TECHNICAL NOTE DATA QUALITY
INTRODUCTION
1 Since the estimates published in this publication are based on information obtained from occupants of a sample of dwellings, they are subject to sampling variability. That is, they may differ from those estimates that would have been produced if all dwellings had been included in the survey. One measure of the likely difference is given by the standard error (SE), which indicates the extent to which an estimate might have varied by chance because only a sample of dwellings (or occupants) was included. There are about two chances in three (67%) that a sample estimate will differ by less than one SE from the number that would have been obtained if all dwellings had been included, and about 19 chances in 20 (95%) that the difference will be less than two SEs.
2 Another measure of the likely difference is the relative standard error (RSE), which is obtained by expressing the SE as a percentage of the estimate.
RSE% = (SE/estimate ) x 100
3 RSEs for Barriers and Incentives estimates have been calculated using the Jackknife method of variance estimation. This process involves the calculation of 30 'replicate' estimates based on 30 different subsamples of the original sample. The variability of estimates obtained from these subsamples is used to estimate the sample variability surrounding the main estimate.
4 Limited publication space does not allow for the separate indication of the SEs and/or RSEs of all the estimates in this publication. However, RSEs for all these estimates are available free-of-charge on the ABS web site <www.abs.gov.au>, released in spreadsheet format as an attachment to this publication, Barriers and Incentives to Labour Force Participation, Australia (cat.no.6239.0). As a guide, the population estimates and RSEs for selected data from table 1 and 2 are presented at table T1 and table T2 in this Technical Note.
5 In the tables in this publication, only estimates (numbers, percentages, means and medians) with RSEs less than 25% are considered sufficiently reliable for most purposes. However, estimates with larger RSEs have been included and are preceded by an asterisk (e.g. *13.5) to indicate they are subject to high SEs and should be used with caution. Estimates with RSEs greater than 50% are preceded by a double asterisk (e.g. **2.1) to indicate that they are considered too unreliable for general use.
CALCULATION OF STANDARD ERROR AND RELATIVE STANDARD ERROR
6 The RSEs have been derived using the Jackknife method. SEs can be calculated using the estimates (counts or means) and the corresponding RSEs.
7 An example of the calculation of the SE from an RSE follows. Table T2 shows that the estimated number of females aged 18-24 years who did not prefer to work more hours is 102,500, and the RSE for this estimate is 18.0%. The SE is:
SE of estimate
= (RSE / 100) x estimate
= 0.18 x 102,500
= 18,500 (rounded to the nearest 100)
8 Therefore, there are about two chances in three that the value that would have been produced if all dwellings had been included in the survey will fall within the range 84,000 to 121,000 and about 19 chances in 20 that the value will fall within the range 65,500 to 139,500. This example is illustrated in the following diagram.
Proportions and percentages
9 Proportions and percentages formed from the ratio of two estimates are also subject to sampling errors. The size of the error depends on the accuracy of both the numerator and the denominator. A formula to approximate the RSE of a proportion is given below. This formula is only valid when x is a subset of y.
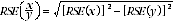
10 Considering table T2, of the 706,700 females who worked 0-15 hours each week, 533,900 or 75.5% did not prefer to work more hours. The RSE of 533,900 is 5.9% and the RSE for 706,700 is 4.5%. Applying the above formula, the RSE for the proportion of females who did not prefer to work more hours is:
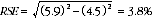
11 Therefore, the SE for the proportion of females working 0-15 hours per week who did not prefer more hours is 2.9 percentage points (= (75.5/100) x 3.8). Therefore, there are about two chances in three that the proportion of females working 0-15 hours per week who did not prefer more hours is between 72.6% and 78.4%, and 19 chances in 20 that the proportion is within the range 69.7% to 81.3%.
Sums or Differences between estimates
12 Published estimates may also be used to calculate the sum of, or difference between, two survey estimates (of numbers, means or percentages). Such estimates are also subject to sampling error.
