ABOUT THIS PUBLICATION
This publication presents results from the Survey of Involvement in Sport and Physical Activity conducted in April 2004. It presents information on the number of persons aged 15 years and over who were involved in organised sport and physical activity over a 12 month period. For persons who were involved in non-playing roles, the 2004 data is compared with data collected in similar surveys in 1993, 1997 and 2001. Data about players have not been compared across surveys due to conceptual differences between surveys (see paragraphs 21 and 22 of the Explanatory Notes).
ABOUT THIS SURVEY
The 2004 Survey of Involvement in Sport and Physical Activity was conducted throughout Australia as part of the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) Monthly Population Survey (MPS).
It collected information about players and participants in organised sport and physical activity, and also about persons involved in non-playing roles, during the 12 months prior to interview in April 2004. The information included characteristics of persons involved, the amount of time spent through involvement in each role, and whether any payment was received. It also included the types of non-playing roles undertaken, whether a course or qualification had been completed for these roles, and whether any involvement was with school or junior sport.
ROUNDING
As estimates have been rounded, discrepancies may occur between sums of the component items and totals.
INQUIRIES
For further information about these and related statistics, contact the National Information and Referral Service on 1300 135 070 or Mike Stratton on Adelaide (08) 8237 7399.
SUMMARY OF FINDINGS
INTRODUCTION
In the 12 months prior to April 2004, an estimated 4.3 million persons aged 15 years and over reported that they were involved in organised sport and physical activity. This represents 27% of the total population. Persons involved in organised sport and physical activity included 3.7 million players (23% of persons aged 15 years and over), as well as 1.5 million persons involved in non-playing roles (10%). Non-playing roles include: coach; instructor or teacher; referee or umpire; committee member or administrator; scorer or timekeeper; medical support; or other role, and exclude persons involved only as a spectator or club member. Of the 1.5 million persons with a non-playing role, 60% also had a playing role.
CHARACTERISTICS OF PERSONS INVOLVED
Sex
A higher percentage of males (31%) than females (23%) were involved in organised sport and physical activity. This was true for involvement as a player, where males had a participation rate of 27% compared with 20% for females, as well as for involvement in a non-playing role (males 11%, females 8%).
Age
The 15 to 24 years age group had the highest rate of involvement with 39% of people participating in organised sport or physical activity. Participation rates declined progressively in older age groups, with those aged 55 to 64 years and 65 years and over having less than half the rate of the 15 to 24 years group.
While the age pattern for players was similar to that for total involvements, among non-players the peak age groups for participation were 35 to 44 years and 45 to 54 years, with non-player participation rates of 15% and 12% respectively. People in the oldest age groups had the lowest rates (6.5% for those aged 55 to 64 years and 4.4% for those aged 65 years and over).
Playing, non-playing and total involvement participation rates, By age

Country of birth
Levels of involvement in sport and physical activity varied according to country of birth. Persons born in Australia and in the main English speaking countries (see Glossary for definition) had participation rates of 31% and 27% respectively, compared with 12% involvement for those born in other countries.
An estimated 27% of Australian born persons had some involvement as players, compared with 22% of those from the main English speaking countries and 10% from other countries.
The rate of involvement as non-players was 11% for those born in Australia, slightly higher than for those born in the main English speaking countries (9%), but almost four times that of those born in other countries (3%).
Area of usual residence
The overall participation rate (30%) for persons residing outside the eight state and territory capital cities was higher than for persons residing in the capital cities (26%). This was also true for player participation where persons outside the capital cities had a participation rate of 26% compared with 22% for those in the capitals. Similarly, 12% of persons outside the capitals were involved in non-playing roles compared with 8% in the capital cities.
Labour force status
Of persons who were employed in the week prior to interview, 32% (3.0 million persons) were involved in organised sport and physical activity at some time during the 12 months prior to April 2004. Unemployed persons and those not in the labour force had participation rates of 27% (151,400 persons) and 19% (1.1 million persons) respectively.
The player participation rates for employed and unemployed persons were 27% and 25% respectively, while for persons not in the labour force the rate was 18%. For non-players the rate was 12% among employed persons compared with 8% for unemployed persons and 5% for persons not in the labour force.
INVOLVEMENT IN NON-PLAYING ROLES
The success of organised sport depends not only on the players, but also on the involvement of people in non-playing roles, such as officials, administrators and other support roles. Additional information about this type of involvement in organised sport and physical activity was collected in the survey, and is presented below.
Of the 1.5 million persons with non-playing involvement
- 67% had one non-playing role
- 21% had two non-playing roles
- 12% had three or more non-playing roles.
