimates of persons is as follows. Table 5 shows the estimated number of female underemployed part-time workers was 297,400. Since this estimate is between 200,000 and 300,000, table T1 shows that the SE for Australia will lie between 5,300 and 6,350 and can be approximated by interpolation using the following general formula:

4 Therefore, there are about two chances in three that the value that would have been produced if all dwellings had been included in the survey will fall within the range 291,100 to 303,700 and about 19 chances in 20 that the value will fall within the range 284,800 to 310,000. This example is illustrated in the following diagram.
5 In general, the size of the SE increases as the size of the estimate increases. Conversely, the RSE decreases as the size of the estimate increases. Very small estimates are thus subject to such high RSEs that their value for most practical purposes is unreliable. In the tables in this publication, only estimates with RSEs of 25% or less are considered reliable for most purposes. Estimates with RSEs greater than 25% but less than or equal to 50% are preceded by an asterisk (e.g.*3.2) to indicate they are subject to high SEs and should be used with caution. Estimates with RSEs of greater than 50%, preceded by a double asterisk (e.g.**0.3), are considered too unreliable for general use and should only be used to aggregate with other estimates to provide derived estimates with RSEs of less than 25%.
MEANS AND MEDIANS
6 The RSEs of estimates of mean duration of insufficient work, median duration of insufficient work and mean preferred number of extra hours are obtained by first finding the RSE of the estimate of the total number of persons contributing to the mean or median (see table T1) and then multiplying the resulting number by the following factors:
- mean duration of insufficient work: 1.6
- median duration of insufficient work: 2.5
- mean preferred number of extra hours: 0.7
7 The following is an example of the calculation of SEs where the use of a factor is required. Table 5 shows that the estimated number of male underemployed part-time workers was 186,500 with a median duration of insufficient work of 24 weeks. The SE of 186,500 can be calculated from table T1 (by interpolation) as 5,100. To convert this to an RSE we express the SE as a percentage of the estimate or 5,100/186,500 =2.7%.
8 The RSE of the estimate of median duration of insufficient work is calculated by multiplying this number (2.7%) by the appropriate factor shown in paragraph 6 (in this case 2.5): 2.7 x 2.5 = 6.8%. The SE of this estimate of median duration of insufficient work is therefore 6.8% of 24, i.e. about 2 (rounded to the nearest whole week). Therefore, there are two chances in three that the median duration of insufficient work for males that would have been obtained if all dwellings had been included in the survey would have been within the range 22-26 weeks, and about 19 chances in 20 that it would have been within the range 20-28 weeks.
PROPORTIONS AND PERCENTAGES
9 Proportions and percentages formed from the ratio of two estimates are also subject to sampling errors. The size of the error depends on the accuracy of both the numerator and the denominator. A formula to approximate the RSE of a proportion is given below. This formula is only valid when x is a subset of y.
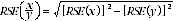
10 Considering the example from paragraph 3, of the 297,400 female underemployed part-time workers, 102,800 or 34.6% had insufficient work for 52 weeks and over. The SE of 102,800 may be calculated by interpolation as 4,000. To convert this to an RSE we express the SE as a percentage of the estimate, or 4,000/102,800 = 3.9%. The SE for 297,400 was calculated previously as 6,300, which converted to an RSE is 6,300/297,400 = 2.1%. Applying the above formula, the RSE of the proportion is:
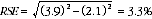
11 Therefore, the SE for the proportion of females who have a current period of insufficient work of 52 weeks or more is 1.1 percentage points (=(34.6/100)x3.3). Therefore, there are about two chances in three that the proportion of females who have a current period of insufficient work of 52 weeks or more was between 33.5% and 35.7% and 19 chances in 20 that the proportion is within the range 32.4% to 36.8%.
DIFFERENCES
12 Published estimates may also be used to calculate the difference between two survey estimates (of numbers or percentages). Such an estimate is subject to sampling error. The sampling error of the difference between two estimates depends on their SEs and the relationship (correlation) between them. An approximate SE of the difference between two estimates (x-y) may be calculated by the following formula:
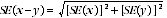
13 While this formula will only be exact for differences between separate and uncorrelated characteristics or subpopulations, it is expected to provide a good approximation for all differences likely to be of interest in this publication.
