|
|
PARTICIPATION IN SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITIES
INTRODUCTION
Sport in Australia enjoys a high profile, especially at the elite level. The extensive media coverage of sporting events serves to heighten public awareness of sports and of top sports people. With the benefits of higher levels of physical activity becoming more widely recognised, participation in sport by all Australians at all levels is seen as increasingly important. The Federal Minister for Sport, Territories and Local Government recently launched a new initiative aimed at making Australians fitter and healthier. The program, Active Australia - a National Participation Framework, aims to have all Australians actively involved in sport, community recreation, fitness and/or outdoor recreation. The focus is on promoting a healthy and active lifestyle, and providing access to sport and recreation facilities and services. The excitement surrounding the preparation for the Sydney Olympics in the year 2000 has provided added stimulus for the development of sport and physical activity policy and participation in Australia.
Participation Sport and Physical Activities, Australia, 1995-96 (4177.0) provides national data on participation in sports and physical activities by Australians five years of age and over. These data will provide benchmarks to assist in measuring the impact of the Olympics on participation in sport at all levels.
Information for the publication was collected by the Population Survey Monitor (PSM). A total of 22,325 people were interviewed throughout the year about their participation in sport and physical activities, including both organised and social involvement. Organised sports and physical activities were those organised through a club, association or school (outside of school hours). The club or association need not have been sporting, but could have included e.g. a social club, church group, old scholars' association or aerobics at the local gymnasium. For organised and children's activities, respondents were asked about the 12 months prior to the interview. In contrast, details of social activities, that is, sport and physical activities not organised by a club or association, were restricted to participation by persons aged 18 years and over during the preceding two weeks.
Participation by age and sex
During the 12 months ended June 1996, over 5.8 million people (35.5% of the population aged five years and over) participated in organised sport and physical activities (see table S4.1).
The highest participation rate was exhibited by children aged 9-11 years (71.0%), with the rate declining for each successive age group. The largest falls occurred between 15-19 year olds and 20-24 year olds (14.0 percentage points) and between 12-14 year olds and 15-19 year olds (12.5 percentage points). The diminishing rates in these age groups coincide with the ages at which people leave school and the years when their interests, preferences and commitments may be changing.
Males had a higher participation rate than females in every age group. The difference was most evident in the 12-14 and 15-19 year age groups where the respective rates for males were 11.2 and 11.3 percentage points higher than those for females.
S4.1 PARTICIPATION IN ORGANISED SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITIES, By Age Group
|
 | Males
| Females
| Persons
|
 | Number | Participation rate | Number | Participation rate | Number | Participation rate |
Age group (years) | '000 |  | '000 |  | '000 | |
|
| 5-14 |  |  |  |  |  |  |
5-8
9-11
12-14
Total
| 274.1
306.8
278.7
859.6 | 51.5
74.3
74.1
65.0 | 230.4
249.8
245.4
725.7 | 46.8
67.2
62.9
57.8 | 504.5
556.7
524.1
1,585.2 | 49.2
71.0
68.4
61.5 |
| 15 and over |  |  |  |  |  |  |
15-19
20-24
25-34
35-44
45-54
55-64
65 and over
Total | 387.0
3±8.0
562.8
407.3
288.1
168.2
182.7
2,314.2 | 61.4
46.3
41.1
30.3
25.2
22.4
20.7
34.0 | 299.7
251.0
466.9
344.3
237.7
148.5
161.8
1,910.0 | 50.1
37.3
33.5
25.0
21.2
20.0
15.3
27.4 | 686.8
569.0
1,029.8
751.6
525.8
316.7
344.5
4,224.2 | 55·9
41.9
37.3
27.6
23.2
21.2
17.7
30.7 |
Total |
3,173.8 |
39.0 |
2,635.7 |
32.1 |
5,809.4 |
35.5 |
|
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |
Source: ABS unpublished data, Population Survey Monitor, 1995-96.
Participation by State and Territory
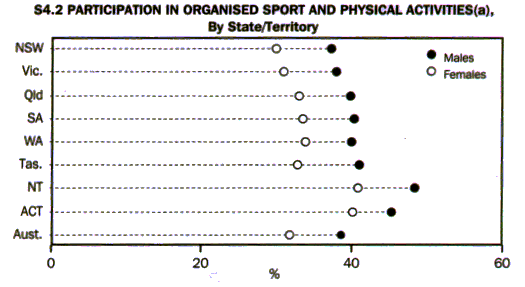
Participation in organised sport and physical activities varied across the States and Territories. The Northern Territory and the Australian Capital Territory had the highest participation rates (44.9% and 43.0% respectively), substantially higher than those of any of the States. South Australia, Western Australia and Tasmania had the highest rates among the States (each 37.2%) while the lowest was recorded for New South Wales (33.9%). The higher rates in the Northern Territory and the Australian Capital Territory could be due to these areas having comparatively lower proportions of aged people as well as higher levels of income.