13 The sampling error of the difference between two estimates depends on their SEs and the relationship (correlation) between them. An approximate SE of the difference between two estimates (x-y) may be calculated by the following formula:
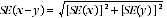
14 The sampling error of the sum of two estimates is calculated in a similar way. An approximate SE of the sum of two estimates (x + y) may be calculated by the following formula:
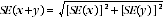
15 An example follows. From paragraph 7 the estimated number of females aged 18-24 years who did not prefer to work more hours is 102,500 and the SE is 18,500. From table T2, the estimate of females aged 25-34 years who did not prefer to work more hours is 98,000, and the SE is 10,800. The estimate of females aged 18-34 years who preferred not to work more hours is:
102,500 + 98,000 = 200,500
16 The SE of the estimate of females aged 18-34 years who did not prefer to work more hours is:
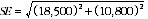
= 21,400 (rounded to the nearest 100)
17 Therefore, there are about two chances in three that the value that would have been produced if all dwellings had been included in the survey will fall within the range 179,100 to 221,900 and about 19 chances in 20 that the value will fall within the range 157,700 to 243,300.
18 While these formulae will only be exact for sums of, or differences between, separate and uncorrelated characteristics or subpopulations, it is expected to provide a good approximation for all sums or differences likely to be of interest in this publication.
SELECTED ESTIMATES AND RSES
T1: PERSONS AGED 18 YEARS AND OVER, Labour force status - By sex |
|  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |  | MALES | FEMALES | PERSONS |  |
|  |
| Persons in the Labour force | '000 | 5 690.0 | 4 710.9 | 10 400.9 |  |
 | Employed | '000 | 5 520.9 | 4 509.7 | 10 030.6 |  |
 |  | Persons who usually worked 16 hours or more per week | '000 | 5 276.0 | 3 803.1 | 9 079.1 |  |
 |  | Persons who usually worked 0-15 hours per week | '000 | 244.9 | 706.7 | 951.5 |  |
 |  |  | Preferred to work more hours | '000 | 100.2 | 172.8 | 273.0 |  |
 |  |  |  | Available to start work with more hours(a) | '000 | 75.6 | 147.2 | 222.8 |  |
 |  |  |  |  | Looked for more hours | '000 | 43.6 | 74.2 | 117.8 |  |
 |  |  |  |  | Did not look for more hours | '000 | *32.0 | 72.9 | 105.0 |  |
 |  |  |  | Not available to start work with more hours | '000 | *24.6 | *25.6 | 50.2 |  |
 |  |  | Did not prefer to work more hours(b) | '000 | 144.6 | 533.9 | 678.5 |  |
 | Unemployed | '000 | 169.1 | 201.2 | 370.2 |  |
| Persons not in the labour force | '000 | 1 871.7 | 3 112.3 | 4 984.0 |  |
 | Wanted a paid job(c) | '000 | 366.8 | 640.3 | 1 007.1 |  |
 |  | Available to start work(a) | '000 | 269.7 | 449.9 | 719.6 |  |
 |  |  | Actively looked for work(d) | '000 | *13.5 | *10.5 | *24.0 |  |
 |  |  | Did not actively look for work(e) | '000 | 256.2 | 439.4 | 695.6 |  |
 |  | Not available or did not know if available to start work | '000 | 97.1 | 190.4 | 287.5 |  |
