BUSINESS MARKETS AND COMPETITION
Geographic markets in which businesses operated
Businesses were asked to identify all geographic markets in which they operated during the year ended 30 June 2006.
Geographic markets in which the business operated, 2005-06(a)(b), by employment size |
|  |
 | Employment size |  |  |
 | 0-4 persons | 5-19 persons | 20-199 persons | 200 or more persons | Total |  |
 | % | % | % | % | % |  |
|  |
| Local | 77.8 | 82.4 | 77.8 | 73.6 | 79.1 |  |
| Outside of local area but within Australia | 44.7 | 45.5 | 55.9 | ^75.2 | 45.9 |  |
| Overseas | 7.1 | 9.5 | 13.8 | 33.6 | 8.4 |  |
|  |
| ^ estimate has a relative standard error of 10% to less than 25% and should be used with caution |
| (a) Proportions are of all businesses in each employment size category. |
| (b) Businesses were asked to identify all geographic markets in which they operated. Businesses could report more than one geographic location. |
Nearly four in five businesses operated in their local area (i.e. the immediate area, town or city in which the business is located) and almost half operated outside the local area but within Australia. Overseas markets were operated in by 8% of businesses overall, ranging from 7% for businesses with 0-4 persons employed to 34% for businesses with 200 or more persons employed.
Market share of businesses
Businesses were asked to self-assess the business's market share based on their perception of the market in which they operated. No guidance related to how the business could make this assessment was provided. Broad percentage ranges were provided for market share.
Market share of businesses, 2005-06(a)(b), by employment size |
|  |
 | Employment size |  |
 | 0-4 persons | 5-19 persons | 20-199 persons | 200 or more persons | Total |  |
 | % | % | % | % | % |  |
|  |
| Less than 10% | 69.6 | 49.1 | 49.5 | 29.8 | 62.3 |  |
| Greater than or equal to 10% and less than or equal to 50% | 22.4 | 37.9 | 36.6 | 53.8 | 27.9 |  |
| Greater than 50% | 8.0 | 13.0 | 13.9 | 16.4 | 9.8 |  |
|  |
| (a) Proportions are of all businesses in each employment size category. |
| (b) Market share was based on the assessment by the business provider. |
Overall, 62% of businesses reported market share of less than 10%, highest for businesses with fewer than 5 persons employed (70%) and lowest for businesses with 200 or more persons employed (30%). Market share of greater than 50% was reported by 8% for businesses with 0-4 persons employed, compared to 16% of businesses that employed 200 or more persons.
Main source of business income
Businesses were asked to identify their main source of income from the sales of goods and services during the year ended 30 June 2006. A list of sources was supplied on the survey form, however definitions for 'large businesses or organisations' and 'small and/or medium businesses or organisations' were not provided.
Main source of business income(a)(b)(c), by employment size |
|  |
 |  | Employment size |  |
 |  | 0-4 persons | 5-19 persons | 20-199 persons | 200 or more persons | Total |  |
 |  | % | % | % | % | % |  |
|  |
| Australian sources |  |  |  |  |  |  |
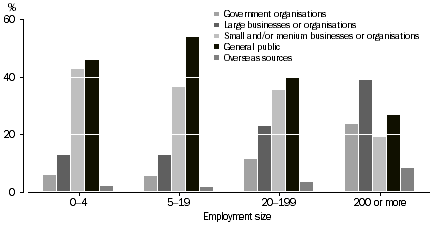
 | Government organisations | 6.1 | 5.5 | 11.6 | ^23.6 | 6.4 |  |
 | Large businesses or organisations | 13.2 | 13.4 | 23.3 | 38.6 | 14.2 |  |
 | Small and/or medium businesses or organisations | 42.7 | 36.5 | 35.3 | 19.2 | 40.3 |  |
 | General public | 45.9 | 54.0 | 39.7 | 26.8 | 47.6 |  |
| Overseas sources | 2.0 | 1.9 | 3.6 | 8.3 | 2.1 |  |
|  |
| ^ estimate has a relative standard error of 10% to less than 25% and should be used with caution |
| (a) Proportions are of all businesses in each employment size category. |
| (b) Businesses were asked to identify their main source of income from the sales of goods and services and were asked to nominate one source only, i.e. overseas or one of the Australian sources. |
| (c) The sum of the component items within employment size categories may not equal 100.0% due to rounding and/or provision of multiple responses where income was equally apportioned across more than one source. |
Overall, the main source of income for 48% of businesses was the general public, with the next main source of income being small and/or medium sized businesses or organisations, reported by 40% of businesses. At the employment size level, this pattern is consistent across businesses within the three smallest employment size ranges, however for businesses with 200 or more persons employed, large businesses or organisations were identified most frequently as their main income source.
