Annual percentage change
A measure of the percentage change in a variable between one time period and another at an annual rate. This measure allows for the compounding of an
increase or decrease over time. Thus an annual percentage increase of 10% results in a figure increasing by 21% over two years. The formula for calculating annual percentage change is:
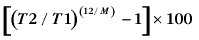
where T1 is the value of the data item at the first time point, T2 is the value at the second time point, and M is the number of months between the two time points.
Articulated trucks
Motor vehicles constructed primarily for load carrying, consisting of a prime mover having no significant load carrying area, but with a turntable device which can be linked to one or more trailers.
Attrition rate
The estimated proportion of motor vehicles taken off the register since the previous MVC. The attrition rate is also referred to as the motor vehicle retirement or scrappage rate. The number of registration lapses is calculated by adding the total registrations at the earlier MVC to the number of new motor vehicle sales between the MVCs, and subtracting the total registrations at the later MVC. The attrition rate measures the number of registration lapses as a percentage of the total potential vehicle fleet, where the potential vehicle fleet is the number of registrations at the first MVC date plus the number of new motor vehicle sales between the two MVCs. To calculate the annualised attrition rate as a percentage apply the following formula:
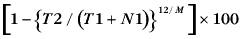
where T1 is the number of registrations at the first time point, N1 is the number of new sales between the first and second time points, T2 is the number of registrations at the second time point and M is the number of months between the two time points.
Average vehicle age
The estimated average age of registered motor vehicles in Australia. The age of a vehicle is defined as the number of years since it was first manufactured. The formula allows for the census being conducted on different days of the year.
For vehicles manufactured in the current year:
Vehicle age = Reference month/24
For vehicles manufactured in previous years:
Vehicle age = Current year - Year of manufacture + (Reference month - 6)/12
The average age is then calculated as the sum of all vehicle ages divided by the total number of vehicles.
Buses
Motor vehicles constructed for the carriage of passengers. Included are all motor vehicles with 10 or more seats, including the driver's seat.
Campervans
Self-propelled motor vehicles containing an area primarily used for accommodation. Included are motor homes and powered caravans.
Caravans
Non-powered vehicles towed behind another vehicle and used primarily for accommodation. Includes rigid and pop-up caravans and tent trailers but excludes campervans.
Estimated Resident Population (ERP)
The official ABS estimate of the Australian population. Based on results from the Census of Population and Housing, it is updated annually between censuses using demographic statistics. To obtain ERP figures, the census count is adjusted for under enumeration and for Australian residents temporarily overseas on census night.
Gross Combination Mass (GCM)
Tare weight (i.e. unladen weight) of the motor vehicle and attached trailers, plus its maximum carrying and towing capacity. GCM is the weight measurement used for trailer towing vehicles such as articulated trucks.
Gross Vehicle Mass (GVM)
Tare weight (i.e. unladen weight) of the motor vehicle, plus its maximum carrying capacity excluding trailers.
Heavy rigid trucks
Rigid trucks of GVM greater than 4.5 tonnes.
Light commercial vehicles
Vehicles primarily constructed for the carriage of goods, and which are less than or equal to 3.5 tonnes GVM. Included are utilities, panel vans, cab-chassis and forward-control load carrying vehicles (whether four-wheel drive or not).
Light rigid trucks
Rigid trucks of GVM greater than 3.5 tonnes and less than or equal to 4.5 tonnes.
Make
The manufacturer of the motor vehicle (e.g. Ford, Holden, Mitsubishi, Toyota).
Motor cycles
Two and three wheeled motor vehicles constructed primarily for the carriage of one or two persons. Included are two and three wheeled mopeds, scooters, motor tricycles and motor cycles with side cars.
Non-freight carrying trucks
Specialist motor vehicles or motor vehicles fitted with special purpose equipment, and having little or no goods carrying capacity (e.g. ambulances, cherry pickers, fire trucks and tow trucks).
Passenger vehicles
Motor vehicles constructed primarily for the carriage of up to nine persons (including the driver). Included are cars, station wagons, four-wheel drive passenger vehicles and forward-control passenger vehicles. Excluded are campervans.
Plant and equipment
Self-propelled vehicles (e.g. tractors) custom built to perform a particular function. Included are tractors and fork-lifts registered for normal road use, mobile cranes, drilling rigs, street sweepers, and road construction and mining equipment. Excluded are trucks whose load-carrying area has been fitted with machinery such as fire engines and tow trucks which are included with non-freight carrying trucks, and garbage trucks which are included in rigid trucks.
Rigid trucks
Motor vehicles of GVM greater than 3.5 tonnes, constructed with a load carrying area. Included are normal rigid trucks with a tow bar, draw bar or other non-articulated coupling on the rear of the vehicle.
Rigid trucks are divided into two categories:
- Light rigid trucks of GVM greater than 3.5 tonnes and less than or equal to 4.5 tonnes
- Heavy rigid trucks of GVM greater than 4.5 tonnes
Size of bus
Size of bus is based on GVM, registered seating capacity, or tare weight. Small buses are those of GVM of 5 tonnes or less, medium buses have greater than 5 but less than or equal to 12 tonnes GVM, and large buses have greater than 12 tonnes GVM. If GVM is not reported, then size is based on registered seating capacity. Small buses have 20 seats or fewer, medium buses have 2140 seats, and large buses have 41 or more seats. If neither GVM nor registered seating capacity are reported then size is based on tare weight. Small buses have tare weight up to and including 3.1 tonnes, medium buses have tare weight over 3.1 tonnes and up to and including 7 tonnes and large buses have greater than 7 tonnes tare weight.
State/territory
The state or territory motor registry at which a vehicle is registered.
Tare weight
The unladen weight of a vehicle.
Trailers
Non-powered vehicles that are towed behind another vehicle and which are primarily used for carrying loads. Included are box trailers, semi trailers, boat trailers, horse floats, trailed machinery and similar vehicles.
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All