GLOSSARY
Age-sex pyramid
An age-sex pyramid is a bar chart graphically representing the age structure of the population, usually in five-year age groups, for males and females separately. The age structure of the population usually approximates the shape of a pyramid because mortality progressively reduces the number in each birth cohort as it ages. The age pyramid is useful to show the existence of unusually large or small cohorts, and in this way, not only conveys information about a country's past demographic history, but also a great deal about its demographic future.
Ageing of the population
Ageing of the population is the consideration of the proportion of the population aged 65 years and over, and the way this proportion is continuing to increase, mostly due to persistent low fertility rates and declining mortality rates.
Age-specific fertility rates
Age-specific fertility rates (ASFR) are the number of live births (occurred or registered) during the calendar year, according to the age of the mother, per 1,000 of the female estimated resident population of the same age at 30 June. For calculating these rates, births to mothers under 15 years are included in the 15-19 years age group, and births to mothers aged 50 years and over are included in the 45-49 years age group. Pro rata adjustment is made for births for which the age of the mother is not given.
Average annual growth rate
The average annual growth rate, r, is calculated as a percentage using the formula:
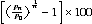
where P0 is the population at the start of the period, Pn is the population at the end of the period and n is the length of the period between P0 and Pn in years.
Average issue
Average issue is the mean number of children ever born alive per woman. Average issue varies by age of woman and is influenced by extreme values of the number of children born. Any grouping of children ever born (e.g. 6 plus) should be given a 'mean' value (6.5 or any other value which must be specified) for the calculation of the average issue.
Baby boom
Baby boom refers to the generation born between the end of World War II and the mid-1960s. Baby boomers are usually taken to be those born in the years 1946 to 1965 inclusive.
Balance of state or territory
The aggregation of all Statistical Divisions (SD) within a state or territory other than its Capital City SD. See Major Statistical Region in Australian Standard Geographical Classification (ASGC) (cat. no. 1216.0).
Birth
The delivery of a child, irrespective of the duration of pregnancy, who, after being born, breathes or shows any evidence of life such as heartbeat.
Capital city
Refers to the Capital City Statistical Divisions of states and territories as defined in the Australian Standard Geographical Classification (ASGC) (cat. no. 1216.0).
Completed fertility
Completed fertility represents the average number of births a cohort of females have borne over their reproductive lifetimes.
Confinement
A pregnancy which results in at least one live birth.
Crude birth rate
The crude birth rate is the number of live births registered during the calendar year per 1,000 estimated resident population at 30 June of that year. For years prior to 1992, the crude birth rate was based on the mean estimated resident population for the calendar year.
Estimated resident population (ERP)
The official measure of the population of Australia is based on the concept of residence. It refers to all people, regardless of nationality or citizenship, who usually live in Australia, with the exception of foreign diplomatic personnel and their families. It includes usual residents who are overseas for less than 12 months. It excludes overseas visitors who are in Australia for less than 12 months.
Exnuptial birth
An exnuptial birth is the birth of a child whose parents are not legally married to each other at the time of the child's birth.
Indigenous
Persons who identify themselves as being of Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander origin.
Indigenous birth
The birth of a live-born child where either the mother or the father was identified as being of Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander origin on the birth registration form.
Indigenous origin
Persons who identify as being of Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander origin.
Intercensal discrepancy
Intercensal discrepancy is the difference between two estimates at 30 June of a census year population, the first based on the latest census and the second arrived at by updating the 30 June estimate of the previous census year with intercensal components of population change which take account of information available from the latest census. It is caused by errors in the start and/or finish population estimates and/or in estimates of births, deaths or migration in the intervening period which cannot be attributed to a particular source.
Marital status
Two separate concepts of marital status are measured by the Australian Bureau of Statistics. These are registered marital status and social marital status.
Registered marital status refers to formally registered marriages and divorces. Registered marital status is a person's relationship status in terms of whether he or she has, or has had, a registered marriage with another person. Accordingly, people are classified as either 'never married', 'married', widowed' or 'divorced'.
Social marital status is the relationship status of an individual with reference to another person who is usually resident in the household. A marriage exists when two people live together as husband and wife, or partners, regardless of whether the marriage is formalised through registration. Individuals are, therefore, regarded as married if they are in a de facto marriage, or if they are living with the person to whom they are registered as married. Under social marital status, a person is classified as either 'married' or 'not married' with further disaggregation of 'married' to distinguish 'registered married' from 'de facto married' person.
Median age at childbearing
The term refers to the age when approximately one-half of the females in a population have their children, either for a birth of particular birth order or for all births. It measures the age at childbearing within the female population, as distinct from the median age of mother at confinement which measures the median age of the females who gave birth in a particular year.
Median value
For any distribution the median value (age, duration, interval) is that value which divides the relevant population into two equal parts, half falling below the value, and half exceeding it. Where the value for a particular record has not been stated, that record is excluded from the calculation.
Mortality
Death.
Multiple birth
A multiple birth is a confinement which results in two or more issue, at least one of which is live-born.
Natural increase
Excess of births over deaths.
Net overseas migration
Net overseas migration is net permanent and long-term overseas migration, plus an adjustment for the effect of differences in duration of stay or absence between initial stated intentions and actual behaviour.
Net population growth
For Australia, net population growth is the sum of natural increase and net overseas migration. For the states and territories, net population growth also includes net interstate migration.