Within each State or Territory, the participation rate for males was higher than for females. However, as graph S4.2 shows, the difference in the rates was least in the Australian Capital Territory (5.2 percentage points) and greatest in Tasmania (8.1 percentage points).
New South Wales (33.9%). The higher rates in the Northern Territory and the Australian Capital Territory could be due to these areas having comparatively lower proportions of aged people as well as higher levels of income.
Within each State or Territory, the participation rate for males was higher than for females. However, as graph 54.2 shows, the difference in the rates was least in the Australian Capital Territory (5.2 percentage points) and greatest in Tasmania (8.1 percentage points).
|
 (a) Persons aged 15 years and over.
Source: Unpublished data, Population Survey Monitor, 1995-96
(a) Persons aged 15 years and over.
Source: Unpublished data, Population Survey Monitor, 1995-96
S4.3 MOST POPULAR SPORTS AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITIES(a), Persons Aged 15 Years and Over
|
 | Males
| Females
| Persons
|
 | Number | Participation rate | Number | Participation rate | Number | Participation rate |
 | '000 |  | '000 |  | '000 |  |
|
Sport and physical activities
|
Aerobics
Golf
Tennis
Netball
Lawn bowls
Swimming
Basketball
Martial arts
Cricket (outdoor)
Tenpin bowling | 93.6
349.4
154.7
41.6
180.4
127.6
146.3
122.9
191.1
79.7 | 1.4
5.1
2.3
0.6
2.6
1.9
2.1
1.8
2.8
1.2 | 566.3
95.3
207.2
287.0
116.1
153.8
93.9
91.3
*5.3
111.1 | 8.1
1.4
3.0
4.1
1.7
2.2
1.3
1.3
*0.1
1.6 | 659.9
444.7
362.0
328.6
296.4
281.4
240.2
214.2
196.4
190.9 | 4.8
3.2
2.6
2.4
2.2
2.0
1.7
1.6
1.4
1.4 |
| Total all activities(a) | 2,314.2 | 34.0 | 1,910.0 | 27.4 | 4,224.2 | 30.7 |
|
(a) Includes activities not listed.
Source: Participation in Sport and Physical Activities, 1995-96 (4177.0). |
Children's organised sport and physical activities
Almost 1.6 million children aged 5-14 years (61.5% of all children in this age group) participated in organised sport and physical activities, either with a club or in school organised activities conducted outside school hours (table S4.4). The most popular sport or activity for 5-14 year olds was swimming, which had 338,800 participants in this age range during 1995-96. This was followed by basketball (300,100 participants), netball (263,900 participants) and soccer (245,000 participants).
For girls, netball and swimming were by far the most popular sports or activities, with participation rates of 20.5% and 15.0% respectively. Next most popular were basketball (8.3%) and tennis (7.7%). Boys had a more even distribution of interests, with soccer being the most popular sport (17.0%), followed by basketball (14.9%), cricket (11.5%) and swimming (11.4%).
Expenditure on sport and physical activities
Annual expenditure on organised sport and physical activities by the 4.2m participants 15 years of age and over totalled $2,755m, an average cost of $652 for each participant (table S4.5). The aggregate amount included almost $550m in membership fees, $986m in transport and weekly participation charges and just over $900m on clothing and equipment.
S4.4 MOST POPULAR SPORTS AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITIES, 5-14 Year Olds
|
 | Males
| Females
| Persons
|
 | Number | Participation | Number | Participation | Number | Participation |
 | '000 | % | '000 | % | '000 | % |
|
Sport and physical activities
|
Swimming
Basketball
Netball
Soccer (outdoor)
Tennis
Cricket (outdoor)
Australian Rules football
Athletics, track and field
Martial arts
Dancing | 150.0
196.3
*7.2
224.8
101.1
151.4
144.8
76.5
76.8
*9.3 | 11.4
14.9
*0.5
17.0
7.7
11.5
11.0
5.8
5.8
*0.7 | 188.8
103.8
256.7
20.1
96.6
10.2
*4.4
70.9
32.6
95.4 | 15.0
8.3
20.5
1.6
7.7
0.8
*0.3
5.6
2.6
7.6 | 338.8
300.1
263.9
245.0
197.8
161.6
149.2
147.4
109.4
104.7 | 13.1
11.6
10.2
9.5
7.7
6.3
5.8
5.7
4.2
4.1 |
| Total all activities(a) | 859.6 | 65.0 | 725.7 | 57.8 | 1,585.2 | 61.5 |
|
(a) Includes activities not listed.