Main source of business income, 2005-06
Number of competitors
The number of competitors a business had during the year ended 30 June 2006 was self-assessed with three response options available. No guidance related to how the business could make this assessment was provided.
Number of competitors, 2005-06(a)(b), by employment size |
|  |
 | Employment size |  |
 | 0-4 persons | 5-19 persons | 20-199 persons | 200 or more persons | Total |  |
 | % | % | % | % | % |  |
|  |
| No effective competition | 21.0 | 10.7 | 11.0 | 6.6 | 17.4 |  |
| One or two competitors | 9.9 | 13.2 | 8.5 | 5.6 | 10.7 |  |
| Three or more competitors | 69.2 | 76.0 | 80.5 | 87.8 | 72.0 |  |
|  |
| (a) Proportions are of all business in each employment size category. |
| (b) Businesses were only asked number of competitors in the broad categories shown in the table. |
Overall, 72% of total businesses reported three or more competitors, 17% reported no effective competition and 11% had one or two competitors. This ranking was consistent across employment size ranges, except for business with 5-19 persons employed, where having one or two competitors was more prevalent than having no effective competition, at 13% and 11% respectively.
Nature and size of competitors
Those businesses with one or more competitors were asked to identify the nature and size of those competitors. Respondents could identify multiple responses for each nature and size.
Similar in nature means that the goods or services provided or the activity undertaken are similar. Different in nature means that the goods or services provided or the activity undertaken include some similar goods, services or activities as part of a much wider range or a much smaller range. For example, if two retailers are both selling clothing only, then they are similar in nature. However, if one sells clothing only while the other is a department store, then they are different in nature.
Nature and size of competitors, 2005-06(a)(b), by employment size |
|  |
 |  |  | Employment size |  |
 |  |  | 0-4 persons | 5-19 persons | 20-199 persons | 200 or more persons | Total |  |
 |  |  | % | % | % | % | % |  |
|  |
| Nature and size of competitors |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 | Similar in nature to the business(c) |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  | Smaller than the business | 14.8 | 28.4 | 35.9 | ^44.8 | 20.7 |  |
 |  | About the same size as the business | 57.2 | 66.5 | 66.1 | 67.3 | 60.7 |  |
 |  | Larger than the business | 54.5 | 46.9 | 48.6 | ^41.1 | 51.7 |  |
 | Different in nature to the business(c) |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  | Smaller than the business | 5.3 | 8.0 | 13.5 | 21.8 | 6.9 |  |
 |  | About the same size as the business | 14.4 | 13.9 | 16.8 | 16.3 | 14.5 |  |
 |  | Larger than the business | 35.5 | 28.6 | 28.1 | 23.4 | 32.8 |  |
|  |
| ^ estimate has a relative standard error of 10% to less than 25% and should be used with caution |
| (a) Proportions are of those businesses that identified having one or more competitors. |
| (b) Nature of competitors is based on the assessment of the business. |
| (c) Businesses were provided with definitions for 'similar in nature' and 'different in nature'. |
Having competitors both similar in nature and similar in size as the selected business was reported by 61% of businesses with at least one competitor. This combination of nature and size was the most commonly reported, followed by competitors similar in nature and larger than the selected business (52%) and competitors different in nature and larger than the selected business (33%).
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All