EXPLANATORY NOTES
INTRODUCTION
1 This publication contains summary information on causes of death for all doctor certified deaths for Australia in 2012.
2 In order to complete a death registration, the death must be certified by either a doctor using the Medical Certificate of Cause of Death, or by a coroner. Approximately 85-90% of deaths each year are certified by a doctor. The remainder are reported to a coroner.
3 In the full Causes of Death dataset the pattern of cause distribution is impacted by the certifier type. Table 1 below presents 2011 data disaggregated by certifier type to demonstrate the chapter by chapter coverage achieved by the doctor certified dataset compared with the full Causes of Death dataset.
Table 1. Selected underlying causes of death - 2011(a)(b) |
|
 | 2011 |
 | Total (b) | Dr cert | Proportion by cause |
| Cause of death and ICD-10 code | no. | no. | % |
|
| Infectious and parasitic diseases (A00-B99) | 2 400 | 2 262 | 94.3 |
| Neoplasms (C00-D48) | 43 721 | 43 216 | 98.8 |
| Blood and immunity disorders (D50-D89) | 467 | 450 | 96.4 |
| Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases (E00-E90) | 6 077 | 5 756 | 94.7 |
| Mental and behavioural disorders (F00-F99) | 7 631 | 7 359 | 96.4 |
| Diseases of the nervous system (G00-G99) | 6 741 | 6 440 | 95.5 |
| Diseases of the eye and adnexa (H00-H59) | 8 | 8 | 100.0 |
| Diseases of the ear and mastoid process (H60-H95) | 10 | 8 | 80.0 |
| Diseases of the circulatory system (I00-I99) | 45 622 | 39 924 | 87.5 |
| Diseases of the respiratory system (J00-J99) | 12 529 | 11 857 | 94.6 |
| Diseases of the digestive system (K00-K93) | 5 199 | 4 634 | 89.1 |
| Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue (L00-L99) | 441 | 425 | 96.4 |
| Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue (M00-M99) | 1 170 | 1 117 | 95.5 |
| Diseases of the genitourinary system (N00-N99) | 3 478 | 3 389 | 97.4 |
| Pregnancy and childbirth (O00-O99) | 12 | – | – |
| Conditions originating in the perinatal period (P00-P96) | 614 | 551 | 89.7 |
| Congenital and chromosomal abnormalities (Q00-Q99) | 546 | 472 | 86.4 |
| Ill-defined causes (R00-R99) | 1 143 | 342 | 29.9 |
| External causes (V01-Y98) | 9 123 | 1 783 | 19.5 |
| Total doctor certified deaths | . . | 129 993 | . . |
| Total coroner certified deaths | 16 939 | . . | . . |
| Total deaths | 146 932 | . . | . . |
|
| . . not applicable |
- nil or rounded to zero (including null cells)
np not available for publication but included in totals where applicable, unless otherwise indicated |
| (a) Data cells with small numbers have been randomly assigned to protect the confidentiality of individuals. As a result, some totals will not equal the sum of their components. Cells with a zero value have not been affected by confidentialisation. |
| (b) Causes of death data for 2011 are preliminary and subject to a revisions process. See 3303.0 Causes of Death, Australia, 2011, Technical Note: Causes of Death Revisions 2009 and 2010. |
4 Reportable deaths that were certified by a coroner will be included in the full Causes of Death, Australia (cat. no. 3303.0) publication to be released in 2014. This publication will present causes of death for all deaths in 2012, whether certified by a doctor or coroner.
5 The registration of deaths is the responsibility of the eight individual state and territory Registrars of Births, Deaths and Marriages. As part of the registration process, information about the cause of death is supplied by the medical practitioner certifying the death or by a coroner. Other information about the deceased is supplied by a relative or other person acquainted with the deceased, or by an official of the institution where the death occurred. The information is provided to the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) by individual Registrars for coding and compilation into aggregate statistics. In addition, the ABS supplements this data with information from the National Coroners Information System (NCIS). The following diagram shows the process undertaken in producing cause of death statistics for Australia.