Overall these 1.5 million persons were involved in 2.2 million different non-playing roles in the 12 months prior to April 2004.
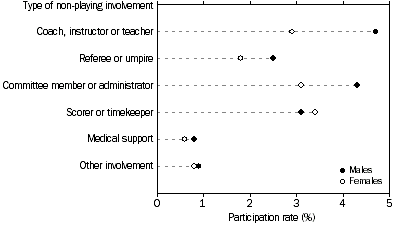
The most common non-playing involvement for males were as a coach, instructor or teacher (4.7%) and committee member or administrator (4.3%), while for females the highest proportions were for involvement as a scorer or timekeeper (3.4%) and committee member or administrator (3.1%).
PARTICIPATION IN NON-PLAYING ROLES, By involvement and sex
Non-playing roles associated with school and junior sport
Of the 1.5 million persons involved in non-playing roles, 803,900 (54%) were associated with school or junior sport for at least some of their non-playing involvement. Of those involved as a coach, instructor or teacher, 71% had some association with school or junior sport. In contrast, only a relatively low proportion (44%) of those involved as a committee member or administrator did so in association with school or junior sport.
Qualifications for non-playing roles
Just over one third (34% or 503,200) of all persons involved in non-playing roles reported that they had completed a course or qualification relevant to their role. The highest proportion of persons with qualifications appropriate to their involvement were in a medical support role. Of the 104,500 persons involved in this role, 93% were qualified.
Comparison of 1993, 1997, 2001 and 2004 data
In 1993, 1997 and 2001, similar surveys were conducted by the ABS. Due to some differences in the questions asked and survey methodologies, caution should be exercised when making comparisons between the surveys, however, some comparisons can be made for persons in non-playing roles. For information about the differences between the surveys, see paragraphs 16 to 26 of the Explanatory Notes.
Overall, the proportion of persons aged 15 years and over involved in sport in a non-playing capacity was at a similar level in 1993, 2001 and 2004 (around 10%), however, the rate was slightly higher in 1997 at 11%. The participation rate was higher for males than females in each survey year.
Participation in non-playing roles, 1993, 1997, 2001 and 2004
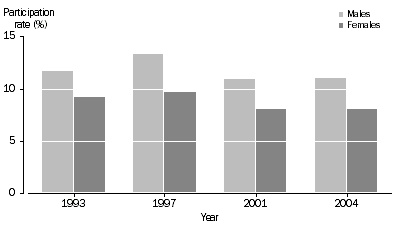
For the roles that allow comparison of participation rates across the four survey years (coach, instructor or teacher; referee or umpire; and committee member or administrator, see paragraph 24 of the Explanatory Notes), the pattern is similar to overall non-playing involvement, with participation being highest in 1997.
Participation in selected roles, 1993, 1997, 2001 and 2004
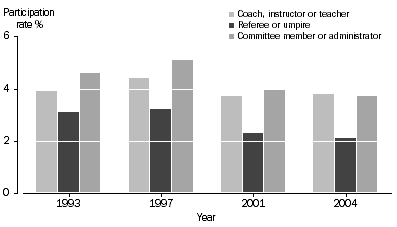
PAYMENT FOR INVOLVEMENT
Of the 4.3 million persons involved in organised sport and physical activity, 7% (297,900 persons) received some type of payment for their involvement. The number of involvements for which these persons were paid totalled 354,800 indicating that a number of persons received payment for involvement in more than one type of role.
Of all payments made for involvement in the 12 months to April 2004, 53% (186,800 involvements) were less than $5,000, and 8% (29,800 involvements) were $20,000 or more.
Of the 2.2 million non-playing involvements, 12% (267,100) attracted some kind of payment. In contrast, only 2% (87,700) of the 3.7 million playing involvements attracted any payment.
Some non-playing roles were more likely to attract payment than others. For example, 23% of persons involved as a referee or umpire and 21% of those involved as a coach, instructor or teacher, received payment, compared with 4% for persons involved as a committee member or administrator and 3% for persons involved in scoring or timekeeping.
TIME INVOLVED
More than half (53%) of the involvements in organised sport and physical activity were for 26 weeks or less in the previous year, one in ten (10%) were for 27 to 39 weeks and over one third (36%) were involved throughout most of the year (between 40 and 52 weeks). These involvements may have related to more than one type of organised sport or physical activity.
Nearly half of involvements (46%) were for 3 to 9 hours per week on average. A further 45% averaged less than 3 hours per week.
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All