 | Did not want a paid job | '000 | 1 504.9 | 2 472.1 | 3 976.9 |  |
| Total | '000 | 7 561.6 | 7 823.3 | 15 384.9 |  |
| Person in the Labour force | RSE% | 0.6 | 1.1 | 0.7 |  |
 | Employed | RSE% | 0.8 | 1.4 | 0.8 |  |
 |  | Persons who usually worked 16 hours or more per week | RSE% | 0.9 | 1.6 | 0.9 |  |
 |  | Persons who usually worked 0-15 hours per week | RSE% | 9.4 | 4.5 | 4.3 |  |
 |  |  | Preferred to work more hours | RSE% | 14.5 | 8.3 | 7.5 |  |
 |  |  |  | Available to start work with more hours | RSE% | 16.7 | 9.2 | 7.8 |  |
 |  |  |  |  | Looked for more hours | RSE% | 24.6 | 12.8 | 12.1 |  |
 |  |  |  |  | Did not look for more hours | RSE% | 27.8 | 13.3 | 12.0 |  |
 |  |  |  | Not available to start work with more hours | RSE% | 41.5 | 26.1 | 24.7 |  |
 |  |  | Did not prefer to work more hours | RSE% | 11.2 | 5.9 | 5.3 |  |
 | Unemployed | RSE% | 9.1 | 7.7 | 5.3 |  |
| Persons not in the labour force | RSE% | 2.0 | 1.5 | 1.4 |  |
 | Wanted a paid job | RSE% | 6.9 | 3.8 | 3.6 |  |
 |  | Available to start work | RSE% | 9.0 | 5.3 | 5.1 |  |
 |  |  | Actively looked for work | RSE% | 46.1 | 32.7 | 30.2 |  |
 |  |  | Did not actively look for work | RSE% | 8.9 | 5.3 | 5.1 |  |
 |  | Not available or did not know if available to start work | RSE% | 14.7 | 8.0 | 7.5 |  |
 | Did not want a paid job | RSE% | 2.0 | 1.8 | 1.4 |  |
| Total | RSE% | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.2 |  |
|  |
| * estimate has a relative standard error of 25% to 50% and should be used with caution |
| (a) Availability refers to in the reference week or within four weeks. |
| (b) Includes people who reported 'Did not know'. |
| (c) Includes people who reported 'Maybe/it depends'. |
| (d) These people were not available to start work in the reference week so are defined as not in the labour force rather than unemployed. |
| (e) Includes 29,300 people (17,000 men and 12,300 women) who wanted a paid job and reported 'Looked, not actively'. |
T2 Estimates: PERSONS AGED 18 YEARS AND OVER, USUALLY WORKED 0-15 HOURS PER WEEK OR WERE NOT EMPLOYED, Whether wanted a job or more hours - By age |
|
 |  |  | PERSONS WHO USUALLY WORKED
0-15 HOURS PER WEEK |  | PERSONS NOT IN
THE LABOUR FORCE |
 |  |  | Preferred
to work
more hours | Did not
prefer to
work more
hours(a) | Total
|
Unemployed
| Wanted
a paid
job(b) | Did not
want
a paid
job(a) | Total |
MALES |
|
| Age group (years) |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 | 18-24 | '000 | 41.1 | 65.7 | 106.8 | *36.7 | 54.7 | 82.8 | 137.5 |
 | 25-34 | '000 | *13.0 | *7.4 | 20.4 | 42.4 | 48.7 | 42.7 | 91.4 |
 | 35-44 | '000 | *12.2 | *9.1 | *21.3 | 35.9 | 45.1 | 65.5 | 110.7 |
 | 45-54 | '000 | *27.4 | *8.3 | 35.6 | *27.9 | 45.9 | 96.9 | 142.8 |
 | 55-64 | '000 | *4.7 | 30.5 | 35.3 | *23.5 | 80.5 | 271.8 | 352.3 |
 | 65 and over | '000 | **1.8 | *23.6 | 25.5 | **2.6 | 91.8 | 945.1 | 1 037.0 |
| Total | '000 | 100.2 | 144.6 | 244.9 | 169.1 | 366.8 | 1 504.9 | 1 871.7 |
| Age group (years) |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 | 18-24 | RSE% | 23.0 | 20.5 | 15.2 | 27.1 | 21.3 | 18.4 | 14.1 |