Net reproduction rate
The net reproduction rate represents the average number of daughters that would be born to a group of females if they are subject to the fertility and mortality rates of a given year during their future life. It indicates the extent to which the population would reproduce itself. The net reproduction rate is obtained by multiplying the age-specific birth rates (for female births only) by the proportion of survivors at corresponding ages in a life table and adding the products.
Nuptial birth
A nuptial birth is the birth of a child born of parents who are legally married at the time of the child's birth.
Nuptial first confinement
A nuptial first confinement is the first confinement in the current marriage and therefore does not necessarily represent the woman's first ever confinement resulting in a live birth.
Nuptiality
Nuptiality relates to the registered marital status of persons and the events such as marriages, divorces and widowhood. Confinements and births are identified as being nuptial where the father registered was married to the mother at the time of birth, or where the husband died during pregnancy. Confinements and children of Indigenous mothers considered to be tribally married are classified as nuptial. Other confinements, and the children resulting from them, are classified as exnuptial whether or not both parents were living together at the time of birth.
Part of state
Part of state is used to refer to the remainder of a state outside the Capital City Statistical Division (SD). See also Balance of state or territory.
Paternity acknowledged birth
A paternity-acknowledged birth refers to an exnuptial birth where paternity was acknowledged.
Population growth
For Australia, population growth is the sum of natural increase and net overseas migration. For states and territories, population growth also includes net interstate migration. After the census, intercensal population growth also includes an allowance for intercensal discrepancy.
Previous births
Previous births refer to children born alive (who may or may not be living) to a mother prior to the registration of the current birth in the processing period. In some states, legitimised and legally adopted children may also be included.
Due to variation in data collection and processing methods across states and territories, different definitions of the concept of previous births have been applied.
All previous births of the mother includes all births prior to the current confinement, regardless of nuptiality and paternity.
Previous births of the current relationship where paternity was acknowledged includes all births prior to the current confinement where the current confinement relates to a nuptial birth, or an exnuptial birth where paternity was acknowledged.
Previous issue
See Previous births.
Rate of population growth
Population change over a period as a proportion (percentage) of the population at the beginning of the period.
Registered marital status
Registered marital status refers to formally registered marriages for which the partners hold a marriage certificate. In this publication the distinction is between married parents (nuptial births) and unmarried parents (exnuptial births).
Replacement fertility
Replacement level fertility is the number of babies a female would need to have over her reproductive life span to replace herself and her partner. Given the current mortality of females up to age 49 years, replacement fertility is estimated at around 2.1 babies per female.
Sex ratio
The sex ratio relates to the number of males per 100 females. The sex ratio is defined for total population, at birth, at death and among age groups by appropriately selecting the numerator and denominator of the ratio.
Social marital status
Social marital status is the consensual union status of a person with reference to another person in the household. In this publication data are only available from midwives' collection. The categories are married/de facto; single; and separated/divorced/widowed.
State or territory of registration
State or territory of registration refers to the state or territory in which the event was registered.
State or territory and Statistical Local Area (SLA) of usual residence
State or territory and Statistical Local Area (SLA) of usual residence refers to the state or territory and SLA of usual residence of:
- the population (estimated resident population)
- the mother (birth collection)
- the deceased (death collection).
In the case of overseas movements, state or territory of usual residence refers to the state or territory regarded by the traveller as the one in which he/she lives or has lived. State or territory of intended residence is derived from the intended address given by settlers, and by Australian residents returning after a journey abroad. Particularly in the case of the former, this information does not necessarily relate to the state or territory in which the traveller will eventually establish a permanent residence.
Statistical Division (SD)
Statistical Divisions (SD) consist of one or more Statistical Subdivisions (SSD). The divisions are designed to be relatively homogeneous regions characterised by identifiable social and economic units within the region, under the unifying influence of one or more major towns or cities. Further information concerning SDs is contained in Australian Standard Geographical Classification (ASGC) (cat. no. 1216.0).
Statistical Local Area (SLA)
Statistical Local Areas (SLA) are, in most cases, identical with, or have been formed from a division of, whole Local Government Areas (LGA). In other cases, they represent unincorporated areas. In aggregate, SLAs cover the whole of a state or territory without gaps or overlaps. In some cases legal LGAs overlap statistical subdivision boundaries and therefore comprise two or three SLAs (Part A, Part B and, if necessary, Part C). Further information concerning SLAs is contained in Australian Standard Geographical Classification (ASGC) (cat. no. 1216.0).
Statistical Subdivision (SSD)
In aggregate, Statistical Subdivisions (SSD) cover the whole of Australia without gaps or overlaps. They are defined as socially and economically homogeneous regions characterised by identifiable links between the inhabitants. In the non-urban areas an SSD is characterised by identifiable links between the economic units within the region, under the unifying influence of one or more major towns or cities. Further information concerning SSDs is contained in Australian Standard Geographical Classification (ASGC) (cat. no. 1216.0).
Total fertility rate
The sum of age-specific fertility rates (live births at each age of mother per female population of that age). It represents the number of children a female would bear during her lifetime if she experienced current age-specific fertility rates at each age of her reproductive life.
Usual residence
Usual residence within Australia refers to that address at which the person has lived or intends to live for a total of six months or more in a given reference year.
Year of occurrence
Data presented on year of occurrence basis relate to the date the event occurred.
Year of registration
Data presented on year of registration basis relate to the date the event was registered.
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All