DISTRIBUTION OF EARNINGS
In August 2016, the mean weekly earnings of employees and owner managers of incorporated enterprises (OMIEs) was higher than median weekly earnings. This difference reflects the asymmetric distribution of earnings, where a relatively small number of employees and OMIEs have comparatively very high earnings. This is illustrated in the graph below.
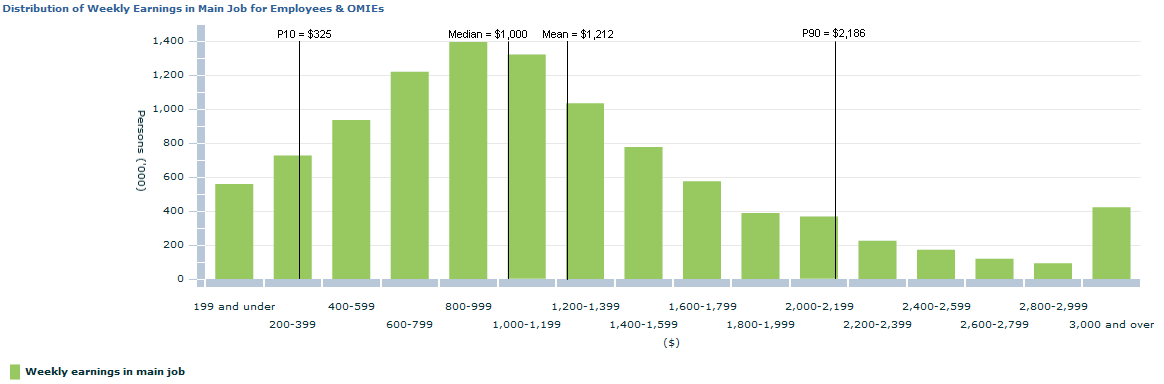
While median and mean earnings provide useful information about earnings distributions, they do not capture all the information about the distribution. It is also useful to consider percentiles, which measure the spread of earnings across the population. For example, the 10th percentile, P10, separates the population into the bottom 10% (lowest earners) and top 90%, while P90 separates the population into the bottom 90% and the top 10% (highest earners). At August 2016, P10 for weekly earnings in main job was $325, while P90 for weekly earnings in main job was $2,186. (Datacube 11)
As would be expected, the distribution of weekly earnings of part-time employees and OMIEs was concentrated in lower earning groups with 57% earning under $600 per week. For full-time employees and OMIEs, 73% earned $1,000 or more per week. For male full-time employees and OMIEs, the mean weekly earnings in main job was $1,602 and the median weekly earnings in main job was $1,334. For female full-time employees and OMIEs, the mean weekly earnings in main job was $1,339 and the median weekly earnings in main job was $1,150. For part-time employees and OMIEs, the mean weekly earnings in main job for males was $575 and the median weekly earnings was $450. Whilst for females the mean weekly earnings was $604 and the median $517. (Datacube 11)
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All
 Quality Declaration
Quality Declaration