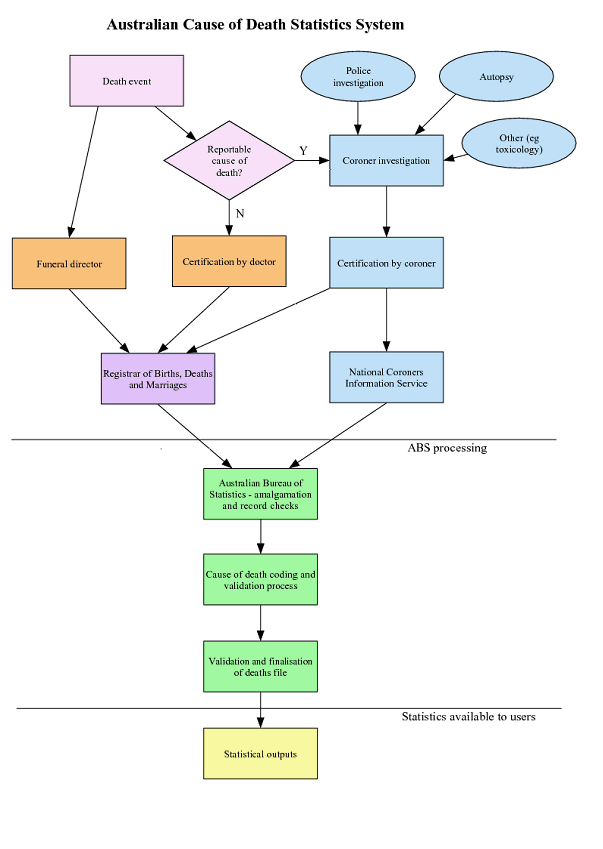
6 The doctor certified deaths data presented in this publication will also be included in the Causes of Death, Australia (cat. no. 3303.0) publication, to be released 2014. The Causes of Death publication also includes deaths which have been certified by a coroner, and therefore presents the full causes of death dataset.
7 A Glossary is also available which details definitions of terminology used throughout this publication.
SCOPE AND COVERAGE
8 The statistics in this publication relate to the number of doctor certified deaths that were registered, not those that actually occurred, in the years shown.
Scope of Causes of Death statistics
9 The scope for each reference year of death registrations includes:
- deaths registered in the reference year and received by the ABS in the reference year
- deaths registered in the reference year and received by ABS in the first quarter of the subsequent year
- deaths registered in the years prior to the reference year but not received by ABS until the reference year or the first quarter of the subsequent year, provided that these records have not been included in any statistics from earlier periods.
10 Death records received by ABS during the March quarter 2013 which were initially registered in 2012 (but for which registration was not fully completed until 2013) were assigned to the 2012 reference year. Any registrations relating to 2012 which were received by ABS from April 2013 were assigned to the 2013 reference year. Approximately 4% to 6% of deaths occurring in one year are not registered until the following year or later.
11 Prior to 2007, the scope for the reference year of the Death Registrations collection included:
- deaths registered in the reference year and received by ABS in the reference year
- deaths registered in the reference year and received by ABS in the first quarter of the subsequent year
- deaths registered during the two years prior to the reference year but not received by ABS until the reference year.
Coverage of causes of death statistics
12 Ideally, for compiling annual time series, the number of events (deaths) should be recorded and reported as those occurring within a given reference period such as a calendar year. However, due to lags in registration of events, not all deaths are registered in the year that they occur. Therefore, the occurrence event is approximated by the ABS through the addition of the event on a state/territory register of deaths. Also, some additions to the register can be delayed in being received by the ABS from a Registrar (processing or data transfer lags).
In effect there are 3 dates attributable to each death registration:
- the date on which the death occurred (date of occurrence)
- the date on which the death is registered with the state and territory registry (date of registration); and
- the month and year in which the registered event is lodged with the ABS (reference year).