 | 25-34 | RSE% | 35.0 | 37.4 | 23.9 | 18.9 | 24.4 | 23.7 | 15.3 |
 | 35-44 | RSE% | 37.7 | 40.0 | 25.3 | 23.9 | 21.7 | 14.7 | 13.7 |
 | 45-54 | RSE% | 27.0 | 43.8 | 21.7 | 26.5 | 17.4 | 10.3 | 7.9 |
 | 55-64 | RSE% | 40.7 | 21.5 | 19.5 | 25.8 | 10.6 | 6.5 | 5.4 |
 | 65 and over | RSE% | 62.7 | 25.2 | 24.0 | 67.2 | 12.9 | 1.8 | 1.4 |
| Total | RSE% | 14.5 | 11.2 | 9.4 | 9.1 | 6.9 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
FEMALES |
|
| Age group (years) |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 | 18-24 | '000 | *44.7 | 102.5 | 147.2 | 46.9 | 81.5 | 105.3 | 186.8 |
 | 25-34 | '000 | 33.3 | 98.0 | 131.3 | 40.6 | 132.8 | 216.3 | 349.1 |
 | 35-44 | '000 | 47.9 | 125.4 | 173.4 | 48.7 | 137.1 | 241.7 | 378.8 |
 | 45-54 | '000 | *29.7 | 96.0 | 125.7 | 38.0 | 129.5 | 172.8 | 302.3 |
 | 55-64 | '000 | *14.2 | 93.4 | 107.6 | *26.3 | 89.2 | 491.6 | 580.8 |
 | 65 and over | '000 | **2.9 | *18.5 | *21.4 | **0.6 | 70.2 | 1 244.4 | 1 314.6 |
| Total | '000 | 172.8 | 533.9 | 706.7 | 201.2 | 640.3 | 2 472.1 | 3 112.3 |
| Age group (years) |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 | 18-24 | RSE% | 25.7 | 18.0 | 15.4 | 18.6 | 16.1 | 14.7 | 9.8 |
 | 25-34 | RSE% | 19.1 | 11.0 | 9.3 | 16.7 | 10.7 | 6.4 | 6.6 |
 | 35-44 | RSE% | 18.3 | 10.0 | 8.5 | 16.2 | 8.2 | 9.1 | 5.9 |
 | 45-54 | RSE% | 29.4 | 12.2 | 11.3 | 16.7 | 9.4 | 8.6 | 5.2 |
 | 55-64 | RSE% | 26.4 | 11.0 | 8.9 | 31.1 | 13.7 | 3.7 | 4.0 |
 | 65 and over | RSE% | 63.3 | 29.2 | 27.6 | 101.2 | 14.4 | 0.9 | 0.8 |
| Total | RSE% | 8.3 | 5.9 | 4.5 | 7.7 | 3.8 | 1.8 | 1.5 |
PERSONS |
|
| Age group (years) |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 | 18-24 | '000 | 85.8 | 168.2 | 254.0 | 83.6 | 136.2 | 188.1 | 324.3 |
 | 25-34 | '000 | 46.3 | 105.4 | 151.7 | 83.0 | 181.5 | 259.0 | 440.5 |
 | 35-44 | '000 | 60.2 | 134.6 | 194.7 | 84.7 | 182.2 | 307.2 | 489.4 |
 | 45-54 | '000 | 57.1 | 104.3 | 161.3 | 66.0 | 175.3 | 269.7 | 445.1 |
 | 55-64 | '000 | 18.9 | 123.9 | 142.9 | 49.8 | 169.7 | 763.4 | 933.1 |
 | 65 and over | '000 | *4.8 | 42.1 | 46.9 | **3.1 | 162.1 | 2 189.5 | 2 351.6 |
| Total | '000 | 273.0 | 678.5 | 951.5 | 370.2 | 1 007.1 | 3 976.9 | 4 984.0 |
| Age group (years) |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 | 18-24 | RSE% | 19.3 | 13.4 | 11.5 | 15.8 | 12.6 | 10.0 | 7.9 |
 | 25-34 | RSE% | 19.4 | 11.0 | 10.1 | 12.9 | 10.1 | 6.3 | 6.4 |
 | 35-44 | RSE% | 14.4 | 9.5 | 7.5 | 13.7 | 8.0 | 8.1 | 5.7 |
 | 45-54 | RSE% | 16.6 | 11.3 | 9.2 | 15.3 | 8.9 | 8.0 | 5.3 |
 | 55-64 | RSE% | 21.8 | 9.9 | 8.6 | 20.1 | 9.0 | 3.2 | 3.1 |
 | 65 and over | RSE% | 42.8 | 20.2 | 18.6 | 61.1 | 9.9 | 0.9 | 0.8 |
| Total | RSE% | 7.5 | 5.3 | 4.3 | 5.3 | 3.6 | 1.4 | 1.4 |
|
| * estimate has a relative standard error of 25% to 50% and should be used with caution |
| ** estimate has a relative standard error greater than 50% and is considered too unreliable for general use |
| (a) Includes people who reported 'Did not know'. |
| (b) Includes people who reported 'Maybe/it depends'. |
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All
 Quality Declaration
Quality Declaration