MAIN FEATURES
EXPENDITURE ON RESEARCH AND EXPERIMENTAL DEVELOPMENT (R&D)
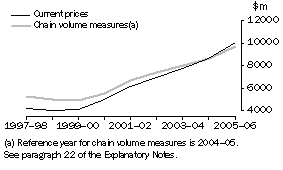
Business expenditure on R&D (BERD) in Australia during 2005-06 was $10,080.7 million. This represented an increase of 16.6% in current price terms over 2004-05 and 11.8% in chain volume terms and was the seventh successive year of increase.
Resources Devoted to R&D |
|  |
 |  |  | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 |  |
|  |
| Expenditure on R&D |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 | Current prices | $m | 6 191.9 | 6 940.3 | r7 769.9 | r8 654.6 | 10 080.7 |  |
 | Chain volume measures(a) | $m | 6 702.7 | 7 397.3 | 8 036.9 | 8 654.6 | 9 679.8 |  |
| Human resources devoted to R&D | PYE | 32 209 | 35 939 | r37 430 | r40 417 | 42 837 |  |
|  |
| r revised |
| (a) The reference year for chain volume measures is 2004-05. See paragraph 22 of the Explanatory Notes. |
Over the five years to 2005-06, BERD increased by an average of 12.6% per year in current price terms and 8.9% per year in chain volume terms.
Business expenditure on R&D
Proportion of GDP
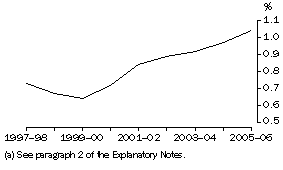
BERD increased as a proportion of GDP between 2004-05 and 2005-06, moving from 0.97% to 1.04%. This was the first time that the ratio of BERD to GDP exceeded 1.0%.
Business expenditure on R&D, proportion of GDP(a)
Although Australia remained below the OECD average of 1.53%, it recorded one of the largest increases in BERD/GDP ratio of all OECD countries between 2004-05 and 2005-06. The following table shows BERD/GDP ratios for selected OECD countries.
BERD/GDP RATIOS OF OECD COUNTRIES(a) |
|  |
 | 2001-02 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 |  |
 | % | % | % | % | % |  |
|  |
| Sweden | 3.28 | na | 2.93 | 2.73 | 2.88 |  |
| Japan | 2.30 | 2.36 | 2.40 | 2.38 | 2.54 |  |
| Finland | 2.35 | 2.34 | 2.42 | 2.42 | 2.47 |  |
| Korea | 1.97 | 1.90 | 2.00 | 2.18 | 2.30 |  |
| United States of America | 2.00 | 1.86 | 1.84 | 1.79 | 1.82 |  |
| Germany | 1.72 | 1.72 | 1.76 | 1.74 | 1.71 |  |
| Denmark | 1.64 | 1.73 | 1.78 | 1.70 | 1.67 |  |
| Austria | na | 1.42 | na | 1.51 | 1.64 |  |
| Iceland | 1.75 | 1.71 | 1.48 | na | 1.45 |  |
| Luxembourg | na | na | 1.48 | 1.46 | 1.34 |  |
| France | 1.39 | 1.41 | 1.36 | 1.34 | 1.32 |  |
| Belgium | 1.51 | 1.37 | 1.31 | 1.29 | 1.24 |  |
| United Kingdom | 1.20 | 1.19 | 1.14 | 1.09 | 1.10 |  |
| Canada | 1.29 | 1.17 | 1.13 | 1.12 | 1.07 |  |
| Australia | 0.84 | 0.89 | 0.92 | 0.97 | 1.04 |  |
| Netherlands | 1.05 | 0.98 | 1.01 | 1.03 | 1.02 |  |
| Czech Republic | 0.72 | 0.73 | 0.76 | 0.80 | 0.92 |  |
| Ireland | 0.77 | 0.76 | 0.80 | 0.82 | 0.83 |  |
| Norway | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.98 | 0.87 | 0.82 |  |
| Spain | 0.48 | 0.54 | 0.57 | 0.58 | 0.61 |  |
| Italy | 0.53 | 0.54 | 0.52 | 0.52 | 0.55 |  |
| New Zealand | 0.42 | na | 0.49 | na | na |  |
| Hungary | 0.37 | 0.35 | 0.34 | 0.36 | 0.41 |  |
| Portugal | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.27 | 0.29 |  |
| Slovak Republic | 0.43 | 0.37 | 0.32 | 0.25 | 0.25 |  |
| Mexico | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.25 |  |
| Poland | 0.22 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.18 |  |
| Turkey | 0.24 | 0.19 | 0.14 | 0.16 | na |  |
| Greece | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.14 |  |
| Total OECD | 1.57 | 1.51 | 1.51 | 1.49 | 1.53 |  |
|  |
| na not available |
| (a) Ranked by 2005-06 BERD/GDP ratio. |
| Main Science and Technology Indicators, 2007/1, OECD, Paris, 2007 |
Industry
In 2005-06, the largest contributors to BERD were Manufacturing ($3,888.7 million or 38.6% of BERD), Property and business services ($1,717.0 million or 17.0%) and Mining ($1,683.4 million or 16.7%). Of all industries, Mining and Manufacturing reported the largest absolute growth from 2004-05, increasing their expenditure on R&D by $417.2 million (33.0%) and $416.5 million (12.0%) respectively. Other industries to record large increases included Property and business services (up $151.1 million or 9.6%) and Wholesale trade (up $105.9 million or 17.8%).
Business expenditure on R&D, by selected industries(a)

Type of expenditure
As in previous years, BERD in 2005-06 was mainly comprised of Current expenditure ($9,439.7 million or 93.6% of BERD). Current expenditure was in turn comprised of $3,886.8 million in Labour costs and $5,553.0 million in Other current expenditure. Capital expenditure in 2005-06 totalled $641.0 million.