From 2007 onwards, data for a particular reference year includes all deaths registered in Australia for the reference year that are received by the ABS by the end of the March quarter of the subsequent year. For example, a death may occur in December 2011, but the death may not be registered until January 2012. Information about the death is then provided to the ABS in April of 2012. This death would have a date of occurrence of December 2011, a date of registration in January 2012, and a reference year of 2012.
13 The ABS Causes of Death - Doctor Certified collection includes all doctor certified
deaths that occurred and were registered in Australia, including deaths of persons whose usual residence is overseas. Deaths of Australian residents that occurred outside Australia may be registered by individual Registrars, but are not included in ABS deaths or causes of death statistics.
14 The current scope of the statistics includes:
- all deaths being registered for the first time
- deaths in Australia of temporary visitors to Australia
- deaths occurring within Australian Territorial waters
- deaths occurring in Australian Antarctic Territories or other external territories (excluding Norfolk Island)
- deaths occurring in transit (i.e. on ships or planes) if registered in the State of 'next port of call'
- deaths of Australian Nationals overseas who were employed at Australian legations and consular offices (i.e. deaths of Australian diplomats while overseas), where able to be identified
- deaths that occurred in earlier reference periods that have not been previously registered (late registrations).
15 The scope of the statistics excludes:
- still births / fetal deaths (detailed information on these deaths will be released in 2014)
- repatriation of human remains where the death occurred overseas
- deaths overseas of foreign diplomatic staff (where these are able to be identified)
- deaths occurring on Norfolk Island.
CLASSIFICATIONS
Socio-Demographic Classifications
16 A range of socio-demographic data are available in the ABS Causes of Death - Doctor Certified collection. Standard classifications used in the presentation of causes of death statistics include age, sex, birthplace, multiple birth and Indigenous status. Statistical standards for social and demographic variables have been developed by the ABS. Where these are not published in the Causes of Death publication or data cubes, they can be sourced on request from the ABS.
Geographic Classifications
Australian Statistical Geography Standard (ASGS)
17 The ABS has developed a new standard classification for geography, the Australian Statistical Geography Standard (ASGS). The ASGS provides a common framework of statistical geography and thereby enables the production of statistics which are comparable and can be spatially integrated. ABS causes of death statistics are coded to mesh blocks and can be produced for aggregates of these, for example, Statistical Areas, Sections of State and State. The ASGS has been applied to causes of death data since the 2011 reference period. For further information about the ASGS refer to the
Australian Statistical Geography Standard (ASGS) (cat. no. 1270.0.55.001).
18 Prior to 2011, causes of death data were coded to the Australian Standard Geographical Classification (ASGC). For further information about the ASGC refer to the
Australian Standard Geographical Classification (ASGC) (cat. no. 1216.0).
Health Classifications
International Classification of Diseases (ICD)
19 The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) is the international standard classification for epidemiological purposes and is designed to promote international comparability in the collection, processing, classification, and presentation of causes of death statistics. The classification is used to classify diseases and causes of disease or injury as recorded on many types of medical records as well as death records. The ICD has been revised periodically to incorporate changes in the medical field. Currently the ICD 10th revision is used for Australian causes of death statistics.
20 ICD-10 is a variable-axis classification meaning that the classification does not group diseases only based on anatomical sites, but also on the type of disease. Epidemiological data and statistical data are grouped according to:
- epidemic diseases
- constitutional or general diseases
- local diseases arranged by site
- developmental diseases
- injuries.
21 For example, a systemic disease such as septicaemia is grouped with infectious diseases; a disease primarily affecting one body system, such as a myocardial infarction is grouped with circulatory diseases; and a congenital condition such as spina bifida is grouped with congenital conditions.
22 For further information about the ICD refer to the
WHO International Classification of Diseases (ICD).
23 The ICD 10th Revision is also available
online.
2012 MORTALITY CODING
24 The extensive nature of the ICD enables classification of causes of death at various levels of detail. In this publication, data is presented at the ICD-10 chapter level, as well as 3 character codes.