Source: Participation in Sport and Physical Activities, 1995-96 (4177.0). |
S4.5 EXPENDITURE, Selected Organised Sport and Physical Activities(a)
|
 | Membership | Transport and weekly fees | Clothing and equipment | Other | Total | Average per participant |
 | $m | $m | $m | $m | $m | $ |
|
Sport and physical activity
|
| Aerobics | 115.8 | 69.7 | 55.1 | 4.4 | 245.1 | 371 |
| Golf | 131.8 | 114.6 | 108.7 | 10.6 | 365.7 | 822 |
| Tennis | 22.1 | 47.1 | 34.6 | 7.2 | 111.0 | 307 |
| Netball | 13.5 | 42.6 | 16.5 | 4.1 | 76.7 | 233 |
| Lawn bowls | 16.3 | 56.7 | 33.2 | 2.9 | 109.1 | 368 |
| Swimming | 13.7 | 28.0 | 14.9 | 6.6 | 63.1 | 224 |
| Basketball | 11.8 | 36.7 | 18.4 | 9.8 | 76.6 | 319 |
| Martial arts | 23.0 | 36.2 | 15.7 | 4.0 | 78.8 | 368 |
| Cricket (outdoor) | 13.0 | 16.4 | 22.9 | 2.5 | 54.8 | 279 |
| Tenpin bowling | 5.1 | 63.8 | 8.7 | 3.1 | 80.6 | 422 |
| Total all activities (b) | 549.6 | 986.3 | 906.7 | 312.6 | 2,755.1 | 652 |
(a) Persons 15 years of age and over.
(b) Includes activities not listed.
Source: Participation in Sport and Physical Activities, Australia, 1995-96 (41.77.0). |
Golf was by far the most expensive of the 10 most popular sports or physical activities. Golfers each spent an average of $822 on their sport, while annual outlays by participants in the other nine sports/physical activities ranged from $224 for swimming to $422 for tenpin bowling.
The sports or physical activities found to incur the highest annual costs were horse riding ($1.833), motor sports ($1,653) and air sports (eg. parachuting. hang-gliding and model aircraft flying) ($1,301). At the lower end of the scale, the average cost met by people who participated in carpet bowls during 1995-96 was a modest $90 for the year. Other low cost organised pursuits were indoor soccer ($154), darts ($160) and walking ($171).
Social participation
In addition to participating in an organised sport or physical activity, many people also participate in sports such as tennis, cycling, weight-lifting, swimming and fishing on a social basis. Table S4.6 shows the number of people who participated in such activities during the two weeks prior to being surveyed, for each of the four surveys conducted during 1995-96. Swimming was the most popular activity in the warmer months (1,319,500 in November and 1,652,000 in February), while cycling was the most popular activity in cooler weather (522,200 in August and 579,300 in May).
Given that social participants were measured as people aged 18 years and over who had participated during the previous two weeks only, it is likely that the total number who were involved in social sport during 1995-96 is understated. Similarly, the estimate of about $1,000m for annual expenditure on social sport should be regarded as a minimum.
Summary
This article has briefly outlined the main findings of an ABS survey regarding participation in sport and physical activities in 1995-96.
With 5.8m people aged five years and over participating in organised sport and physical activities during 1995-96, and $2,755m spent by participants 15 years and over, and another $1,000m spent on social participation, the popularity and economic significance of sport and physical activities in Australia are clear.
The survey found that participation in organised sport and physical activities was highest among the younger age groups, with participation rates steadily declining with age. Males had a higher participation rate than females in all age groups, while the Northern Territory and the Australian Capital Territory had higher participation rates than any of the States.
For further details see the ABS publication Participation in Sport and Physical Activities, Australia 1995-96 (4177.0).
S4.6 PARTICIPANTS, Selected Social Sport and Physical Activities(a)
|
 | Aug 1995 | Nov 1995 | Feb 1996 | May 1996 |
 | '000 | '000 | '000 | '000 |
|
Sport and physical activities
|
| Aerobics | 340.1 | 409.0 | 413.8 | 361.1 |
| Cycling | 522.2 | 656.1 | 643.8 | 579.3 |
| Fishing | 463.2 | 660.2 | 835.0 | 490.2 |
| Golf | 350.4 | 367.7 | 412.4 | 366.2 |
| Horse riding | 131.3 | 163.0 | 115.9 | 69.5 |
| Ice/snow sports | 200.3 | (b) | (b) | (b) |
| Squash/racquet ball | 89.4 | 172.8 | 108.8 | 151.7 |
| Surf sports | 118.7 | 241.4 | 192.0 | 79.2 |
| Swimming | 474.8 | 1 319.5 | 1 652.0 | 524.8 |
| Tenpin bowling | 127.8 | 70.4 | 123.8 | 91.7 |
| Tennis | 221.8 | 311.5 | 429.0 | 211.1 |
| Water-skiing/powerboating | (b) | 129.7 | 178.2 | 91.3 |
| Weight-lifting | 500.0 | 763.9 | 586.4 | 515.3 |
(a) Persons aged 18 years and over in the two weeks before each survey.
(b) Subject to relative standard error greater than 50%.
Source: Participation in Sport and Physical Activities, 1995-96, Australia, (4177.0). |
|
 Print Page
Print Page