Retail trade had the highest level of Labour costs as a proportion of BERD (56.5%), while Mining and Construction reported the lowest levels (at 16.0% and 18.9% respectively).
At $289.8 million, Manufacturing accounted for 45.2% of all Capital expenditure on R&D in 2005-06. The next highest level of Capital expenditure was reported by Mining at $100.2 million.
Source of funds
The Business sector was the main source of R&D funds in 2005-06, with $9,191.8 million (91.2%) coming from Own funds and $223.3 million (2.2%) from Other businesses. Commonwealth government and Overseas organisations were the next largest funders of R&D, at $396.4 million (3.9%) and $177.6 million (1.8%) respectively.
Property and business services and Health and community services had the lowest proportions of self-funded research, at 76.5% and 78.2% respectively.
Type of activity
In 2005-06, the majority of R&D activity was directed into Experimental development (62.4% or $6,288.8 million) and Applied research (32.9% or $3,312.1 million). Applied research showed the largest growth between 2004-05 and 2005-06, increasing by 15.4% or $485.4 million.
Location
Locations in New South Wales and Victoria continued to record the highest levels of BERD in 2005-06, at $3,331.3 million (33.0%) and $2,954.4 million (29.3%) respectively. Victoria also reported the highest level of growth in BERD (up $541.7 million or 22.5%), between 2004-05 and 2005-06, followed by Western Australia (up $392.7 million or 35.9%) and Queensland (up $201.0 million or 18.8%).
Business expenditure on R&D, by location(a)
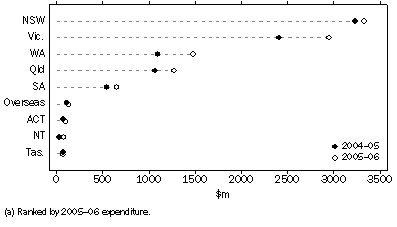
Making the largest contribution to BERD in Victoria and New South Wales, in 2005-06, was Manufacturing, with expenditure on R&D in each state of $1,486.6 million (50.3%) and $1,004.1 million (30.1%) respectively. While Manufacturing was also the largest contributor to R&D expenditure in Queensland ($444.0 million or 34.9%), Mining was the most dominant industry in Western Australia ($703.7 million or 47.4%).
Victoria (1.27%) and Western Australia (1.25%) also reported the highest state percentages of BERD as a proportion of Gross State Product (GSP).
Business expenditure on R&D, by location - proportion of GSP(a) |
|  |
 | NSW | Vic. | Qld | SA | WA | Tas. | NT | ACT |  |
 | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % |  |
|  |
| 2003-04 | 1.02 | 1.02 | 0.65 | 1.02 | 0.86 | 0.50 | 0.76 | 0.37 |  |
| 2004-05 | 1.06 | 1.09 | 0.67 | 0.92 | 1.07 | 0.45 | 0.29 | 0.42 |  |
| 2005-06 | 1.04 | 1.27 | 0.70 | 1.04 | 1.25 | 0.42 | 0.64 | 0.51 |  |
|  |
| (a) See paragraph 2 of the Explanatory Notes. |
Employment size
In 2005-06, businesses with 200 or more employees made the largest contribution to BERD ($6,738.2 million or 66.8%), followed by those with 20-199 employees ($2,026.5 million or 20.1%). Making the smallest contribution to BERD were businesses with 0-4 employees ($354.0 million or 3.5%) and those with 5-19 employees ($962.0 million or 9.5%). Businesses with 200 or more employees contributed 70.1% ($1,004.7 million) of the total growth in BERD between 2004-05 and 2005-06.
Socio-economic objectives (SEO)
Much of the growth in BERD, between 2004-05 and 2005-06, occurred in the Energy resources (up $324.6 million), Manufacturing (up $292.8 million) and Mineral resources (up $224.2 million) SEOs. Together these three SEOs accounted for 58.8% of the total growth in BERD over the period.
Research fields
Accounting for 82.7% of BERD in 2005-06 were the Research fields of Engineering and technology ($5,856.6 million or 58.1%) and Information, computing and communication sciences ($2,484.8 million or 24.6%). The largest growth in expenditure within these Research fields, between 2004-05 and 2005-06, was recorded for Resource engineering (up $466.8 million or 45.2%) and Computer software (up $191.1 million or 20.0%).
HUMAN RESOURCES DEVOTED TO R&D
Human resources devoted to R&D in 2005-06 totalled 42,837 person years of effort (PYE), an increase of 6.0% over 2004-05.
Industry
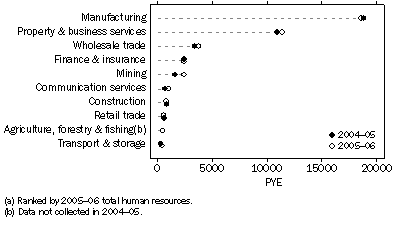
In 2005-06, Manufacturing and Property and business services were the main contributors to total Human resources devoted to R&D, at 43.3% and 26.5% respectively. Mining and Property and business services recorded the largest increases in Human resources devoted to R&D from 2004-05, increasing by 782 PYE (47.2%) and 450 PYE (4.1%) respectively.
Business human resources devoted to R&D, by selected industries(a)
Type of resource
Researchers continued to be the main type of human resource devoted to R&D (53.9% of total PYE) in 2005-06. However, Technicians reported the largest growth, between 2004-05 and 2005-06, increasing by 1,478 PYE or 12.3%.
Employment size
Businesses with 200 or more employees accounted for 23,914 PYE (55.8%) of total Human resources devoted to R&D in 2004-05, while those with 0-4 employees contributed 1,392 PYE (3.2%).
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All