25 To enable the reader to see the relationship between the various summary classifications used in this publication, all tables show in brackets the ICD-10 codes which constitute the causes of death covered.
Updates to ICD-10
26 The Updating and Revision Committee (URC), a WHO advisory group on updates to ICD-10, maintains the cumulative and annual lists of approved updates to the ICD-10 classification. The updates to ICD-10 are of numerous types including addition and deletion of codes, changes to coding instructions and modification and clarification of terms.
27 The cumulative list of ICD-10 updates can be found
online.
Automated coding
28 The ABS uses the Medical Mortality Data System (MMDS), software for automated cause of death coding. The MMDS applies ICD rules to all death records, diseases and conditions listed on the death certificate. Approximately 70-80% of records are coded using the MMDS without manual intervention.
State and Territory Data
29 Causes of death statistics for states and territories in this publication have been compiled in respect of the state or territory of usual residence of the deceased, regardless of where in Australia the death occurred and was registered. Deaths of persons usually resident overseas which occur in Australia are included in the state/territory in which their death was registered.
30 Statistics compiled on a state or territory of registration basis are available on request.
DATA QUALITY
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander deaths
31 The ABS Death Registrations collection identifies a death as being Indigenous where the deceased is identified as being of Aboriginal and/or Torres Strait Islander origin through the death registration process. Detailed explanatory notes regarding the data quality of this variable can be found in Explanatory Notes 29-36 of the
Deaths, Australia, 2011 (cat. no. 3302.0) publication.
DEATHS BY TYPE OF CERTIFIER
32 For deaths registered in 2012, 88.3%
were certified by a doctor. The remainder were reported to, and certified by, a coroner.
SPECIFIC ISSUES FOR 2012 DATA
33 As outlined below, the following issues should be taken into account by users when analysing the 2012 doctor certified causes of death data.
34 Dementia (F01,F03)
Since 2006, there has been a substantial increase in the number of deaths coded to Dementia (F01,F03). Updates to the coding instructions in ICD-10 has resulted in the assignment of some deaths shifting from Cerebrovascular diseases (I60-I69) to Vascular dementia (F01). In addition, changes to the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986 and Military Rehabilitation and Compensation Act 2004, and a subsequent promotional campaign targeted at health professionals, now allow for death from vascular dementia of veterans or members of the defence forces to be related to relevant service. This is believed to have had an effect on the number of deaths attributed to dementia.
STANDARDISED DEATH RATES (SDR)
35 Standardised death rates (SDRs) enable the comparison of death rates between populations with different age structures by relating them to a standard population. The current standard population is all persons in the Australian population at 30 June 2001. SDRs are expressed per 1,000 or 100,000 persons.
For 2010 deaths data onwards, the ABS has implemented a new set of principles for the use of direct age standardisation in production of mortality rates. See the Deaths, Australia, 2010 (cat. no 3302.0) Explanatory Notes 39-42 and Appendix 1: Principles on the use of direct age-standardisation for further information.
CONFIDENTIALISATION OF DATA
36 Data cells with small values have been randomly assigned to protect confidentiality. As a result some totals will not equal the sum of their components. Cells with 0 values have not been affected by confidentialisation.
EFFECTS OF ROUNDING
37 Where figures have been rounded, discrepancies may occur between totals and sums of the component items.
ABS PRODUCTS
38 ABS products and publications are available free of charge from the ABS website. Click on Statistics to gain access to the full range of ABS statistical and reference information. For details on products scheduled for release in the coming week, click on the Future Releases link on the ABS homepage.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
39 The ABS' publications draw extensively on information provided freely by individuals, businesses, governments and other organisations. The efforts of Registries of Births, Deaths and Marriages to improve the data quality, coverage and timeliness of death registration information, processes and systems are noted and valued by the ABS. Their continued cooperation is very much appreciated; without it, the wide range of statistics published by the ABS would not be available. Information received by the ABS is treated in strict confidence as required by the Census and Statistics Act 1905.
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All