STANDARD ERRORS
T1 STANDARD ERRORS OF ESTIMATES |
|  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | Aust. |  |
 | NSW | Vic. | Qld. | SA | WA | Tas. | NT | ACT | SE | RSE |  |
| Size of estimate (persons) | no. | no. | no. | no. | no. | no. | no. | no. | no. | % |  |
|  |
| 100 | 290 | 250 | 250 | 150 | 160 | 100 | 90 | 140 | 100 | 100.0 |  |
| 200 | 380 | 330 | 330 | 210 | 220 | 140 | 140 | 180 | 180 | 90.0 |  |
| 300 | 440 | 390 | 390 | 250 | 260 | 180 | 170 | 200 | 240 | 80.0 |  |
| 500 | 540 | 470 | 470 | 300 | 330 | 220 | 230 | 230 | 350 | 70.0 |  |
| 700 | 620 | 540 | 540 | 350 | 380 | 260 | 270 | 260 | 430 | 61.4 |  |
| 1000 | 710 | 620 | 610 | 400 | 440 | 300 | 320 | 280 | 540 | 54.0 |  |
| 1500 | 830 | 730 | 710 | 470 | 520 | 340 | 380 | 320 | 690 | 46.0 |  |
| 2000 | 920 | 810 | 790 | 530 | 590 | 370 | 420 | 340 | 820 | 41.0 |  |
| 2500 | 1 000 | 900 | 850 | 550 | 650 | 400 | 450 | 350 | 900 | 36.0 |  |
| 3000 | 1 100 | 950 | 900 | 600 | 700 | 400 | 500 | 400 | 1 000 | 33.3 |  |
| 3500 | 1 150 | 1 000 | 950 | 650 | 750 | 450 | 500 | 400 | 1 100 | 31.4 |  |
| 4000 | 1 200 | 1 050 | 1 000 | 700 | 750 | 450 | 500 | 400 | 1 200 | 30.0 |  |
| 5000 | 1 300 | 1 150 | 1 100 | 750 | 850 | 500 | 550 | 450 | 1 300 | 26.0 |  |
| 7000 | 1 500 | 1 300 | 1 250 | 850 | 950 | 550 | 700 | 500 | 1 550 | 22.1 |  |
| 10000 | 1 700 | 1 500 | 1 400 | 950 | 1 100 | 650 | 850 | 600 | 1 800 | 18.0 |  |
| 15000 | 2 000 | 1 750 | 1 600 | 1 100 | 1 250 | 800 | 1 150 | 750 | 2 100 | 14.0 |  |
| 20000 | 2 200 | 1 950 | 1 800 | 1 200 | 1 400 | 950 | 1 450 | 850 | 2 300 | 11.5 |  |
| 30000 | 2 600 | 2 300 | 2 050 | 1 450 | 1 600 | 1 250 | 1 950 | 1 100 | 2 650 | 8.8 |  |
| 40000 | 2 850 | 2 550 | 2 250 | 1 700 | 1 750 | 1 500 | 2 500 | 1 350 | 2 900 | 7.3 |  |
| 50000 | 3 100 | 2 800 | 2 450 | 1 900 | 1 950 | 1 750 | 2 950 | 1 500 | 3 100 | 6.2 |  |
| 100000 | 4 050 | 3 600 | 3 400 | 2 900 | 3 050 | 2 600 | 5 300 | 2 050 | 4 000 | 4.0 |  |
| 150000 | 4 800 | 4 350 | 4 250 | 3 700 | 4 100 | 3 200 | 7 500 | 2 350 | 4 700 | 3.1 |  |
| 200000 | 5 550 | 5 200 | 5 100 | 4 400 | 4 950 | 3 650 | 9 700 | 2 450 | 5 300 | 2.7 |  |
| 300000 | 7 100 | 6 800 | 6 800 | 5 450 | 6 250 | 4 300 | 14 050 | 2 550 | 6 350 | 2.1 |  |
| 500000 | 9 950 | 9 300 | 9 550 | 6 900 | 7 950 | 5 150 | . . | 2 550 | 8 100 | 1.6 |  |
| 1000000 | 14 950 | 13 700 | 13 500 | 9 000 | 10 050 | 6 250 | . . | . . | 11 600 | 1.2 |  |
| 2000000 | 21 350 | 19 350 | 16 550 | 11 000 | 11 400 | . . | . . | . . | 17 150 | 0.9 |  |
| 5000000 | 31 500 | 28 550 | 17 350 | 13 000 | 11 500 | . . | . . | . . | 29 250 | 0.6 |  |
| 10000000 | 39 750 | 36 450 | 15 250 | . . | . . | . . | . . | . . | 39 200 | 0.4 |  |
| 15000000 | . . | . . | . . | . . | . . | . . | . . | . . | 44 050 | 0.3 |  |
|  |
| . . not applicable |
T2 LEVELS AT WHICH ESTIMATES HAVE RELATIVE STANDARD ERRORS OF 25% AND 50%(a) |
|  |
 | NSW | Vic. | Qld. | SA | WA | Tas. | NT | ACT | Aust. |  |
 | no. | no. | no. | no. | no. | no. | no. | no. | no. |  |
RSE OF 25% |  |
|  |
| Mean duration of current period of insufficient work | 11 700 | 10 400 | 9 200 | 4 300 | 6 000 | 2 400 | 3 000 | 2 000 | 12 900 |  |
| Median duration of current period of insufficient work | 28 800 | 24 600 | 23 600 | 13 200 | 14 200 | 5 700 | 14 200 | 6 800 | 24 900 |  |
| Mean preferred number of extra hours | 3 300 | 3 200 | 2 500 | 1 500 | 1 800 | 900 | 1 100 | 700 | 3 000 |  |
| All other estimates | 5 400 | 4 400 | 4 100 | 2 200 | 2 600 | 1 300 | 1 500 | 1 200 | 5 500 |  |
RSE OF 50% |  |
|  |
| Mean duration of current period of insufficient work | 3 800 | 3 400 | 3 100 | 1 400 | 2 000 | 800 | 1 000 | 800 | 3 700 |  |
| Median duration of current period of insufficient work | 9 500 | 8 000 | 8 300 | 4 600 | 4 800 | 2 300 | 6 200 | 2 700 | 8 200 |  |
| Mean preferred number of extra hours | 1 100 | 1 000 | 800 | 500 | 600 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 500 |  |
| All other estimates | 1 800 | 1 400 | 1 400 | 700 | 800 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 1 200 |  |
|  |
| (a) Refers to the number of people contributing to the estimate. |
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All